Nordstrom 2001 Annual Report Download - page 22
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 22 of the 2001 Nordstrom annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Blk + 1 pms PAGE 20 pms
550
Cyan Mag Yelo Blk
20200324 NORDSTROM
2001 Annual Report • VERSION
8.375 x 10.875 • SCITEX • 175 lpi • Kodak 80# Cougar
20 NORDSTROM INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Dollars in thousands except per share amounts
Note 1: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The Company: Nordstrom, Inc. is a fashion specialty retailer
offering a wide selection of high-quality apparel, shoes and
accessories for women, men and children, in the United States
through 80 Nordstrom full-line stores, 46 Nordstrom Rack and
clearance stores, 4 Façonnable boutiques and 2 free-standing
shoe stores. The Company also operates 24 Façonnable boutiques
located primarily in Europe. Additionally, the Company generates
catalog and Internet sales through Nordstrom.com LLC and service
charge income through Nordstrom Credit, Inc.
Basis of Presentation: The consolidated financial statements
include the balances of Nordstrom, Inc. and its subsidiaries for
the entire fiscal year. All significant intercompany transactions
and balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates: Management makes estimates and assumptions
that affect the reported amounts in the financial statements and
accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those
estimates.
Reclassifications: Certain reclassifications of prior year balances
have been made for consistent presentation with the current year.
Revenue Recognition: Revenues are recorded net of estimated
returns and exclude sales tax. Revenue is recorded at the point
of sale for retail stores. Catalog and e-commerce sales include
shipping revenue and are recorded upon shipment to the customer.
Buying and Occupancy Costs: Buying costs consist primarily
of salaries and expenses incurred by the Company’s merchandise
managers, buyers and private label product development group.
Occupancy costs include rent, depreciation, property taxes and
operating costs related to the Company’s retail and distribution
facilities.
Shipping and Handling Costs: The Company's costs for shipping
and handling to customers include payments to third-party shippers
and costs incurred to store, move and prepare merchandise for
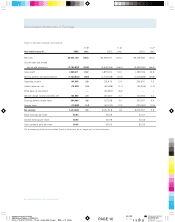
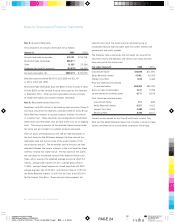
shipment. Shipping and handling costs of $30,868, $38,062
and $29,085 in 2001, 2000 and 1999 were included in selling,
general and administrative expenses.
Advertising: Costs for newspaper, television, radio and other media
are generally expensed as incurred. Direct response advertising
costs, consisting primarily of catalog book production and printing
costs, are deferred and recognized over the expected life of the
catalog, not to exceed six months. Total advertising expenses were
$145,341, $190,991 and $160,957 in 2001, 2000 and 1999.
Store Preopening Costs: Store opening and preopening costs
are charged to expense when incurred.
Cash Equivalents: Cash equivalents represent short-term investments
with a maturity of three months or less from the time of purchase.
Cash Management: The Company’s cash management system
provides for the reimbursement of all major bank disbursement
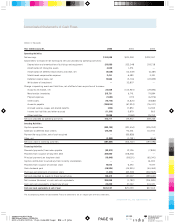
accounts on a daily basis. Accounts payable at January 31, 2002
includes $31,817 of checks not yet presented for payment drawn
in excess of cash balances.
Customer Accounts Receivable: In accordance with industry
practices, installments maturing in more than one year and deferred
payment accounts receivable are included in current assets.
Merchandise Inventories: Merchandise inventories are stated
at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out basis) or market, using
the retail method.
Land, Buildings and Equipment: Depreciation is computed using
a combination of accelerated and straight-line methods. Estimated
useful lives by major asset category are as follows:
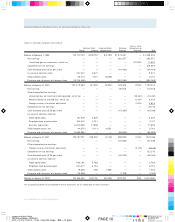
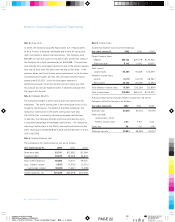
Asset Life (in years)
Buildings 5-40
Store fixtures and equipment 3-15
Leasehold improvements Shorter of life of lease or asset life
Software 3-7
Asset Impairment: The Company reviews its intangibles and
other long-lived assets for impairment when events or changes
in circumstances indicate the carrying value of these assets may
not be recoverable.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements