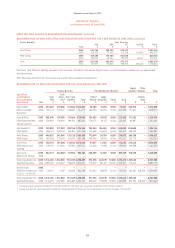
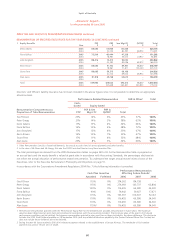
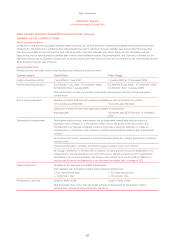
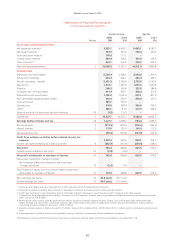
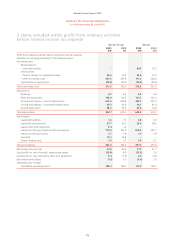
Qantas 2005 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2005 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.69
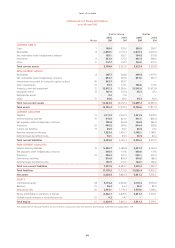
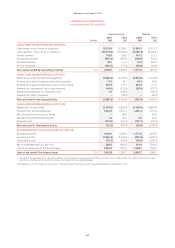
Qantas Annual Report 2005
~Notes to the Financial Statements~
for the year ended 30 June 2005
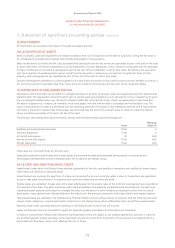
1. Statement of significant accounting policies continued
(d) DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Qantas Group is subject to foreign currency, interest rate, fuel price and credit risks. Derivative financial instruments are used to
hedge these risks. Qantas Group policy is not to enter, issue or hold derivative financial instruments for speculative trading purposes.
Principal amounts outstanding under individual cross-currency swaps are disclosed as a net asset or liability. Interest payments and
receipts under cross-currency swaps are recognised on an accruals basis in the Statements of Financial Performance. Premiums paid on
interest rate options are included in other assets and are amortised over the period of the hedge.
Gains and losses on derivatives used as hedges are accounted for on the same basis as the underlying exposures to which they relate.
Accordingly, hedge gains and losses are included in the Statements of Financial Performance when the gains and losses arising on the
related hedged position are recognised in the Statements of Financial Performance. Further details are outlined in Note 31.
When the anticipated transaction is no longer expected to occur as designated, the deferred gains and losses relating to the hedged
transaction are recognised immediately in the Statements of Financial Performance.
Where a hedge transaction is terminated early and the anticipated transaction is still expected to occur as designated, the deferred gains
and losses that arose on the hedge prior to its termination continue to be deferred and are included in the measurement of the purchase,
sale or interest transaction when it occurs. When a hedge transaction is terminated early because the anticipated transaction is no longer
expected to occur as designated, deferred gains and losses that arose on the hedge prior to its termination are included in the Statements
of Financial Performance for the year.
(e) REVENUE RECOGNITION
PASSENGER, FREIGHT AND TOURS AND TRAVEL SALES REVENUE
Passenger, freight and tours and travel sales revenue is included in the Statements of Financial Performance at the fair value of the
consideration received net of sales discount passenger and freight interline/IATA commission and goods and services tax (GST). Tours
and travel sales commissions are treated as a cost of sale. Passenger, freight and tours and travel sales are credited to revenue received
in advance and subsequently transferred to revenue when passengers or freight are uplifted or when tours and travel air tickets and land
content are utilised.
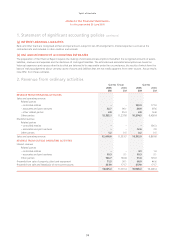
CONTRACT WORK REVENUE
Contract work revenue is recognised in proportion to the stage of completion of the contract when the stage of contract completion can
be reliably measured.
CATERING REVENUE
Revenue from the sale of catering products is recognised when control of the goods passes to the customer and is disclosed as part of
contract work revenue.
INTEREST REVENUE
Interest revenue is recognised as it accrues, taking into account the effective yield on the financial asset.
ASSET SALES
The gross proceeds of asset sales are included as revenue at the date control of the asset passes to the buyer, usually when the purchaser
takes delivery of the asset. The gain or loss on disposal is calculated as the difference between the carrying amount of the asset at the
time of disposal and the net proceeds on disposal.
AIRCRAFT FINANCING FEES
Fees relating to linked transactions involving the legal form of a lease are recognised as revenue only when there are no significant
obligations to perform or refrain from significant activities, there are no significant limitations on use of the underlying asset and the
possibility of reimbursement is remote. Where these criteria are not met, fees are brought to account as revenue or expenditure over the
period of the respective lease or on a basis which is representative of the pattern of benefits derived from the leasing transactions.
DIVIDENDS
Distributions from controlled entities are recognised as revenue by Qantas when dividends are declared by the controlled entities.
Dividends/distributions from associates and joint ventures and other investments are recognised when dividends are received.
Dividend/distribution revenue is recognised net of any franking credits.