Samsung 2009 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2009 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.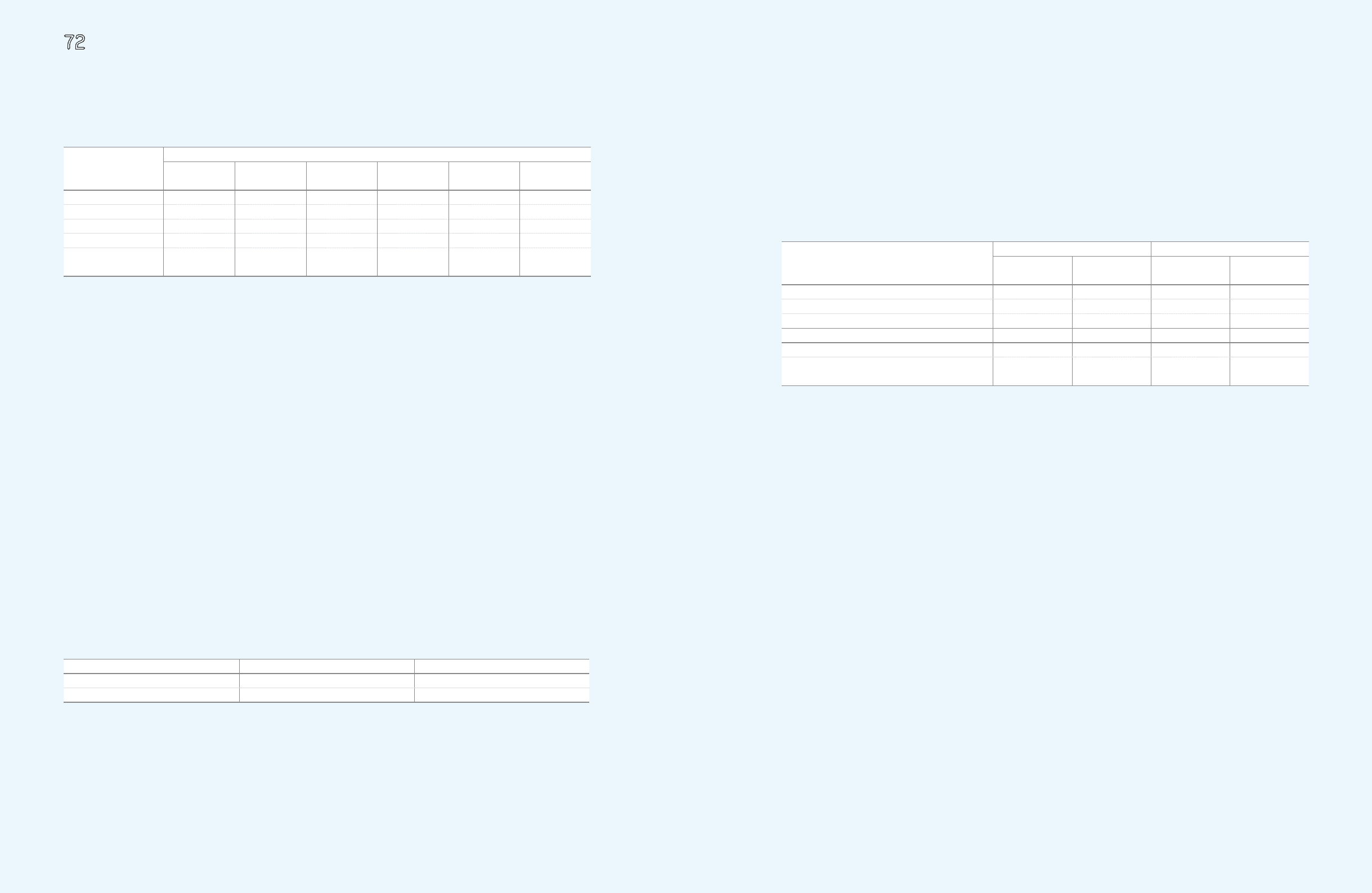
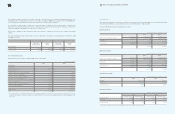
72 73 NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
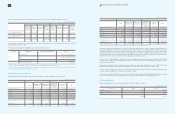
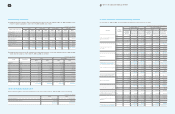
(In millions of Korean won)
2008
Reference January 1,
2008 Increase Decrease Others1December 31,
2008
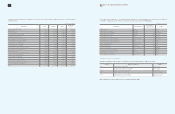
Warranty reserves (A)
₩
929,077
₩
1,756,994
₩
1,489,231
₩
146,852
₩
1,343,692
Royalty expenses (B) 1,342,932 661,551 691,147 12,903 1,326,239
Long-term incentives (C) 39,145 178,329 40,587 - 176,887
Point reserves (D) 146,875 173,573 157,349 - 163,099
Allowance for undrawn
commitment (E) - 232,880 - - 232,880
1. Others include amounts from changes in consolidated subsidiaries and foreign currency exchange rates.
(A) The Company accrues warranty reserves for estimated costs of future service, repairs and recalls, based on historical experience
and terms of guarantees (1~4 years).
(B) The Company makes provisions for estimated royalty expenses related to technical assistance agreements that have not been
settled. The timing of payment depends on the settlement of agreement.
(C) The Company introduced long-term incentive plans for its executives based on a three-year management performance criteria and
has made a provision for the estimated incentive cost for the accrued period.
(D) Samsung Card, a domestic subsidiary, accrues point reserves based on estimated expenses of future service to reward loyal
members and expand customer base.
(E) Samsung Card, a domestic subsidiary, accrues allowance for undrawn commitment based on credit conversion factor and forward-
looking criteria according to regulations on supervision of credit-specialized financial business.
19. Commitments and Contingencies
(A) As of December 31, 2009, SEC is contingently liable for guarantees of indebtedness, principally for related parties, approximating
₩
9,791 million in loans and US$1,401 million on drawn facilities which have a maximum limit of US$4,655 million.
As of December 31, 2009, SEC is contingently liable for guarantees of indebtedness up to a limit of
₩
138,848 million for
employees' housing rental deposits.
As of December 31, 2009, SEC is providing a US$23 million guarantee for Samsung Electronics Hungarian relating to the
investment incentive contract with the Hungarian government.
In addition, as of December 31, 2009, the Company’s overseas subsidiaries enter into “Cash Pooling Arrangement” contracts and
“Banking Facility” agreements with overseas financial institutions to provide mutual guarantees of indebtedness.
(B) As of December 31, 2009, SEC and its domestic subsidiaries have been insured against future contract commitments of up to
₩
151,354 million. In addition, Samsung Card has been provided with a guarantee amounting to US$ 3 million from Woori Bank, in
relation to its payment to AMEX, and
₩
1,000 million from Hana Bank.
(C) As of December 31, 2009, the Company has technical assistance agreements with certain companies requiring payment for use of
the technology or from sales of products manufactured using such technology.
(D) The Company leases certain property, plant and equipment under various finance lease arrangements. Assets recorded under
finance lease agreements are included in property, plant and equipment with a net book value of
₩
102,971 million (2008:
₩
52,857
million). Depreciation expense for the finance lease assets amounted to
₩
19,963 million (2008:
₩
5,644 million) for the year ended
December 31, 2009.
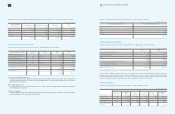
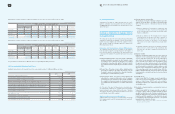
The minimum lease payments under finance lease agreements and their present value as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, are as follows:
(E) The United States Department of Justice Antitrust Division (the Justice Department), European Commission and other countries'
anti-trust authorities initiated an investigation into alleged anti-trust violations by sellers of TFT-LCD, DRAM, SRAM and Flash
Memory, including the Company. Following the investigation by the Justice Department and European Commission, several civil
class actions were filed against the Company and its subsidiaries in the United States and Europe. As of balance sheet date, the
outcome of the investigation and civil actions is uncertain and accordingly, the ultimate effect of this matter on the financial position
of the Company cannot be determined.
(F) Based on the agreement entered on August 24, 1999, with respect to Samsung Motor Inc.’s (“SMI”) bankruptcy proceedings,
Samsung Motor Inc.’s creditors (“the Creditors”) filed a civil action against Mr. Kun Hee Lee, former chairman of the Company,
and 28 Samsung Group affiliates including the Company under joint and several liability for failing to comply with such agreement.
Under the suit, the Creditors have sought
₩
2,450 billion for loss of principal on loans extended to SMI, a separate amount for
breach of the agreement, and an amount for default interest.
On January 31, 2008, Seoul Administrative Court made the ruling on this case. Under the ruling, Samsung Group affiliates were
ordered to pay approximately
₩
1,634 billion to the Creditors by disposing 2,334,045 shares of Samsung Life Insurance (the
“Shares”) donated by Mr. Lee, excluding 1,165,955 shares already sold by the Creditors. If the proceeds from sale of Shares are not
sufficient to satisfy their obligations, Samsung Group affiliates were obligated to satisfy the shortfall by either participating in the
Creditors’equity offering or purchasing subordinated debentures issued by the Creditors. In addition, Samsung Group affiliates were
ordered to pay default interest on
₩
1,634 billion at 6% per annum for the period from January 1, 2001, to the date of settlement.
The Company, other Samsung Group affiliates, Mr. Lee, and the Creditors all have appealed the ruling, and currently, the second
trial for this case is pending at Seoul High Court. The ultimate outcome of this case can not be determined at this time. Since
the amount of Company’s obligation is uncertain, the effects of this matter on the Company’s financial statements can not be
reasonably determined.
(G)
As of December 31, 2009, the Company was named as a defendant in legal actions filed by 25 overseas companies including
Sharp Corporation, and as the plaintiff in legal actions against 5 overseas companies including Spansion Inc. for alleged patent
infringements.
On January 19, 2010, the Company and certain subsidiaries located in the United States, agreed to a settlement with Rambus
Inc. Under the terms of the settlement, US $200 million will be paid to Rambus Inc. for dismissal of the anti-trust litigation and the
alleged patent infringement regarding DRAM. The settlement also included a royalty agreement for which certain amounts will be
paid to Rambus, Inc. for the next five years: For 2010 and the first two quarters of 2011, the future royalty payment will be US $25
million per quarter. For the remainder of the five year royalty period, the quarter payment will be based on the Company's sales
volume of related product, subject to certain minimum and maximum amounts.
In addition, there is an agreement for which the Company would acquire 8.3% shares acquisition of Rambus for US $200 million.
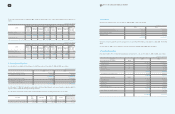
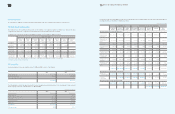
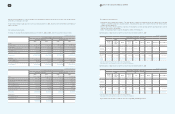
Area Participating Subsidiaries Financial Institutions
Europe SEUK and 18 other subsidiaries Citibank
Asia SAPL and 7 other subsidiaries Bank of America
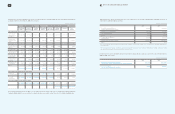
2009 2008
Minimum Lease
Payments Present Values Minimum Lease
Payments Present Values
Within one year
₩
15,200
₩
13,358
₩
10,659
₩
8,770
From one year to five years 58,441 49,213 32,866 25,045
More than five years 167,140 94,983 70,403 38,564
240,781
₩
157,554 113,928
₩
72,379
Present value adjustment (83,227) (41,549)
Financing lease liabilities
₩
157,554
₩
72,379
(In millions of Korean won)