Mazda 2011 Annual Report Download - page 29
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 29 of the 2011 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
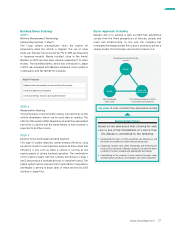
Building Block Strategy
STEP 1
Battery Management Technology
(Idling Stop System “i-stop”)
The i-stop system automatically shuts the engine off
temporarily when the vehicle is stopped. The use of i-stop
alone can improve fuel economy by 7% to 10% (as measured
in Japanese models). Mazda installed i-stop in the Axela/
Mazda3 in 2009 and has been steadily expanding it to other
models. The facelifted Demio, which was introduced in Japan
in 201 1, was equipped with Mazda’s advanced i-stop system in
combination with the SKYACTIV-G engine.
STEP 2
Regenerative Braking
This technology converts kinetic energy into electricity as the
vehicle decelerates, which can be used later as needed. The
effects of the system differ depending on what the regenerated
electricity is used for, but the improvement in fuel economy is
expected to be 5% or more.
STEP 3
Electric Drive Technology (Hybrid System)
This type of system improves overall energy efficiency using
an electric motor to assist gasoline engines at times when fuel
efficiency is low, such as when a vehicle is running at low
engine speeds or during low-load operation. The combination
of this hybrid system with the systems mentioned in steps 1
and 2 can produce a substantial boost in overall efficiency. The
hybrid system will be licensed from Toyota Motor Corporation,
and Mazda is aiming to begin sales of these vehicles by 2013
starting in Japan first.
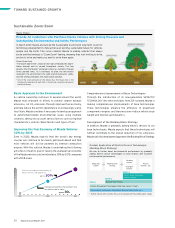
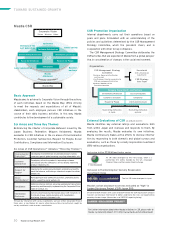
Basic Approach to Safety
Mazda’s aim is to achieve a safe, accident-free automotive
society from the three perspectives of vehicles, people, and
roads and infrastructure. To this end, the Company has
formulated the Mazda Safety Policy and is working to deliver a
steady stream of technologies and solutions based on it.
Major Progress
Reduced fuel consumption when restarting the engine
Increased operating frequency
Increased energy recovery during deceleration
People
Developing and commercializing
safe cars
Vehicles
Roads and
infrastructure
Educating people
about safety
Participating vigorously in efforts
to build traffic environments
Mazda Safety Policy
Based on the awareness that striving for safe
cars is one of the foundations of a worry-free
life, Mazda is committed to the following:
1. Researching the ways in which customers use Mazda cars and
the traffic environment in which they are being used
2. Deepening research into safety technology and reflecting the
results of this research in Mazda’s products in a way that offers
customers the best available and appropriate technology
3. Contributing to the creation of safe societies through safety
communication (products, technologies and safety education)
Our vision:
Mazda Annual Report 201 1 27