Kia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2009 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NOTES TO NONCONSOLIDATED
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2009 and 2008
PRESENTATION
Trading securities, available-for-sale securities which mature within one year from the end of the reporting period or where the likelihood of
disposal within one year from the end of the reporting period is probable, held-to-maturity securities which mature within one year from end
of the reporting period, short-term deposits and short-term loans are combined and presented as current assets. All other available-for-sale
securities and held-to-maturity securities are combined and presented as long-term investments.
IMPAIRMENT
The Company reviews investments in securities whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the
investments may not be recoverable. Impairment losses are recognized when the reasonably estimated recoverable amounts are less than the
carrying amount and it is not obviously evidenced that impairment is unnecessary.
An impairment loss is reversed if the reversal can be related objectively to an event occurring after the impairment loss was recognized and a
reversal of an impairment loss shall not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined (net of amortization or depreciation)
had no impairment loss been recognized in the asset in prior years. For nancial assets measured at amortized cost and available-for-sale
assets that are debt securities, the reversal is recognized in prot or loss. For available-for-sale nancial assets that are equity securities, the
reversal is recognized directly in equity.
(f) Investments in Associates and Subsidiaries
Associates are entities of the Company and its subsidiaries that have the ability to signicantly inuence the nancial and operating policies.
It is presumed to have signicant inuence if the Company holds directly or indirectly 20 percent or more of the voting power unless it can be
clearly demonstrated that this is not the case. Subsidiaries are entities controlled by the Company.
Investments in associates and subsidiaries are accounted for using the equity method of accounting and are initially recognized at cost.
The Company’s investments in associates and subsidiaries include goodwill identified on the acquisition date (net of any accumulated
impairment loss). Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the acquisition cost of an investment in an associate or subsidiary over the Company’s
share of the fair value of the identiable net assets acquired. Goodwill is amortized using the straight-line method over its estimated useful life.
Amortization of goodwill is recorded together with equity income (losses).
When events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of goodwill may not be recoverable, the Company reviews goodwill for
impairment and records any impairment loss immediately in the statement of income.
The Company’s share of its post-acquisition profits or losses in investments in associates and subsidiaries is recognized in the income
statement, and its share of post-acquisition movements in equity is recognized in equity. The cumulative post-acquisition movements are
adjusted against the carrying amount of each investment. Changes in the carrying amount of an investment resulting from dividends by
an associate or subsidiary are recognized when the associate or subsidiary declares the dividend. When the Company’s share of losses in an
associate or subsidiary equals or exceeds its interest in the associate or subsidiary, including preferred stock or other long term loans and
receivables issued by the associate or subsidiary, the Company does not recognize further losses, unless it has incurred obligations or made
payments on behalf of the associate or subsidiary.
If an associate or a subsidiary uses accounting policies or estimates other than those of the Company for like transactions and events in similar
circumstances, the Company makes appropriate adjustments to conform the associate’s accounting policies to those of the Company when
the associate’s nancial statements are used by the Company in applying the equity method. However, under the revised SKAS No. 15 Equity
Method of Accounting, in the event that accounting policies and estimates dier due to the application of Exceptions to Accounting for Small
and Medium-Sized Entities or Korean International Financial Reporting Standards (K-IFRS), no adjustments are made.
If the investee is a subsidiary, net income and net assets of the parent company’s separate nancial statements should agree with the parent
company’s share in the net income and net assets of the consolidated financial statements, except when the Company discontinues the
application of the equity method due to its investment in a subsidiary being reduced to zero.
Unrealized gains on transactions between the Company and its associates or subsidiaries are eliminated to the extent of the Company’s
interest in each associate or subsidiary.
(g) Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except in the case of revaluations made in accordance with the Asset Revaluation Law, which
allowed for asset revaluation prior to the Law being revoked on December 31, 2000. Assets acquired through investment in kind or donation is
recorded at their fair value upon acquisition.
Signicant additions or improvements extending useful lives of assets are capitalized. However, normal maintenance and repairs are charged
to expense as incurred.
Depreciation is computed by the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows:
The Company recognizes interest costs and other nancial charges on borrowings associated with the production, acquisition, construction of
property, plant and equipment as an expense in the period in which they are incurred.
The Company reviews property, plant and equipment for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying
amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment loss would be recognized when the expected estimated undiscounted future net
cash ows from the use of the asset and its eventual disposal are less than its carrying amount.
As of January 1, 2008, the Company adopted the revaluation model in accordance with the revised SKAS No.5 Property, Plant and Equipment.
The book value of lands is accounted at fair value as of the date of the revaluation less accumulated impairment loss. If an asset’s book value
increases as a result of the revaluation, the amount of the increase is recognized in other comprehensive income, of which, the amount of
the increase that reverses a revaluation decrease of the same asset previously recognized in prot and loss is recognized in prot and loss in
the current period. On the other hand, if an asset’s book value decreases as a result of the revaluation, that decrease is recognized as a loss
for the current period, and the portion of the amount of decrease included in the credit balance in the revaluation surplus recorded in other
comprehensive income is deducted from other comprehensive income.
(h) Leases
The Company classies and accounts for leases as either operating or capital leases, depending on the terms of the lease. Leases where the
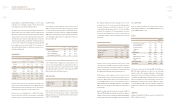
Useful lives (years)
Buildings and structures 20-40
Machinery and equipment 15
Dies, molds and tools 5
Vehicles 5
Other equipment 5
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009
REDEFINING
MOBILITY
KIA MOTORS
ANNUAL REPORT
2009