Samsung 2009 Annual Report Download - page 30
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 30 of the 2009 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
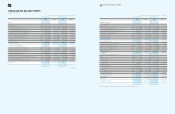
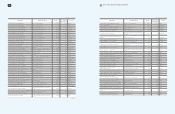
56 57 NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
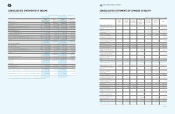
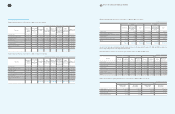
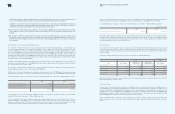
4. Cash Subject to Withdrawal Restrictions
Cash deposits subject to withdrawal restrictions as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, consist of the following:
5. Short-Term Available-For-Sale Securities
Short-term available-for-sale securities as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, consist of the following:
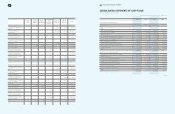
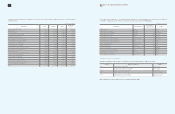
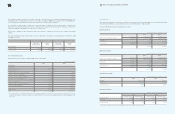
1. Beneficiary certificates as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, consist of the following
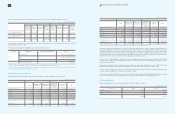
(In millions of Korean won)
2009 2008
Short-term financial instruments Government-sponsored
research and development projects
₩
54,336
₩
24,505
Other activities 15,731 36,228
₩
70,067
₩
60,733
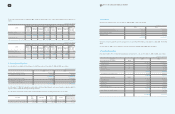
Long-term deposits and other assets Special deposits
₩
51
₩
60
Other activities 8 9
₩
59
₩
69
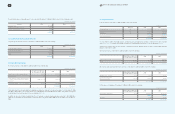
(In millions of Korean won)
2009 2008 Maturity
Beneficiary certificates 1
₩
2,104,420
₩
982,067 Within 1 year
₩
2,104,420
₩
982,067
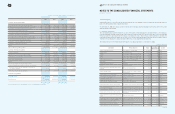
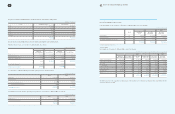
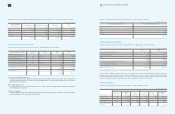
(In millions of Korean won)
2009 2008
Call loan
₩
8,670
₩
157
Certificates of deposit 118,689 231,561
Bonds 1,569,532 622,911
Time deposits 390,738 127,307
Others 16,791 131
In accordance with the National Pension Act, a certain portion
of the accrued severance benefits is deposited with the National
Pension Fund and deducted from the accrued severance benefits
liability.
Revenue Recognition
Sales of products and merchandise are recognized upon delivery
when the significant risks and rewards of ownership of goods
are transferred to the buyer. Revenue from rendering services is
recognized using the percentage-of-completion method.
Foreign Currency Translation
Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are
translated into Korean won at the rate of exchange in effect as
of the balance sheet date. Gains and losses resulting from the
translation are reflected as either income or expense for the period.
Deferred Income Tax Assets and Liabilities
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized based
on estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences
between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets
and liabilities and their respective tax bases, and operating loss and
tax credit carryforwards.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are computed on such
temporary differences by applying statutory tax rates applicable to
the years when such differences are expected to be reversed. Tax
assets related to tax credits and exemptions are recognized to the
extent of the Company’s certain taxable income.
The balance sheet distinguishes the current and non-current
portions of the deferred tax assets and liabilities, whose balances
are offset against each other by tax jurisdiction.
Long-Term Receivables and Payables
Long-term receivables and payables that have no stated interest
rate or whose interest rate are different from the market rate are
recorded at their present values using the market rate of discount.
The difference between the nominal value and present value of
the long-term receivables and payables are amortized using the
effective interest rate method with interest income or expense
adjusted accordingly.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company uses the fair-value method in determining
compensation costs of stock options granted to its employees and
directors. The compensation cost is estimated using the Black-
Scholes option-pricing model and is accrued and charged to
expense over the vesting period, with a corresponding increase in a
separate component of equity.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net income
available to common shareholders by the weighted-average number
of common shares outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings per
share is calculated using the weighted-average number of common
shares outstanding adjusted to include the potentially dilutive effect
of common equivalent shares outstanding.
Provisions and Contingent Liabilities
When there is a probability that an outflow of economic benefits will
occur due to a present obligation resulting from a past event, and
whose amount is reasonably estimable, a corresponding amount of
provision is recognized in the financial statements. However, when
such outflow is dependent upon a future event, is not certain to
occur, or cannot be reliably estimated, a disclosure regarding the
contingent liability is made in the notes to the financial statements.
Derivative Instruments
All derivative instruments are accounted for at fair value with the
resulting valuation gain or loss recorded as an asset or liability. If the
derivative instrument is not designated as a hedging instrument, the
gain or loss is recognized in earnings in the period of change.
Fair value hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument
with the purpose of hedging the exposure to changes in the fair
value of an asset or a liability or a firm commitment (hedged item)
that is attributable to a particular risk. The gain or loss, both on the
hedging derivative instrument and on the hedged item attributable
to the hedged risk, is reflected in current operations.
Cash flow hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument
with the purpose of hedging the exposure to variability in expected
future cash flows of an asset or a liability or a forecasted transaction
that is attributable to a particular risk. The effective portion of the
gain or loss on a derivative instrument designated as a cash flow
hedge is recorded as a accumulated other comprehensive income
and the ineffective portion is recorded in current operations. The
effective portion of the gain or loss recorded as accumulated other
comprehensive income is reclassified to current operations in the
same period during which the hedged forecasted transaction affects
earnings. If the hedged transaction results in the acquisition of an
asset or the incurrence of a liability, the gain or loss recognized as
accumulated other comprehensive income is added to or deducted
from the asset or the liability.
Asset Impairment
When the book value of an asset is significantly greater than its
recoverable value due to obsolescence, physical damage, or the
decline in the fair value of the asset, the decline in value is deducted
from the book value and recognized as an asset impairment loss in
the current period.
3. United States Dollar Amounts
The Company operates primarily in Korean won and its official
accounting records are maintained in Korean won. The U.S. dollar
amounts, provided herein, represent supplementary information
solely for the convenience of the reader. All won amounts are
expressed in U.S. dollars at the rate of ₩1,167 to US$1, the
exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2009. Such presentation
is not in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
in either the Republic of Korea or the United States, and should
not be construed as a representation that the won amounts shown
could be readily converted, realized or settled in U.S. dollars at this
or at any other rate.
The 2008 U.S. dollar amounts, which were previously expressed at
₩1,257 to US$1, the rate in effect on December 31, 2008, have
been restated to reflect the exchange rate in effect on December
31, 2009.