Samsung 2009 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2009 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
90 91 NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
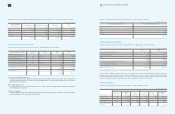
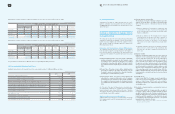
Operating data of entities classified according to geographic area as of and for the year ended December 31, 2009:
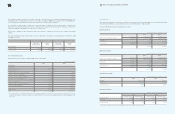
Operating data of entities classified according to geographic area as of and for the year ended December 31, 2008:
The presentation and classification of 2008 was revised for comparability with 2009 presentation.
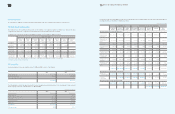
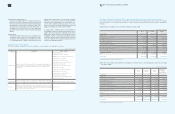
35. Transaction Not Affecting Cash Flows
Significant transactions not affecting cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, are as follows:
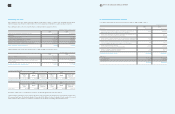
(In millions of Korean won)
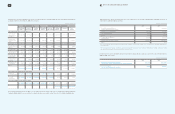
2009 Summary of Business by Geographic Area
Korea Americas Europe Asia China Elimination Consolidated
Domestic Export
Gross sales
₩
23,621,415
₩
89,803,515
₩
57,989,166
₩
61,858,546
₩
31,974,561
₩
57,906,677
₩
(184,160,209)
₩
138,993,671
Intersegment sales (7,675,455) (81,114,716) (24,280,566) (25,675,454) (11,267,712) (34,146,306) 184,160,209 -
Net sales
₩
15,945,960
₩
8,688,799
₩
33,708,600
₩
36,183,092
₩
20,706,849
₩
23,760,371 - 138,993,671
Operating profit
₩
7,159,467
₩
693,309
₩
1,519,223
₩
900,295
₩
1,372,120
₩
(66,763)
₩
11,577,651
Total assets
₩
107,984,087
₩
21,718,611
₩
17,188,362
₩
8,659,632
₩
13,744,617
₩
(51,013,821)
₩
118,281,488
(In millions of Korean won)
2008 Summary of Business by Geographic Area
Korea Americas Europe Asia China Elimination Consolidated
Domestic Export
Gross sales
₩
21,398,073
₩
69,074,728
₩
45,246,448
₩
54,416,816
₩
29,242,661
₩
46,674,677
₩
(144,759,084) 121,294,319
Intersegment sales (5,935,230) (60,976,594) (19,804,936) (20,186,680) (10,053,631) (27,802,013) 144,759,084 -
Net sales
₩
15,462,843
₩
8,098,134
₩
25,441,512
₩
34,230,136 19,189,030 18,872,664 - 121,294,319
Operating profit
₩
4,648,865
₩
90,559
₩
261,827
₩
301,440
₩
404,699
₩
324,473
₩
6,031,863
Total assets
₩
94,013,961
₩
18,887,777
₩
13,927,357
₩
7,218,168
₩
9,161,228
₩
(37,907,841)
₩
105,300,650
(In millions of Korean won)
2009 2008
Write-off of accounts receivables and others
₩
330,405
₩
502,243
Increase in gain on valuation of available-for-sale securities 195,045 656,703
Increase in loss on valuation of available-for-sale securities 673 28,656
Decrease in gain on valuation of available-for-sale securities due to disposal 9,147 3,983
Decrease in loss on valuation of available-for-sale-securities due to disposal - 143
Increase in share of equity-method investees’ accumulated other comprehensive income 104,588 7,111
Decrease in share of equity-method investees’ accumulated other comprehensive loss 4,152 6,309
Current maturities of long-term prepaid expenses 2,279,226 217,812
Current maturities of long-term debts 4,852 71,465
Reclassification of construction-in-progress and machinery-in-transit to other property, plant
and equipment accounts 8,697,452 10,297,439
Current maturities of other long-term liabilities 1,702,836 303,914
Current maturities of long-term advances received - 168,650
Current maturities of long-term accrued expenses 321,500 270,702
36. Subsequent Event
Subsequent to December 31, 2009, Samsung Card, one of SEC
domestic subsidiary issued unguaranteed bonds amounting to
₩
320,000 million (bond issue number 1831 through 1844) as of the
date of this report.
37. Transition to International Financial Reporting
Standards as Adopted by the Republic of Korea
from Generally Accepted Accounting Principle in
the Republic of Korea.
The Company will adopt the International Financial Reporting
Standards as Adopted by the Republic of Korea (“Korean IFRS”)
from the fiscal year 2010 (the date of first-time adoption to Korean
IFRS: January 1, 2010). The Company’s approach to adopt Korean
IFRS is illustrated as follows:
Preparation and implementation of Korean IFRS adoption
The Company formed a task force to prepare for its transition
from Generally Accepted Accounting Principle in the Republic of
Korea (“Korean GAAP”) to Korean IFRS. The three phases being
conducted for the transition to Korean IFRS by the task force are as
follows:
(1)
Analysis and Planning Phase : This phase includes a preliminary
analysis and impact assessments over the Company’s current
accounting policies, financial reporting process including
determination of reporting entity, and the IT systems to identify
key areas that would be impacted by the transition to Korean
IFRS.
(2) Design Phase: This phase includes further detailed analysis
and employee training on the impact assessments over the
Company’s current accounting policies, financial information
generating process and information systems.
(3) Implementation Phase: This phase includes applying and
embedding the changes identified above in the Company’s
operational processes and system. The Company anticipates
the completion of this phase enables the Company to provide
accountable financial information in accordance with Korean
IFRS.
As of the date of the report, all three phases as described above
are substantially completed. The Company has been preparing
financial statements under Korean IFRS from the date of transition
and onwards and expects that financial information for the fiscal
year 2010 will be Korean IFRS compliant.
Significant differences in accounting policies
Significant differences between the accounting policies chosen by
the Company under Korean IFRS and under previous Korean GAAP
are as follows:
(1) First time adoption of Korean IFRS
The Company elected the following exemptions upon the
adoption of Korean IFRS in accordance with Korean IFRS
1011, First-time adoption of international financial reporting
standards:
1) Business combination: Past business combinations that
occurred before the date of transition to Korean IFRS will
not be retrospectively restated under Korean IFRS 1103,
Business combinations.
2) Fair value as deemed cost: The Company elects to measure
certain land assets at fair value at the date of transition to
Korean IFRS and use the fair value as its deemed cost.
Valuations were made on the basis of recent market
transactions on the arm's length terms by independent
valuers.
3) Cumulative translation differences: All cumulative translation
gains and losses arising from foreign subsidiaries and
associates as of the date of transition to Korean IFRS are
reset to zero.
(2) Employee benefits
Employees and directors with at least one year of service are
entitled to receive a lump-sum payment upon termination
of their employment with SEC, its Korean subsidiaries
and certain foreign subsidiaries, based on their length of
service and rate of pay at the time of termination. Under
the previous severance policy pursuant to Korean GAAP,
Accrued severance benefits represented the amount which
would be payable assuming all eligible employees and
directors were to terminate their employment as of the end
of the reporting period. However, under Korean IFRS, the
liability is determined based on the present value of expected
future payments calculated and reported using actuarial
assumptions.
(3) Intangible assets
Under Korean GAAP the Company recorded expenditures
related to research and development activities as current
expense. Under Korean IFRS if such costs related to
development activities meet certain criteria they are recorded
as intangible assets.
(4) Goodwill or bargain purchase acquired by business
combinations
Under Korean GAAP, the Company amortizes goodwill or
recognizes a gain in relation to bargain purchase (negative
goodwill
1
) acquired as a result of business combinations on a
straight-line method over five years from the year of acquisition.
Under Korean IFRS, goodwill is not amortized but reviewed
for impairment annually. Bargain purchase is recognized
immediately in the statement of income.
1. Negative goodwill under Korean GAAP is referred to as bargain
purchase under Korean IFRS