Samsung 2011 Annual Report Download - page 26
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 26 of the 2011 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
46
47
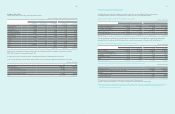
D) Changes in scope of consolidation
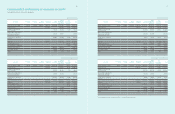
(1) Subsidiaries newly included in consolidation for the year ended December 31, 2011 are as follows :
Location Name of Subsidiaries Remark
Domestic
Prosonic Newly acquired
Samsung Venture Capital Union #20 Newly acquired
Samsung Medison Newly acquired
Medison Healthcare Newly acquired
CSL Newly acquired
Medison Xray Newly acquired
SU Materials Newly acquired
High Pioneer Private Investment Trust #1 Newly incorporated
Samsung Venture Capital Union #21 Newly acquired
Samsung Venture Capital Union #22 Newly acquired
America
Samsung Medison America (SMUS) Newly acquired
Samsung Medison Brasil (SMBR) Newly acquired
Grandis (GRANDIS) Newly acquired
NexusDX (Nexus) Newly acquired
HX Diagnostics (HX) Newly acquired
HX Reagents (HX Reagent) Newly acquired
Deltapoint Cardiac Diagnostics (Deltapoint) Newly acquired
Europe
SonoAce Deutschland (SMDE) Newly acquired
Samsung Medison Italia (SMIT) Newly acquired
Samsung Medison France (SMFR) Newly acquired
Samsung Medison Europe (SMNL) Newly acquired
Samsung Moscow Research Centre (SMRC) Newly incorporated
Nanogen Recognomics (Nanogen) Newly acquired
Middle East and Africa Samsung Electronics East Africa (SEEA) Newly incorporated
China
Samsung Medison Shanghai Medical Instrument (SMS1) Newly acquired
Medison (Shanghai) (SMS2) Newly acquired
Medison Medical Equipment (Shanghai) (MMS) Newly acquired
Samsung Suzhou LCD (SSL) Newly incorporated
Rest of Asia
Samsung Medison Japan (SMJP) Newly acquired
Samsung Medison India (SMIN) Newly acquired
Medison Medical Systems (India) (MI) Newly acquired
TNP Small / Medium Size & Venture Enterprises Growth
Promotion Investment Limited partnership (TSUNAMI) Newly acquired
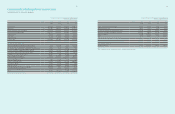
(2) Details of subsidiaries deconsolidated for the year ended December 31, 2011, are as follows :
Location Name of Subsidiaries Remark
Domestic
Samsung Gwangju Electronics Merged
CSL Disposed
Medison Xray Disposed
China Samsung Electronics Shenzhen (SESZ) Liquidated
2.1 Basis of Presentation
The Company first adopted the International Financial Reporting
Standards as adopted by the Republic of Korea (“Korean IFRS”) from
January 1, 2010. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have
been adopted by the Korean Accounting Standards Board as Korean
IFRS based on standards, amendments and interpretations published
by the International Accounting Standards Board.
The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these
consolidated financial statements are set out below. These policies have
been consistently applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise
stated.
New standards, amendments and interpretations issued but not effective
for the financial year beginning January 1, 2011 and not early adopted are
set out below :
K-IFRS 1012, ‘Deferred Tax : Recovery of Underlying Assets’
The amendment addresses the measurement of deferred tax liabilities
and deferred tax assets to reflect the tax consequences that would follow
from the manner in which the entity expects, at the end of the reporting
period, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities.
The amendments to the standard are mandatory for the first time for
the financial year beginning January 1, 2012. The Company expects the
impact of this amendment on the consolidated financial statements to be
immaterial.
K-IFRS 1107, ‘Disclosures—Transfers of Financial Assets’
The amendments will help users of financial statements evaluate the
risk exposures relating to transfers of financial assets and the effect of
those risks on an entity’s financial position and will promote transparency
in the reporting of transfer transactions, particularly those that involve
securitization of financial assets. The amendments to the standard are
mandatory for the first time for the financial year beginning January
1, 2012. The Company expects the impact of this amendment on the
consolidated financial statements to be immaterial.
K-IFRS 1113, ‘Fair value measurement’
The standard aims to improve consistency and reduce complexity by
providing a precise definition of fair value and a single source of fair value
measurement and disclosure requirements for use across IFRSs. The
requirements, which are largely aligned between IFRSs and US GAAP,
do not extend the use of fair value accounting but provide guidance on
how it should be applied where its use is already required or permitted by
other standards within IFRSs or US GAAP. The Company is yet to assess
K-IFRS 1113’s full impact and intends to adopt K-IFRS 1113 no later than
the accounting period beginning January 1, 2013.
K-IFRS 1019, ‘Employee benefits’
The main impacts on the Company will be that the corridor approach will
no longer be applied and instead all actuarial gains and losses will be
recognized in OCI as they occur; all past service costs will be immediately
recognized, and interest cost and expected return on plan assets will be
replaced with a net interest amount calculated by applying the discount
rate to the net defined benefit liability (asset). The Company is still in the
process of assessing the impact of the amendment on the consolidated
financial statements.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
2.2 Consolidation
The Company prepares annual consolidated financial statements in
accordance with Korean IFRS 1027, Consolidated and Separate
Financial Statements.
A) Subsidiaries
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of SEC and
its controlled subsidiaries. Control over a subsidiary is presumed to exist
when the Company has the power to govern the financial and operating
policies of an entity to obtain benefits from its activities generally
accompanying a shareholding of more than one half of the voting rights.
The existence and effects of potential voting rights that are exercisable
or convertible at the end of the reporting period are considered in
determining whether the Company controls another entity. Subsidiaries
are fully consolidated from the date when control is transferred to the
Company and de-consolidated from the date which control ceases to
exist.
The purchase method of accounting is used to account for the acquisition
of subsidiaries by the Company. The cost of an acquisition is measured
at the fair value of the assets given, equity instruments issued and
liabilities incurred or assumed at the date of exchange. Identifiable assets
acquired and liabilities and contingent liabilities assumed in a business
combination are measured initially at their fair values at the acquisition
date, irrespective of the extent of any non-controlling interest. The excess
of the cost of acquisition over the fair value of the Company’s share of
the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. If the cost of
acquisition is less than the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary
acquired, the difference is recognized directly in the statement of income.
For each business combination, the Company shall measure any non-
controlling interest in the acquiree at the non-controlling interest’s
proportionate share of the acquiree’s identifiable net assets.
In a business combination achieved in stages, the acquisition date fair
value of the acquirer’s previously held equity interest in the acquiree is
remeasured to fair value at the acquisition date through profit or loss.
Transactions with non-controlling interests that do not result in loss of
control are accounted for as equity transactions – that is, as transactions
with the owners in their capacity as owners. The difference between fair
value of any consideration paid and the relevant share acquired of the
carrying value of net assets of the subsidiary is recorded in equity. Gains
or losses on disposals to non-controlling interests are also recorded in
equity.
All inter-company transactions and balances are eliminated as part of the
consolidation process. Inter-company transactions, balances, income and
expenses on inter-company transactions are eliminated. Unrealized losses
are eliminated upon assessing the impairment of the transferred assets.
When the Company ceases to have control any retained interest in the
entity is re-measured to its fair value at the date when control is lost, with
the change in carrying amount recognized in profit or loss. The fair value
is the initial carrying amount for the purposes of subsequently accounting
for the retained interest as an associate, joint venture or financial asset.
In addition, any amounts previously recognized in other comprehensive
income in respect of that entity are accounted for as if the company