Nissan 2006 Annual Report Download - page 49
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 49 of the 2006 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Nissan Annual Report 2005 47
Technology
Development Concept
Safety Life on
Board
Dynamic
Performance
Environment
Vision 2015
Traffic Circumstance
Driving Behavior
Vehicle
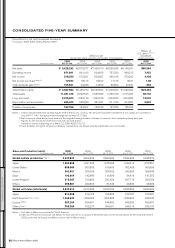
600
500
(Billion yen) (% of net revenue)
400
300
200
100
0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
’99 ’00 ’01 ’02 ’03 ’04 ’05
239 232 262 300 354 398 448
4.0% 4.2%
3.8%
4.4% 4.8% 4.8%
4.6%
R&D Investment
The system assists the driver control the distance
between the driver and the vehicle in front, through
the use of a radar sensor installed in the front
bumper of the car behind. If the car in front
decelerates, the system automatically applies the
brakes in the rear car. Furthermore, if the system
determines that the car in front is too close and that
braking is required in the car behind, an indicator will
appear on the instrument panel and a buzzer will
sound simultaneously. The gas pedal will then
automatically move upwards against the foot of the
driver to assist the driver in switching to the brakes.
Our goal for the second facet of Vision 2015, the
environment, is to reduce CO2emissions to the
targeted value. Target value for technology
development in CO2emission reductions is 40
percent by 2015, compared to 2005 level. To
achieve this goal, we have a “Triple-layered
Approach” concept that addresses the vehicle itself,
driving behavior, and the traffic conditions.
We are currently developing fuel cell, electric and
hybrid electric vehicle technologies.
Reducing the size, weight and cost of motors
and batteries are the key factors in promoting HEV,
FCV, and EV. The lithium ion battery is a good
example. We are ranked number one in research in
this area, even above companies that specialize in
battery manufacture.
We are also committed to fuel cell stack
technology. We decided to develop our own after
purchasing stacks from an outside vendor for a time,
and managed that in fiscal 2005. Our first practical
application came out this year.
In addition to developing these advanced
technologies, we continue to further strengthen our
current technologies such as the CVT because we
need to find a good cost-benefit balance. The CVT is
a low-cost and effective solution in reducing CO2
emission and another longtime strength of Nissan
technology. Other car companies do use CVTs, but
only Nissan incorporates them on models with
higher-displacement engines such as 3.5-liter power
engines. I believe our CVTs are the most
sophisticated and best integrated in the world.
For the second layer, driving behavior, we’re
working on “Eco-driving Support.” As an example,
we’ve found that including a meter on the instrument
panel showing real-time fuel use can change driving
INVESTMENT FOR THE FUTURE
Vision 2015 The Triple-Layered Approach