Mazda 2011 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2011 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
TOWARD SUSTAINED GROWTH
Basic Policy
Provide All Customers who Purchase Mazda Vehicles with Driving Pleasure and
Outstanding Environmental and Safety Performance
In March 2007, Mazda announced the Sustainable Zoom-Zoom long-term vision for
technology development to help achieve an exciting, sustainable future for vehicles,
people and the Earth. This vision commits Mazda to making vehicles that always
excite and that embody a “Zoom-Zoom” feeling, meaning they look inviting to drive,
are fun to drive and make you want to drive them again.
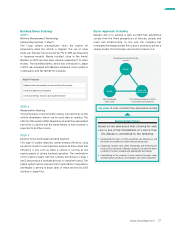
Zoom-Zoom tree
“The Zoom-Zoom tree”, shown on the right, embodies the Zoom-
Zoom concept and its spread throughout society. The tree
absorbs the One Mazda* corporate culture as nutrients through
firmly planted roots. As it continues to grow, the left branch
represents the environment, the right branch represents safety,
and the treetop embodies the Zoom-Zoom concept.
* One of the seven principles of the Mazda Way. The Mazda Way is the
fundamental approach to work that is shared and valued by everyone in
the Mazda Group.
Basic Approach to the Environment
As vehicle ownership continues to expand around the world,
Mazda must redouble its efforts to achieve cleaner exhaust
emissions, cut CO2 emissions through improved fuel economy,
and help reduce the world’s dependence on increasingly scarce
fossil fuels. Mazda considers it necessary to develop an approach
to automobile-related environmental issues using multiple
solutions, taking into account various factors such as regional
characteristics, vehicle characteristics and types of fuel.
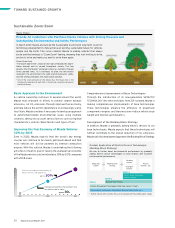
Improving the Fuel Economy of Mazda Vehicles
30% by 2015
Even in 2020, Mazda expects that the world’s key energy
sources will continue to be mainly petroleum-based and that
most vehicles will still be powered by internal combustion
engines. With this outlook, Mazda is undertaking the following
activities to meet its goal of raising the average fuel economy
of the Mazda vehicles sold worldwide by 30% by 2015 compared
with 2008 levels.
Comprehensive Improvement of Base Technologies
Through the introduction of its new-generation SKYACTIV
TECHNOLOGY into vehicle models from 201 1 onward, Mazda is
making comprehensive improvements of base technologies.
These technologies enhance the efficiency of powertrain
components—engines and transmissions—reduce vehicle body
weight and improve aerodynamics.
Development of the Building Block Strategy
In addition, Mazda is gradually adding electric devices to our
base technologies. Mazda expects that these technologies will
further contribute to the overall reduction of CO2 emissions.
Mazda calls this development approach the Building Block Strategy.
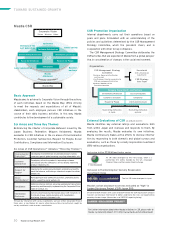
Sustainable Zoom-Zoom
2001 2008 2015
Average fuel economy improvement ratio
for vehicles sold in Japan:
approx. 30%
Plan to raise average fuel economy of
Mazda vehicles sold globally by
approx. 30%
Average fuel economy for all cars
Gradual Application of Electric Devices Technologies
(Building Block Strategy)
We aim to further boost environmental performance by gradually
adding electric device technologies to base engines with excellent
environmental performance.
* Hybrid vehicle with a battery that can be charged with household power supply
Electric Drive Technology
(Hybrid System)
STEP-3
STEP-2
STEP-1
Battery Management Technology (Idling Stop System “i-stop”)
Regenerative Braking
Improved Base Technologies (Powertrains, Reduced Body Weight, etc.)
Idling stop
system
Regenerative
braking
Gasoline
hybrids
Hydrogen
hybrids
Plug-in
hybrids*, etc.
26 Mazda Annual Report 201 1