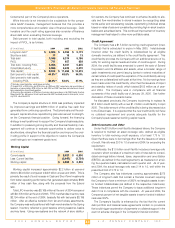
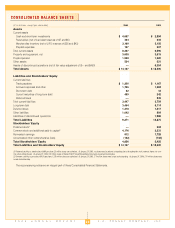
JCPenney 2004 Annual Report Download - page 18
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 18 of the 2004 JCPenney annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
J.C. PENNEY COMPANY, INC.2 004 ANNUAL REPORT
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
16
established and consists of associates dedicated full-time to man-
aging the ongoing process of monitoring and self-testing key con-
trols throughout the organization, documenting and testing signifi-
cant changes to internal controls over financial reporting and meet-
ing all of the related reporting requirements.
Independent Support Functions
— Internal Audit, Legal and
Finance support the Company’s risk management function. They
operate independently of the operating divisions of the Company.
As an important component of the Company’s control structure, the
Internal Audit department reports functionally to the Audit
Committee of the Board of Directors. Internal Audit performs
reviews and completes test work to ensure that: (a) risks are appro-
priately identified and managed; (b) interaction with various inter-
nal governance groups, such as the legal compliance coordina-
tors, occurs as needed; (c) significant financial, managerial and
operating information is reliable and timely; (d) associates’ actions
are in compliance with policies, standards, procedures and appli-
cable laws and regulations; (e) resources are acquired economi-
cally, used efficiently and adequately protected; (f) quality and con-
tinuous improvement are fostered in the organization’s control
process; and (g) significant legislative or regulatory issues impact-
ing the organization are recognized and addressed appropriately.
Legal compliance coordinators, working with Internal Audit, are
responsible for ensuring that all areas of the Company have effec-
tive procedures in place to comply with various laws and regula-
tions and any changes thereto.
Categories of Risk
Management defines risk as the potential deviation from planned
operating results that may have a negative impact on investor enter-
prise value in the short or long term. The deviation can arise from
inadequate or ineffective internal processes or systems, external
events or Company personnel. The Company’s key risks and relat-
ed risk mitigation/management practices are discussed below.
Business
•Strategic —The Company’s key business risk would be the
failure to consistently execute in a centralized environment and
achieve sustainable operating performance at the Company’s
targeted levels. In addition, it will be critical to continue the
positive momentum experienced over the last four years to
transition from a turnaround to a leadership position in both sales
and profitability.
A strong foundation has been built as the Company has made
the transition to a centralized merchandising model, improved the
merchandise assortments and related marketing and strength-
ened the Company’s core private brands. The Company has
established centralized store distribution centers and inventory
systems that allow the Company to improve the planning of mer-
chandise assortments, allocate inventory and stock stores and
better track sales trends enabling prompt replenishment and
timely pricing decisions. The Company’s overall goal is to provide
customers with stylish merchandise at competitive prices in an
exciting and consistent store environment. The Company’s initia-
tives over the next few years will be to improve the customer
experience by leveraging the Company’s multiple shopping
channels with coordinated merchandise assortments and mar-
keting events, continue to build and improve the Company’s
strong private brands, invest in the renewal of high-potential
stores, expand the Company’s presence through the addition of
off-mall stores and invest in new technology.
While results have been positive and the turnaround is essen-
tially complete, the Company will face continued challenges, par-
ticularly as it moves beyond the turnaround to its longer-term
strategic priorities. Key to meeting the Company’s long-term cus-
tomer and financial goals is continued realization of the benefits
from centralized buying and allocation. The effectiveness of
these processes and systems is an important component of the
Company’s ability to have the right inventory at the right place,
time and price. Also key to success will be the customer’s
response to initiatives related to new private brands being rolled
out, such as nicole by Nicole Miller, expansion of other private
brands, such as the Chris Madden for JCPenney Home
Collection, Turning Home into Haven, as well as investments to
make the shopping experience easier, such as the new point-of-
sale technology that will be rolled out in 2005 and 2006.
•Management —Since 2000, the Company has hired
seasoned individuals, including executive level and
others with a breadth of experience in merchandising,
marketing, buying and allocation under a centralized model, as
well as to manage Catalog and Internet operations. The Board of
Directors dedicated significant effort during 2004 to
identify and appoint the right individual to lead the Company
beyond the turnaround. This search led to the appointment of
Myron E. Ullman, III, as the Company’s new Chairman of the
Board and Chief Executive Officer effective December 1, 2004.
While the risk always exists that key management associates
could decide to leave the Company, the depth of experience in
all critical areas of the Company mitigates that risk to a certain
degree. In addition, one of the CEO’s priorities is to make
JCPenney a great place to work. This initiative, combined with
the sense of accomplishment for the progress that has been
made over the past few years, creates an atmosphere where
associates want to be part of a winning team and should con-
tribute to the Company’s ability to retain quality personnel over
the longer term.
Financial
•Financial Position and Liquidity —The Company’s successful
execution of its financing strategy over the past four years,
combined with the sale of Eckerd in 2004, has mitigated the
strategic risk inherent during the turnaround period by providing the
financial resources necessary to increase capital spending to
fund planned department store renewals, new mall and off-mall
stores and relocations, and to make additional investments in
technology. This has allowed the operating leadership within
the Company time to focus on converting to a centralized
merchandising organization, enhance the merchandise
assortments and marketing efforts, with the ultimate goal of