Nissan 2009 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2009 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Nissan Annual Report 2009 41
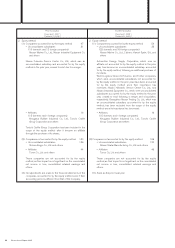
Prior fiscal year Current fiscal year
From April 1, 2007 From April 1, 2008
[
To March 31, 2008
][
To March 31, 2009
]
(6) Hedge accounting
1) Hedge accounting
Deferral hedge accounting is adopted for derivatives
which qualify as hedges, under which unrealized gain or
loss is deferred.
2) Hedging instruments and hedged items
·Hedging instruments ...... Derivative transactions
·Hedged items ....................... Hedged items are primarily
forecast sales denominated in foreign currencies
and receivables and payables denominated in
foreign currencies.
3) Hedging policy
It is the Company’s policy that all transactions
denominated in foreign currencies are to be hedged.
4) Assessment of hedge effectiveness
Hedge effectiveness is not assessed if the substantial
terms and conditions of the hedging instruments and the
hedged forecasted transactions are the same.
5) Risk management policy with respect to hedge accounting
The Company manages its derivative transactions in
accordance with its internal “Policies and Procedures for
Risk Management.”
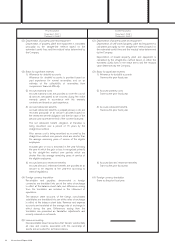
(7) Accounting for consumption tax
Transactions subject to consumption tax are recorded at
amounts exclusive of consumption tax.
(8) Adoption of consolidated taxation system
The Company and some of its subsidiaries adopted the
consolidated taxation system effective from the fiscal year
ended March 31, 2008.
(9) Accounting policies adopted by foreign consolidated subsidiaries
The financial statements of the Company’s consolidated
subsidiaries in Mexico have been prepared based on general
price-level accounting. The related revaluation adjustments
made to reflect the effect of inflation in Mexico in the
accompanying consolidated financial statements have been
charged or credited to operations and are directly reflected
in valuation, translation adjustments and others.
5. Valuation of assets and liabilities of consolidated subsidiaries
Assets and liabilities of consolidated subsidiaries acquired through
business combinations are carried at fair value at the time of acquisition.
6. Amortization of goodwill and negative goodwill
Goodwill and negative goodwill have been amortized evenly over
periods not exceeding 20 years, during which their effect can be
recognized, determined based on their materiality. However,
immaterial goodwill and negative goodwill are charged or
credited to income in the year of acquisition.
7.
Cash and cash equivalents in the consolidated statements of cash flows
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand, cash in banks
which can be withdrawn at any time and short-term investments with
a maturity of three months or less when purchased which can easily
be converted to cash and are subject to little risk of change in value.
(5) Hedge accounting
1) Hedge accounting
Deferral hedge accounting is adopted, in principle. Foreign
exchange contracts, except those for accounts receivable
denominated in a foreign currency, are subject to appropriation
if they satisfy the requirements for appropriation treatment. For
interest rate swaps, preferential treatment is applied if the
swaps satisfy the requirements for preferential treatment.
2) Hedging instruments and hedged items
·Hedging instruments ...... Same as the prior fiscal year
·Hedged items ....................... Hedged items are primarily
receivables and payables denominated in foreign
currencies.
3) Hedging policy
Foreign exchange and interest volatility risks are hedged
within a certain range in accordance with the Company’s
“Policies and Procedures for Risk Management and
Authority Regarding Derivative Transactions.”
4) Assessment of hedge effectiveness
Hedge effectiveness is not assessed if the substantial
terms and conditions of the hedging instruments and the
hedged transactions are the same.
(6) Accounting for consumption tax
Same as the prior fiscal year.
(7) Adoption of consolidated taxation system
The Company and some of its subsidiaries have been
adopted the consolidated taxation system.
5. Valuation of assets and liabilities of consolidated subsidiaries
Same as the prior fiscal year.
6. Amortization of goodwill and negative goodwill
Same as the prior fiscal year.
7.
Cash and cash equivalents in the consolidated statements of cash flows
Same as the prior fiscal year.
8. Reporting of revenue from finance lease transactions
Instead of reporting the revenue, amounts equivalent to the
interest are distributed over the fiscal years concerned.