Kia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2009 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NOTES TO NONCONSOLIDATED
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2009 and 2008
Company assumes substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership are classied as capital leases. All other leases are classied as operating
leases.
Substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership are evidenced when one or more of the criteria listed below are met:
- Ownership of the leased property will transfer to the lessee at the end of the lease term.
- The lessee has a bargain purchase option, and it is reasonably certain at the inception of the lease that the option will be exercised.
- The lease term is equal to 75% or more of the estimated economic useful life of the leased property.
- The present value at the beginning of the lease term of the minimum lease payments equals or exceeds 90% of the fair value of the leased
property.
In addition, if the leased property is specialized to the extent that only the lessee can use it without any major modication, it is considered a
capital lease.
Payments made under operating leases are charged to the income statement on a straight-line basis over the period of the lease.
Where the Company is a lessee under a capital lease, the present value of future minimum lease payments is capitalized and a corresponding
liability is recognized. In a sale and leaseback contract, the Company recognizes the sale and leaseback transaction, respectively. However,
the Company does not immediately recognize any excess of sales proceeds over the carrying amount as gain, but defers and amortizes the
amount over the lease term.
(i) Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses, if any. Impairment losses are determined as the
amount required to reduce the carrying amount of an intangible asset to its recoverable amount.
The criteria for determining whether an incurred cost qualies as an intangible asset and the periods of amortization for each classication of
intangible asset are described below.
(i) Research and Development Costs
To assess whether an internally generated intangible asset meets the criteria for recognition, the Company classies the expense generation
process into a research phase and a development phase. All costs incurred during the research phase are expensed as incurred. Costs incurred
during the development phase are recognized as assets only if the following criteria are met for recognition in SKAS No. 3 Intangible Assets:
(1) completion of the intangible asset is technically feasible so that it will be available for use or sale; (2) the Company has the intention and
ability to complete the intangible asset and use or sell it; (3) there is evidence that the intangible asset will generate probable future economic
benet; (4) the Company has adequate technical, nancial and other resources to complete the development of the intangible asset and
the intangible asset will be available; and (5) the expenditures attributable to the intangible asset during its development can be reliably
determined.
If the costs incurred fail to satisfy these criteria, they are recorded as expenses as incurred. Where development costs satisfy the criteria, they
are capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over three years. The expenditure capitalized includes the cost of materials, direct labor
and an appropriate proportion of overheads.
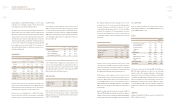
(ii) Other Intangible Assets
Other intangible assets, which consist of industrial property rights, franchise rights and software, are amortized using the straight-line method
over the following periods.
(j) Bonds with Warrants
When accounting for bonds with stock purchase warrants, the liability component and the equity component of a bond are separated.
The liability component of a bond is recognized initially at fair value. Fair value is the present value of a similar debt security that does not have
stock purchase warrants. The equity component is recognized initially as the dierence between the fair value of the bond as a whole, which
are the gross proceeds of the bond received at the date of issuance, and the fair value of the liability component. In the case of bonds with
detachable stock warrants, the fair values of the liability and equity components are calculated separately. The equity component of bonds
with stock purchase warrants are presented as part of capital surplus within equity.
Subsequent to initial recognition, the liability component is measured at amortized cost using the eective interest rate method. The equity
component is not remeasured subsequent to initial recognition.
(k) Discount (Premium) on Debentures
Discount (premium) on debentures issued, which represents the difference between the face value and issuance price of debentures, is
amortized (accreted) using the effective interest method over the life of the debentures. The amount amortized (accreted) is included in
interest expense.
(l) Retirement and Severance Benets
Employees who have been with the Company for more than one year are entitled to lump-sum payments based on salary rates and length of
service at the time they leave the Company. The Company’s estimated liability under the plan which would be payable if all employees left at
the end of the reporting period, is accrued in the accompanying non-consolidated statements of nancial position. A portion of the liability
is covered by an employees’ severance benets trust where the employees have a vested interest in the deposit with the insurance company
in trust. The deposit for severance benets held in trust is, therefore, reected in the accompanying non-consolidated statements of nancial
position as a reduction of the liability for retirement and severance benets.
Through March 1999, under the National Pension Scheme of Korea, the Company transferred a certain portion of retirement allowances for
employees to the National Pension Fund. The amount transferred will reduce the retirement and severance benet amount to be payable to
the employees when they leave the Company and is accordingly reected in the accompanying non-consolidated statements of nancial
position as a reduction of the retirement and severance benefits liability. However, due to the new regulation effective April 1999, such
transfers to the National Pension Fund are no longer required.
(m) Valuation of Receivables and Payables at Present Value
Receivables and payables arising from long-term loans/borrowings and other similar transactions are stated at present value. The dierence
Useful lives (years)
Rights of trademark 5
Patent rights 10
Rights of utilization 10
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009