Avon 2000 Annual Report Download - page 7
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 7 of the 2000 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
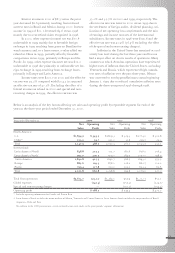
In Europe, sales increased 1% to $885.6 versus
1999 but increased 13% in local currency on 12%
growth in units and 15% higher active Representatives.
The euro, pound and zloty devalued significantly in 2000
and, as a result, negatively affected u.s. dollar results.
Sales growth in Central and Eastern Europe, primarily
Poland, and in Russia was partially offset by declines in
most Western European markets, most significantly in
Germany. The sales improvement in Central Europe
resulted from double-digit increases in units, active
Representatives and customers served. New Represent-
ative leadership programs and a new campaign cycle also
favorably impacted sales in Poland. The sales increase
in Russia was due to double-digit increases in units and
active Representatives and an improved economic envi-
ronment resulting from the stability of the Russian ruble.
In Germany, the sales decline reflected a continuing
weak economic climate. In the United Kingdom, sales
increased in local currency but u.s. dollar results were
negatively impacted by foreign currency exchange.
Operating profit in Europe grew 3% to $129.5 in
2000 due to the sales increases, discussed above, coupled
with operating margin improvements in Central and
Eastern Europe, particularly Poland, and Russia, partially
offset by increased spending on incentives and advertising
throughout the region and the impact of weaker curren-
cies. In the Europe region, operating margin in 2000
improved 30 basis points over 1999. In Poland, gross
margin improved due to a shift in mix to higher margin
items, partially offset by the cost of shipping increased
orders. The operating margin improvement in Russia was
primarily due to a favorable comparison against the prior
year’s discount pricing policy and product sourcing, as
well as tight expense controls on a higher sales base. A
decline in the United Kingdom’s operating margin was
primarily due to increased advertising, consumer motiva-
tion and sampling activities to support sales growth,
as well as increased shipping, distribution and volume
related costs due to reduced capacity of shipping lines
during transition to a new shipping system.
In the Pacific region, sales increased 11% to $799.4
in 2000 due to increases in all major markets resulting
from an 18% increase in the number of units sold and
31% increase in active Representatives. In 2000, dollar
sales for most markets were negatively impacted by for-
eign currency exchange, excluding Japan and Taiwan,
where foreign currency exchange had a positive impact
on dollar sales. In Japan, sales increased double-digits
due to an increase in units sold and active Representatives
despite a reduction in consumer spending due to eco-
nomic pressures, as well as a favorable exchange rate
impact versus 1999. In China, sales growth of 44% was
driven by channel expansion, led by beauty boutiques. In
the Philippines, dollar sales grew in the mid-single dig-
its, but local currency sales increased solid double-digits.
In the Philippines, increased advertising and consumer
promotions resulted in strong increases in units sold,
customers served and active Representatives. Excluding
the impact of foreign exchange, sales in the Pacific region
rose 13%.
Operating profit in the Pacific region increased
15% to $117.8 in 2000 due to the sales increases, dis-
cussed above, and operating margin improvements, pri-
marily in Japan and China, partially offset by operating
margin declines in Taiwan and the Philippines. In the
Pacific region, 2000 operating margin improved 60 basis
points over 1999. In Japan, operating margin was favor-
ably impacted by an improvement in gross margin due
to product cost savings initiatives and a favorable change
of product mix from non-cft to higher margin cft
products. China’s operating margin improvement was
driven primarily by increased sales growth and new
higher margin products. Operating margin declined in
Taiwan primarily due to increased costs resulting from
moving to a new distribution facility and increased
spending to support sales growth. Operating margin
in the Philippines was negatively impacted by a lower
gross margin resulting from higher sales of lower margin
items, and higher advertising expenses.
37