Mazda 2014 Annual Report Download - page 60
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 60 of the 2014 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
(Additional Information)
(Adjustment of deferred tax assets and liabilities for enacted changes in tax laws
and rates)
On March 31, 2014, “Partial Amendment of the Income Tax Act, etc.” (Act No.10, 2014)
was enacted into law. As a result of the amendment, special corporate tax for reconstruc-
tion will be abolished from the fiscal year commencing on or after April 1, 2014. Based on
this amendment, the statutory income tax rates, which the Domestic Companies have
utilized for the measurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the year ended March
31, 2014, has been changed from the previous 37.8% to 35.4% for the temporary differ-
ences expected to be reversed in the year beginning April 1, 2014.
Due to this change in statutory income tax rates, net deferred tax assets decreased by
¥3,494 million ($33,922 thousand) as of March 31, 2014 and deferred income tax expense
recognized for the year ended March 31, 2014 increased by ¥3,449 million ($33,485 thou-
sand). Furthermore, deferred gains/(losses) on hedges in accumulated other comprehen-
sive income decreased by ¥45 million ($437 thousand) as of March 31, 2014.
15 DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND
HEDGING TRANSACTIONS
The Group uses forward foreign exchange contracts as derivative financial instruments
only for the purpose of mitigating future risks of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange
rates. Also, only for the purpose of mitigating future risks of fluctuations in interest rates
with respect to borrowings, the Group uses interest rate swap contracts.
Forward foreign exchange contracts are subject to risks of foreign exchange rate
changes. Also, interest rate swap contracts are subject to risks of interest rate changes.
Use of derivatives to manage these risks could result in the risk of a counterparty
defaulting on a derivative contract. However, the Company believes that the risk of a coun-
terparty defaulting is minimum since the Group uses only highly credible financial institu-
tions as counterparties.
Derivative transactions are conducted in compliance with internal control rules and pro-
cedures that prescribe transaction authority. The policies for derivative transactions of the
Group are approved by the Company’s President or Financial Officer. Transactions are
approved in advance by either the Company’s Financial Services Division General
Manager or Treasury Department General Manager. Based on these approvals, the
Treasury Department conducts and books the transactions as well as confirms the balance
between the counterparty of the derivatives contract. The operation of the transaction is
segregated from its clerical administration, in order to maintain internal check within the
Treasury Department, and is audited periodically by the Global Auditing Department.
Derivative transactions are reported, upon execution, to the Company’s Financial Officer,
Financial Services Division General Manager, and Treasury Department General Manager.
The consolidated subsidiaries also follow internal control rules and procedures pursuant to
those of the Company, obtain approval of the Company, and conduct and manage the
transactions according to the approval.
The following summarizes hedging derivative financial instruments used by the Group
and items hedged:
Hedging instruments: Hedged items:
Forward foreign exchange contracts Foreign currency-denominated
transactions planned in the future
Interest rate swap contracts Interest on borrowings
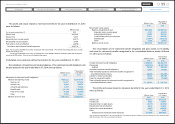
The following tables summarize fair value information as of March 31, 2014 and 2013
of derivative transactions for which hedge accounting has not been applied:
Millions of yen Thousands of U.S. dollars
As of March 31, 2014
Contract
amount
Estimated
fair value Difference
Contract
amount
Estimated
fair value Difference
Forward foreign
exchange contracts:
Sell:
U.S. dollar ¥20,682 ¥ (921) ¥ (921) $200,796 $ (8,941) $ (8,941)
Euro 2,002 (121) (121) 19,437 (1,175) (1,175)
Canadian dollar 5,200 80 80 50,485 777 777
Australian dollar 9,725 (260) (260) 94,417 (2,524) (2,524)
Sterling pound 955 (73) (73) 9,272 (709) (709)
Russian ruble 7,279 282 282 70,670 2,738 2,738
Buy:
U.S. dollar 355 6 6 3,447 58 58
Australian dollar 1,380 (110) (110) 13,398 (1,068) (1,068)
Thai baht 2,468 71 71 23,961 689 689
Total ¥50,046 ¥(1,046) ¥(1,046) $485,883 $(10,155) $(10,155)
58
Mazda Annual Report 2014
CONTENTS
Foundations Underpinning
Sustainable Growth
Financial Section
Review of Operations
Message from Management
Introduction
Brand Value Management