Blackberry 2006 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2006 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
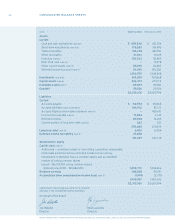
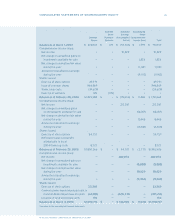
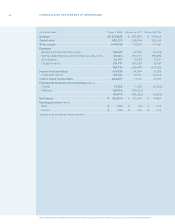
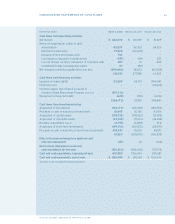
Research In Motion Limited
50
Research In Motion Limited • Incorporated Under the Laws of Ontario (In thousands of United States dollars, except per share data, and except as otherwise indicated)
(s) Statements of comprehensive income (loss)
U.S. GAAP, SFAS 130,
Reporting Comprehensive Income
, establishes standards for the reporting and display
of comprehensive income and its components in general-purpose nancial statements. Comprehensive
income is dened as the change in net assets of a business enterprise during a period from transactions
and other events and circumstances from non-owner sources, and includes all changes in equity during a
period except those resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. The reportable
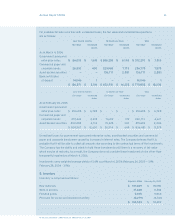
items of comprehensive income are cash ow hedges as described in note 19, and changes in the fair value
of investments available for sale as described in note 4. Realized gains or losses on available-for-sale
investments are reclassied into earnings using the specic identication basis.
(t) Earnings per share
Earnings per share is calculated based on the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the
year. The treasury stock method is used for the calculation of the dilutive effect of stock options.
(u) Stock-based compensation plans
The Company has stock-based compensation plans, which are described in note 11(b).
Stock options are granted with an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the shares on the day
of grant of the stock options. Any consideration paid by employees on exercise of stock options is credited
to capital stock. Compensation expense is recognized when stock options are issued with an exercise price
of the stock option that is less than the market price of the underlying stock on the date of grant. The
difference between the exercise price of the stock option and the market price of the underlying stock on
the date of grant is recorded as compensation expense (“intrinsic value method”). The exercise price of
stock options granted by the Company is the market value of the underlying stock at the date of grant;
consequently, no compensation expense is recognized. This method is consistent with U.S. GAAP, APB
Opinion 25, Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees.
At the Company’s Annual General Meeting on July 18, 2005, shareholders approved the establishment of
the Restricted Share Unit (“RSU”) Plan. The eligible participants under the RSU Plan include any ofcer or
employee of the Company or its subsidiaries. The RSU Plan received regulatory approval in August 2005.
RSU’s are redeemed for either common shares issued from treasury, common shares purchased on the
open market or the cash equivalent on the vesting dates established by the Company. Compensation
expense will be recognized upon issuance of RSU’s over the vesting period.
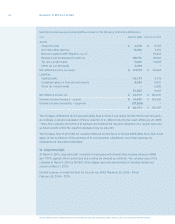
SFAS 123,
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation
, requires proforma disclosures of net income and
earnings per share, as if the fair value method, as opposed to the intrinsic value method of accounting for
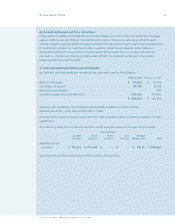
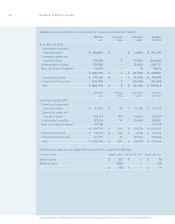
employee stock options, had been applied. The disclosures in the following table present the Company’s
net income and earnings per share on a proforma basis using the fair value method as determined using
the Black-Scholes option pricing model: