Kia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 33
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 33 of the 2009 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009
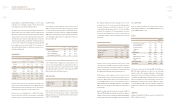
Salary expense accruals increased temporarily as ongoing
negotiations caused a portion of wages to be deferred to 2010.
Borrowings, meanwhile, declined by KRW 1.073 trillion to KRW
4.56 trillion. This was due mainly to a reduced need for short-term
borrowings, including commercial paper and short-term loans.
The proportion of short-term borrowings among total borrowings
therefore posted a sharp decline from 23% in 2008 to 2% in 2009.
In total, year-on-year fourth-quarter net borrowings dropped from
KRW 2.648 trillion to approximately KRW 2 trillion in 2009.
Kia Motors’ strong sales performance in 2009 led to an
improvement in the company’s nancial structure, particularly in
terms of borrowings. The overall debt ratio and net borrowings
ratio both improved to 129.7% and 35.9%, respectively. Going
forward, Kia’s management intends to continue to improve the
company’s nancial structure by steadily reducing borrowings.
EQUITY
Kia Motors’ capital stock amounted to KRW 7.376 trillion, up KRW
1.635 trillion from the fourth quarter of the previous year. The
increase is attributable to a higher net income of KRW 1.45 trillion
and issuance of new stock worth KRW 249 billion.
CAPEX
Total CAPEX investment amounted to KRW 1.541 trillion on a
consolidated basis in 2009, posting a slight increase over the
previous year. The portion of R&D investment comprises 4.3%
of total revenue. Approximately 86% of R&D spending was
expensed in Korea, among which new vehicle-related R&D costs
were recorded as intangible assets and new vehicle facility costs
as tangible assets. Both are amortized according to predefined
schedules (3 years for intangible assets, starting from the time that
mass-production of new vehicles commences, and 15 years on
(KRW Billion)
2008 2009 Dierence
R&D 882 796 -86
(% of Revenue) 5.4% 4.3%
Maintenance 183 199 15
Korea 1,065 995 -70
Overseas 456 547 91
CAPEX Total 1,521 1,541 21
* CAPEX totals include R&D costs recognized in the current period, and therefore
are not identical to the gures contained in the consolidated statement of cash
ows.
* The above contents may dierent from nancial reporting standards.
* In case of Overseas CAPEX, F/X evaluation is not considered.
MANAGEMENT’S
DISCUSSION & ANALYSIS
average for the depreciation period of tangible assets).
CAPEX investments recognized overseas rose by KRW 91 billion
year-on-year, as plants in China, Slovakia and the US were outtted
for new vehicle production.
Construction on major facilities abroad was completed in 2009,
but continuing investments will be made as new vehicles and
facilities are introduced. Following the relatively large CAPEX
investments in 2009, new vehicle development spending will
continue in 2010, but to a smaller degree than in the past.
CREDIT RATINGS
Despite the deterioration in global economic conditions, Kia Motors’
business fundamentals strengthened due to the company’s solid
financial performance. Kia’s short- and long-term credit ratings
remained high at A1 for short-term credit as of 2009 and AA- for
long-term credit. The long-term rating was revised upward to AA in
March of 2010.
The company’s overseas credit ratings and outlook were revised
downward, as credit evaluation agencies lowered their projections
for the auto industry amid generally poor performances by the
majority of the world’s major automakers. In January 2009, Moody’s
lowered Kia’s credit outlook, followed by a downgrade from S&P in
April.
However, overseas ratings on Kia Motors were later revised upward,
following the company’s strong sales performance in comparison
with its competitors. Moody’s upgraded the company’s outlook in
November 2009, and S&P followed suit in January of 2010.
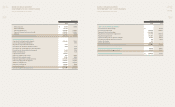
(KRW Billion)
2008 2009 Dierence
Account Payable 1,807 2,405 597
Short-term debt 1,287 79 -1,208
Current portion of long-term debt 890 1,735 846
Provision for warranties 291 228 -63
Others 919 1,398 479
Current Liabilities 5,194 5,846 651
Long-term debt 3,457 2,746 -711
Provision for warranties 446 372 -75
Accural for retirement 492 328 -164
Others 122 114 -8
Non-current Liabilities 4,517 3,720 -797
Total Liabilities 9,711 9,565 -146
Total Debt 5,633 4,560 -1,073
Cash & Deposits 1,017 1,912 895
Total Net Debt 4,616 2,648 -1,968
(KRW Billion)
2008 2009 Dierence
Capital Stock 1,849 2,054 206
Capital surplus 1,705 1,761 57
Capital adjustment -2 -2 0
Retained earnings 1,104 2,365 1,261
Accumulated other
comprehensive gain (losses) 1,086 1,198 111
Equity 5,741 7,376 1,635
End of 2008 As of March 2010
Domestic Korea Ratings AA- (Stable) AA (Stable)
Korea Investors Service AA- (Stable) AA (Stable)
NICE Investors Service AA- (Stable) AA (Stable)
Overseas Moody’s Baa3 (Stable) Ba1 (Stable)
Standard & Poor’s BBB- (Stable) BBB- (Stable)