Abercrombie & Fitch 2008 Annual Report Download - page 61
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 61 of the 2008 Abercrombie & Fitch annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
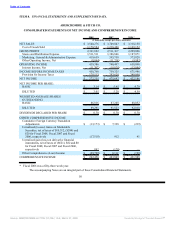
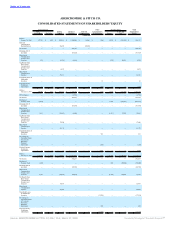
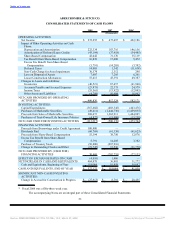
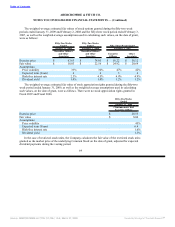
ABERCROMBIE & FITCH CO.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the software, generally not
exceeding seven years.
INCOME TAXES
Income taxes are calculated in accordance with SFAS No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes”
(“SFAS No. 109”), which requires the use of the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are recognized based on the difference between the financial statement carrying amounts of
existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
measured using current enacted tax rates in effect for the years in which those temporary differences are
expected to reverse. Inherent in the measurement of deferred balances are certain judgments and
interpretations of enacted tax law and published guidance with respect to applicability to the Company’s
operations. A valuation allowance is established against deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not
that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The Company has recorded a
valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset arising from the net operating loss of certain foreign
subsidiaries. No other valuation allowances have been provided for deferred tax assets. The effective tax
rate utilized by the Company reflects management’s judgment of expected tax liabilities within the
various tax jurisdictions.
The provision for income taxes is based on the current estimate of the annual effective tax rate
adjusted to reflect the tax impact of items discrete to the quarter. The Company records tax expense or
benefit that does not relate to ordinary income in the current fiscal year discretely in the period in which it
occurs pursuant to the requirements of Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 28, “Interim Financial
Reporting” and FASB Interpretation No. 18, “Accounting for Income Taxes in Interim Periods — an
Interpretation of APB Opinion No. 28” (“FIN 18”). Examples of such types of discrete items include, but
are not limited to, changes in estimates of the outcome of tax matters related to prior years,
provision-to-return adjustments, tax-exempt income and the settlement of tax audits.
See Note 12, “Income Taxes” for discussion regarding the Company’s policies for FIN 48.
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION
The majority of the Company’s international operations use local currencies as the functional
currency. In accordance with SFAS No. 52, “Foreign Currency Translation” (“SFAS No. 52”), assets and
liabilities denominated in foreign currencies were translated into U.S. dollars (the reporting currency) at
the exchange rate prevailing at the Consolidated Balance Sheet date. Equity accounts denominated in
foreign currencies were translated into U.S. dollars at historical exchange rates. Revenues and expenses
denominated in foreign currencies were translated into U.S. dollars at the monthly average exchange rate
for the period. Gains and losses resulting from foreign currency transactions are included in the results of
operations; whereas, translation adjustments are reported as an element of other comprehensive income
(loss) in accordance with SFAS No. 130, “Reporting Comprehensive Income.”
DERIVATIVES
Derivative contracts are accounted for in accordance with SFAS No. 133, “Accounting for Derivative
Instruments and Hedging Activities” (“SFAS No. 133”). See Note 14, “Derivatives” for additional detail.
57
Source: ABERCROMBIE & FITCH CO /DE/, 10-K, March 27, 2009 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠