Family Dollar 2013 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
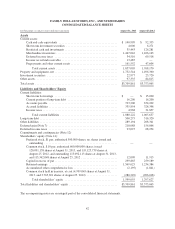
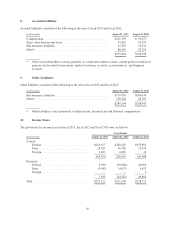
Please find page 50 of the 2013 Family Dollar annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.liability risks and are not designated for general corporate purposes. These cash and cash equivalents balances
totaled $2.7 million as of the end of fiscal 2013 and $19.0 million as of the end of fiscal 2012.
Investment securities
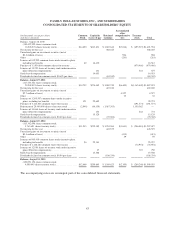
The Company classifies all investment securities as available-for-sale. Securities accounted for as available-for-
sale are required to be reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, excluded from net
income and shown separately as a component of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income within
Shareholders’ Equity on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company’s short-term investment securities
currently consist primarily of short-term bond mutual funds, municipal debt securities, and equity securities. The
Company’s long-term investment securities currently consist of auction rate securities. See Notes 2 and 3 for
more information on the Company’s investment securities.
In addition to the cash and cash equivalents balances discussed above, the Company’s wholly-owned captive
insurance subsidiary also maintains balances in investment securities that are not designated for general corporate
purposes. These investment securities balances were $27.0 million as of the end of fiscal 2013 and $30.0 million
as of the end of fiscal 2012.
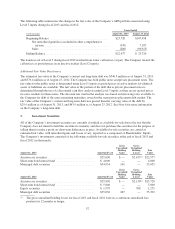
Restricted cash and investments
The Company has restricted cash and investments that serve as collateral for certain of the Company’s insurance
obligations. These restricted funds cannot be withdrawn from the Company’s account without the consent of the
secured party. As of August 31, 2013, the Company held $55.5 million in this restricted account, of which
$35.4 million was included in Restricted Cash and Investments and $20.1 million was included in Other Assets in
the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The classification between current and non-current is based on the timing of
expected payments of the secured insurance obligations. Previously, these obligations were collateralized using
standby letters of credit under the Company’s revolving credit facilities.
Additionally, in conjunction with the sale-leaseback transactions completed in fiscal 2013 and fiscal 2012,
certain proceeds from the transactions were placed into an escrow account with an independent third-party in
connection with like-kind exchange transactions, which permits the deferral of a portion of the tax gain
associated with the sale of the stores. The Company intended to use these proceeds to purchase additional new
stores and was required to do so within 180 days from the closing of the transactions to realize the deferral.
During the 180-day deferral period, these assets were classified as Restricted Cash and Investments in the
Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company had no restricted cash and investments balance related to these
transactions as of the end of fiscal 2013 and $80.4 million as of the end of fiscal 2012.
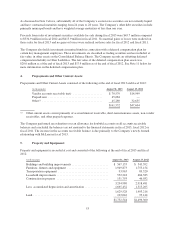
Merchandise inventories
Inventories are valued using the retail method, based on retail prices less mark-on percentages, which
approximates the lower of first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost or market. The Company records adjustments to
inventory through cost of goods sold when retail price reductions, or markdowns, are taken against on-hand
inventory. In addition, the Company makes estimates and judgments regarding, among other things, initial
markups, markdowns, future demand for specific product categories and market conditions, all of which can
significantly impact inventory valuation. These estimates and judgments are based on the application of a
consistent methodology each period. The Company estimates inventory losses for damaged, lost or stolen
inventory (inventory shrinkage) for the period from the most recent physical inventory to the financial statement
date. The accrual for estimated inventory shrinkage is based on the trailing twelve-month actual inventory
shrinkage rate and can fluctuate from period to period based on the timing of the physical inventory counts.
Stores conduct a physical inventory at least annually.
46