Royal Caribbean Cruise Lines 2014 Annual Report Download - page 77
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 77 of the 2014 Royal Caribbean Cruise Lines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
76 Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd.
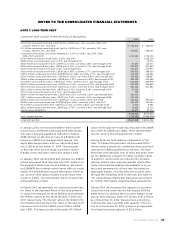
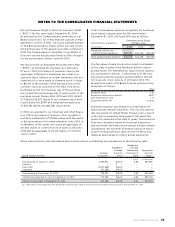
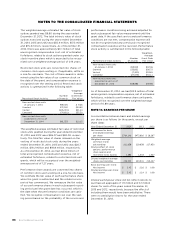
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Derivative Instruments
We enter into various forward, swap and option con-
tracts to manage our interest rate exposure and to
limit our exposure to fluctuations in foreign currency
exchange rates and fuel prices. These instruments are
recorded on the balance sheet at their fair value and
the vast majority are designated as hedges. We also
have non-derivative financial instruments designated
as hedges of our net investment in our foreign oper-
ations and investments. Although certain of our deriv-
ative financial instruments do not qualify or are not
accounted for under hedge accounting, we do not
hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trad-
ing or other speculative purposes.
At inception of the hedge relationship, a derivative
instrument that hedges the exposure to changes in
the fair value of a firm commitment or a recognized
asset or liability is designated as a fair value hedge.
A derivative instrument that hedges a forecasted
transaction or the variability of cash flows related to
a recognized asset or liability is designated as a cash
flow hedge.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are desig-
nated as fair value hedges are offset against changes
in the fair value of the underlying hedged assets,
liabilities or firm commitments. Gains and losses on
derivatives that are designated as cash flow hedges
are recorded as a component of Accumulated other
comprehensive (loss) income until the underlying
hedged transactions are recognized in earnings. The
foreign currency transaction gain or loss of our non-
derivative financial instruments designated as hedges
of our net investment in foreign operations and invest-
ments are recognized as a component of Accumulated
other comprehensive (loss) income along with the
associated foreign currency translation adjustment of
the foreign operation.
On an ongoing basis, we assess whether derivatives
used in hedging transactions are “highly effective”
in offsetting changes in the fair value or cash flow of
hedged items. We use the long-haul method to assess
hedge effectiveness using regression analysis for each
hedge relationship under our interest rate, foreign
currency and fuel hedging programs. We apply the
same methodology on a consistent basis for assessing
hedge effectiveness to all hedges within each hedging
program (i.e., interest rate, foreign currency and fuel).
We perform regression analyses over an observation
period of up to three years, utilizing market data rele-
vant to the hedge horizon of each hedge relationship.
High effectiveness is achieved when a statistically
valid relationship reflects a high degree of offset and
correlation between the changes in the fair values
of the derivative instrument and the hedged item.
The determination of ineffectiveness is based on the
amount of dollar offset between the change in fair
value of the derivative instrument and the change in
fair value of the hedged item at the end of the report-
ing period. If it is determined that a derivative is not
highly effective as a hedge or hedge accounting is
discontinued, any change in fair value of the deriva-
tive since the last date at which it was determined to
be effective is recognized in earnings. In addition, the
ineffective portion of our highly effective hedges is
immediately recognized in earnings and reported in
Other income (expense) in our consolidated statements
of comprehensive income (loss).
Cash flows from derivative instruments that are
designated as fair value or cash flow hedges are
classified in the same category as the cash flows from
the underlying hedged items. In the event that hedge
accounting is discontinued, cash flows subsequent to
the date of discontinuance are classified within invest-
ing activities. Cash flows from derivative instruments
not designated as hedging instruments are classified
as investing activities.
We consider the classification of the underlying hedged
item’s cash flows in determining the classification for
the designated derivative instrument’s cash flows. We
classify derivative instrument cash flows from hedges
of benchmark interest rate or hedges of fuel expense
as operating activities due to the nature of the hedged
item. Likewise, we classify derivative instrument cash
flows from hedges of foreign currency risk on our new-
build ship payments as investing activities and deriva-
tive instrument cash flows from hedges of foreign
currency risk on debt payments as financing activities.
Foreign Currency Translations and Transactions
We translate assets and liabilities of our foreign sub-
sidiaries whose functional currency is the local cur-
rency, at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet
date. We translate revenues and expenses at weighted-
average exchange rates for the period. Equity is
translated at historical rates and the resulting foreign
currency translation adjustments are included as a
component of Accumulated other comprehensive
(loss) income, which is reflected as a separate compo-
nent of Shareholders’ equity. Exchange gains or losses
arising from the remeasurement of monetary assets
and liabilities denominated in a currency other than
the functional currency of the entity involved are
immediately included in our earnings, except for cer-
tain liabilities that have been designated to act as a
hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation or
investment. Exchange gains (losses) were $49.5 mil-
lion, $13.4 million and $(11.8) million for the years
2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and were recorded
within Other income (expense). The majority of our