Mazda 2016 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2016 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.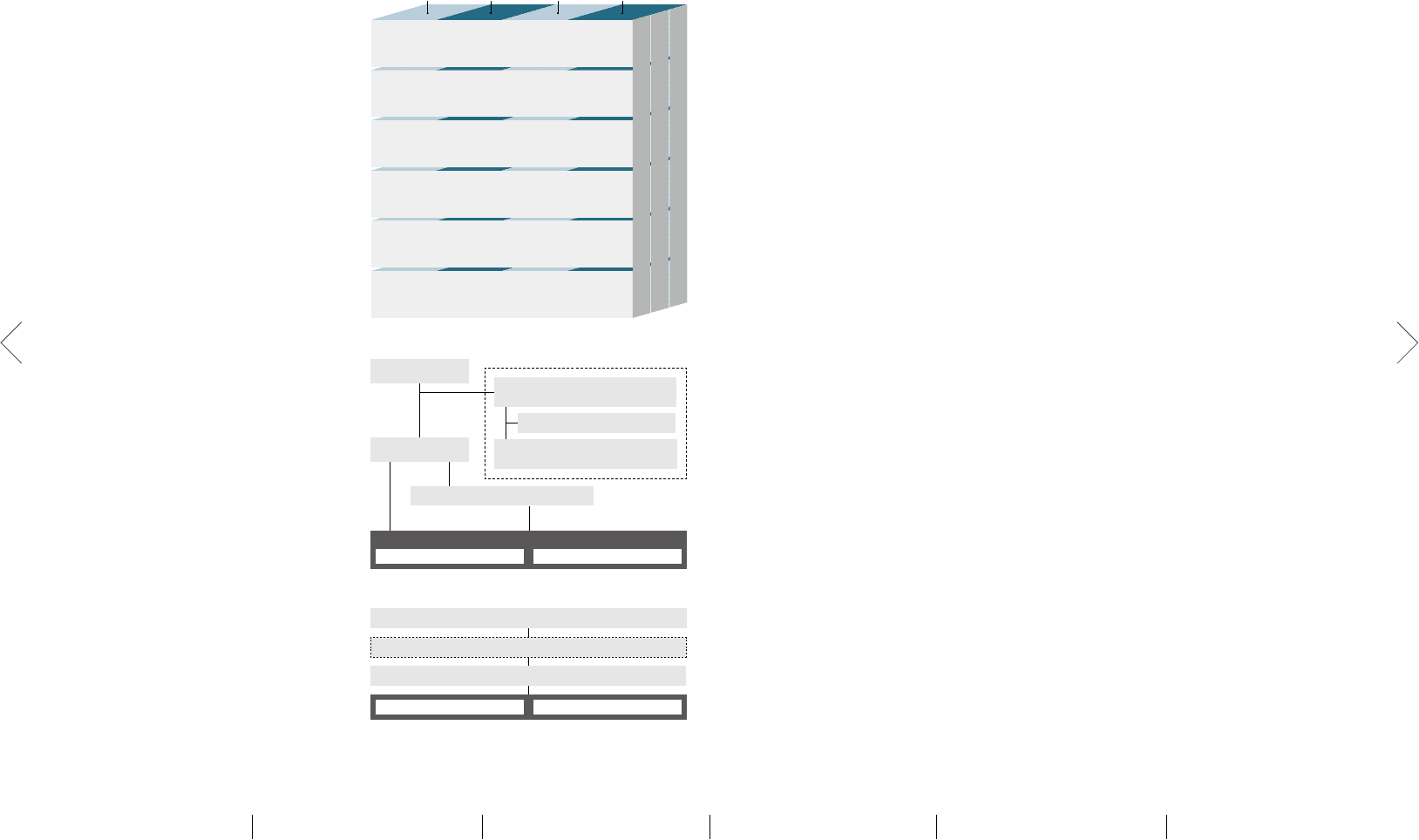
Business Management System
revised in order to improve the level of system establishment.
Moreover, to prevent suspension of its businesses from causing a serious impact on society, Mazda
has been developing measures for possible future large-scale earthquakes, such as the expected
Nankai Trough earthquake.
Response to Accidents and Other Emergencies
Mazda has been systematically undertaking preparatory measures for major earthquakes since the
March 2004 fiscal year. Examples of such “hardware” and “software” measures include quake-proofing
buildings and facilities, and raising embankments, as well as maintaining emergency-contact networks,
organizing self-disaster-defense teams, developing response manuals, selecting tsunami evacuation
areas, and carrying out evacuation drills. Disaster drills are held annually both jointly with the fire
authorities and solely by Mazda’s self-disaster-defense teams to confirm initial response to an emergency.
Further, based on lessons learned from the Great East Japan Earthquake, Mazda has communi-
cated to all employees the procedures for initial responses and manuals for operating self-disaster-
defense teams, which were newly clarified in the March 2014 fiscal year, with the aim of confirming
and reviewing the precautions and initial responses in each workplace. Steady efforts to enhance both
“hardware” and “software” aspects of emergency readiness will continue in preparation for the
Nankai Trough earthquake or other large earthquakes and tsunami associated therewith. Mazda also
supports local communities’ disaster prevention activities through dispatching fire engines and
other means.
Information Security
Personal information and other important information are appropriately managed and protected
based on the established information management policies and internal regulations, so as to ensure
information security. To raise employees’ awareness about information security, Mazda requires its
employees to execute training on the management of confidential information, protection of personal
information, and IT security. Upon newly joining the Company, management of confidential informa-
tion is covered in the introduction program, while e-learning is used for personal information protec-
tion and IT security training. Other continuous education efforts are also available, including an
Intranet site dedicated to information and knowledge on information security.
For companies in the Mazda Group, Mazda provides guidelines and educational tools regarding
information security, realizing a Group-wide effort to ensure information security. Moreover, Mazda
newly established the Regulations for the Handling of Specific Personal Information in October 2015,
to be prepared for the enforcement of the Social Security and Tax Number System. The Company also
supported the initiatives in its Group companies.
IT Security Management Rules
The IT security policy based on the BS 7799* framework has been established as IT security manage-
ment rules, under which the mechanisms for security control and monitoring that should be incorpo-
rated into IT systems are determined. Whether such mechanisms are properly installed and operated
is confirmed on both a regular and random basis.
* Standards on information security management established by the British Standards Institution (BSI), on which ISO/IEC27001 &
27002, the current international standards for information security management, are based.
Internal Controls
Mazda has established the Mazda Corporate
Ethics Code of Conduct, which states action
guidelines for employees, the Finance Control
Guideline for global financial control, and other
guidelines. Based on these guidelines, each
department develops rules, procedures,
manuals, etc., to promote establishment of
internal control.
For Group companies, cooperative systems
have been established, in accordance with the
Domestic Affiliates Administration Rules and
the Overseas Affiliates Administration Rules.
At Mazda, the department responsible for
each Group company supports training and
system improvement at respective Group
companies.
Risk Management
Mazda makes continuous efforts to identify
and reduce various internal and external risks
in accordance with the Basic Policy on Risk
Management, Risk Management Regulations,
and other related internal regulations, so as to
ensure continuous and stable progress of
business activities. Among the risks identified,
considering the level of importance, individual
business risks are managed by the department
in charge of that business area, while Compa-
ny-wide risks are handled by departments that
carry out business on a Company-wide basis.
These departments manage the risks appropri-
ately, following the PDCA cycle.
In the event of an emergency, such as a
natural disaster or situation that creates serious
managerial consequences, Mazda takes appropri-
ate measures in reference to its internal regula-
tions, including establishing an emergency
response task force when necessary. In the March
2016 fiscal year, Mazda and its Group companies
engaged in efforts to visualize the status of
establishing systems to manage risks. The
position of the Risk & Compliance Committee was
Mazda Internal Controls
Enhancement of IT Security
•
Setting IT Security Management Regulations
•
IT system auditing, etc.
Monitoring
•
Self-diagnosis of internal controls
•
Internal auditing, etc.
Information and Communication
•
Internal control sign-off system
•
Mazda Global Hotline, etc.
Control Activities
•
Developing / operating work processes
(Developing procedures, manager approvals, etc.)
Risk Assessment
•
Risk Compliance Committee
•
Revising self-diagnosis checklist, etc.
Efficacy / Efficiency Financial
Reporting
Compliance Asset
Protection
Control Environment
•
Mazda Corporate Ethics Code of Conduct
• Finance Control Guideline, etc.
Overseas Group Companies
Group Companies in Japan
Mazda
Emergency Risk Management Structure
Executive Officer in charge of Risk Management
Emergency Response Task force
Representative Director and President
Departments within Mazda Mazda Group Companies
For incidents that fall outside the scope of existing risk management
organizations and require a coordinated interdepartmental response, the
executive officer in charge of risk management will consult with the
president, establish an emergency response task force, and appoint a
general manager for this task force.
Instruction, assistance
Promotion
Risks at Company-
wide level
Risk Management Structure in Normal Times
Executive Officer in charge of
Compliance & Risk Management
Department in charge of promoting
risk management
Department responsible for each risk
Risk Compliance Committee
Representative
Director and President
Executive Officers
in charge
Departments within Mazda Mazda Group companies
Individual business risks
MAZDA ANNUAL REPORT 2016
36 Foundations Underpinning
Sustainable Growth
Message from
Management
Review of Operations
Drivers of Value Creation
Financial Section
Contents