Samsung 2011 Annual Report Download - page 30
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 30 of the 2011 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
54
55
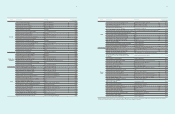
3. Critical Estimates and Judgments
The preparation of consolidated financial statements requires management
to exercise significant judgment and assumptions based on historical
experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that
are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances.
The Company makes estimates and assumptions concerning the future.
The resulting accounting estimates will, by definition, seldom equal
the related actual results. The estimates and assumptions that have a
significant risk of causing a material adjustment to the carrying amounts
of assets and liabilities within the next financial year are addressed below.
A) Revenue recognition
The Company uses the percentage-of-completion method in accounting
for its fixed-price contracts to deliver installation services. Use of the
percentage-of-completion method requires the company to estimate
the services performed to date as a proportion of the total services to
be performed. Revenues and earnings are subject to significant change,
effected by early steps in a long-term projects, change in scope of a
project, cost, period, and plans of the customers.
B) Provision for warranty
The Company recognizes provision for warranty at the point of recording
related revenue. The company accrues provision for warranty based
on the best estimate of amounts necessary to settle future and existing
claims on products sold as of each balance sheet date. Continuous
release of products, that are more technologically complex and changes
in local regulations and customs could result in additional allowances
being required in future periods.
C) Fair value of derivatives and other financial instruments
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active
market is determined by using valuation techniques. The Company uses
its judgement to select a variety of methods and make assumptions
that are mainly based on market conditions existing at the end of each
reporting period.
D) Pension benefits
The present value of the pension obligations depends on a number of
factors that are determined on an actuarial basis using a number of
assumptions. The assumptions used in determining the net cost (income)
for pensions include the discount rate. Any changes in these assumptions
will impact the carrying amount of pension obligations. The Company
determines the appropriate discount rate at the end of each year. This
is the interest rate that should be used to determine the present value
of estimated future cash outflows expected to be required to settle the
pension obligations. In determining the appropriate discount rate, the
Company considers the interest rates of high-quality corporate bonds that
are denominated in the currency in which the benefits will be paid and
that have terms to maturity approximating the terms of the related pension
obligation.
E) Estimated impairment of goodwill
The Company tests at the end of each reporting period whether goodwill
has suffered any impairment in accordance with the accounting policy
described in Note 2.11. The recoverable amounts of cash generating
units have been determined based on value-in-use calculations. These
calculations require the use of estimates.
F) Legal contingencies
Legal proceedings covering a wide range of matters are pending or
threatened in various jurisdictions against the Company. Provisions are
recorded for pending litigation when it is determined that an unfavorable
outcome is probable and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated.
Due to the inherent uncertain nature of litigation, the ultimate outcome or
actual cost of settlement may materially vary from estimates.
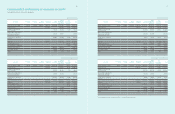
4. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, deposits held at call
with banks, and other short-term highly liquid investments (MMDA and
etc.) with original maturities of less than three months.
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, consist of
the following :
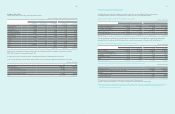
(In millions of Korean won)
2011 2010
Cash on hand ₩16,042 ₩5,897
Bank deposits, etc. 14,675,719 9,785,522
Total ₩14,691,761 ₩9,791,419
5. Financial Assets Subject to
Withdrawal Restrictions
Financial instruments subject to withdrawal restrictions as of December
31, 2011 and 2010, consist of the following :
(In millions of Korean won)
2011 2010
Short-term financial instruments ₩39,770 ₩46,371
Other non-current assets
- long-term financial instruments 16 26
6. Financial Instruments by Category
A) Financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, consist of the following :
(1) Assets
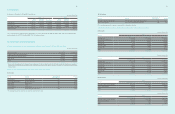
(In millions of Korean won)
2011
Assets at fair
value through
the profit and loss
Loans
and
receivables
Available-
for-sale
financial assets
Total
Cash and cash equivalents ₩-₩14,691,761 ₩-₩14,691,761
Short-term financial instruments - 11,529,905 -11,529,905
Long and short-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 3,879,567 3,879,567
Trade and other receivables - 24,153,028 -24,153,028
Deposits -791,863 -791,863
Other financial assets 130,057 1,289,447 -1,419,504
Total ₩ 130,057 ₩ 52,456,004 ₩ 3,879,567 ₩ 56,465,628
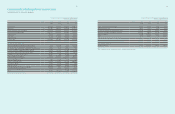
(In millions of Korean won)
2010
Assets at fair
value through
the profit and loss
Loans
and
receivables
Available-
for-sale
financial assets
Total
Cash and cash equivalents ₩-₩9,791,419 ₩-₩9,791,419
Short-term financial instruments - 11,529,392 -11,529,392
Long and short-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 4,199,358 4,199,358
Trade and other receivables - 21,308,834 -21,308,834
Deposits -655,662 -655,662
Other financial assets 34,458 1,013,771 -1,048,229
Total ₩ 34,458 ₩ 44,299,078 ₩ 4,199,358 ₩ 48,532,894
(2) Liabilities
(In millions of Korean won)
2011
Liabilities at
fair value through
profit and loss
Financial liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other financial
liabilities Total
Trade and other payables ₩-₩18,509,490 ₩-₩18,509,490
Long-term other payables - 1,024,804 -1,024,804
Long and short-term borrowings - 8,482,567 4,878,383 13,360,950
Debentures -1,285,661 -1,285,661
Other financial liabilities 40,932 7,788,449 -7,829,381
Total ₩ 40,932 ₩ 37,09 0,971 ₩ 4,878,383 ₩ 42,010,286
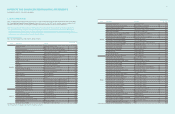
(In millions of Korean won)
2010
Liabilities at
fair value through
profit and loss
Financial liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other financial
liabilities Total
Trade and other payables ₩-₩ 16,049,800 ₩-₩16,049,800
Long-term other payables - 1,072,661 -1,072,661
Long and short-term borrowings - 4,992,14 4 5,090,433 10,082,577
Debentures -692,797 -692,797
Other financial liabilities 24,638 7,78 9, 567 -7,814,205
Total ₩ 24,638 ₩ 30,596,969 ₩ 5,090,433 ₩ 35,712,040