Costco 2013 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2013 Costco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
55
While options and RSUs granted to employees generally vest over five years, all grants allow for quarterly
vesting of the pro-rata number of stock-based awards that would vest on the next anniversary of the grant
date in the event of retirement or voluntary termination. The Company does not reduce stock-based
compensation for an estimate of forfeitures because the estimate is inconsequential in light of historical
experience and considering the awards vest on a quarterly basis. The impact of actual forfeitures arising in
the event of involuntary termination is recognized as actual forfeitures occur. Stock options have a ten-year
term. Stock-based compensation expense is predominantly included in selling, general and administrative
expenses on the consolidated statements of income. See Note 7 for additional information on the Company’s
stock-based compensation plans.
Leases
The Company leases land and/or buildings at warehouses and certain other office and distribution facilities,
primarily under operating leases. Operating leases expire at various dates through 2062, with the exception
of one lease in the Company’s United Kingdom subsidiary, which expires in 2151. These leases generally
contain one or more of the following options which the Company can exercise at the end of the initial lease
term: (a) renewal of the lease for a defined number of years at the then-fair market rental rate or rate stipulated
in the lease agreement; (b) purchase of the property at the then-fair market value; or (c) right of first refusal
in the event of a third-party purchase offer.
The Company accounts for its lease expense with free rent periods and step-rent provisions on a straight-
line basis over the original term of the lease and any exercised extension options, from the date the Company
has control of the property. Certain leases provide for periodic rental increases based on price indices, and
some of the leases provide for rents based on the greater of minimum guaranteed amounts or sales volume.
The Company has entered into capital leases for warehouse locations, expiring at various dates through
2040. Capital lease assets are included in buildings and improvements in the accompanying consolidated
balance sheets. Amortization expense on capital lease assets is recorded as depreciation expense and is
predominately included in selling, general and administrative expenses. Capital lease liabilities are recorded
at the lesser of the estimated fair market value of the leased property or the net present value of the aggregate
future minimum lease payments and are included in other current liabilities and deferred income taxes and
other liabilities. Interest on these obligations is included in interest expense.
The Company’s asset retirement obligations (ARO) are primarily related to leasehold improvements that at
the end of a lease must be removed in order to comply with the lease agreement. These obligations are
recorded as a liability with an offsetting capital asset at the inception of the lease term based upon the
estimated fair market value of the costs to remove the leasehold improvements. These liabilities are accreted
over time to the projected future value of the obligation using the Company’s incremental borrowing rate.
The capitalized ARO assets are depreciated using the same depreciation convention as the respective
leasehold improvement assets and are included with buildings and improvements. Estimated ARO liabilities
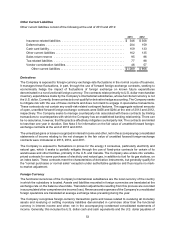
associated with these leases amounted to $50 and $44 at the end of 2013 and 2012, respectively, and are
included in deferred income taxes and other liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Preopening Expenses
Preopening expenses related to new warehouses, new regional offices and other startup operations are
expensed as incurred.
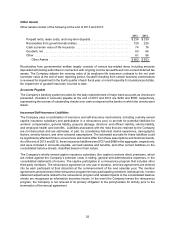
Interest Income and Other, Net
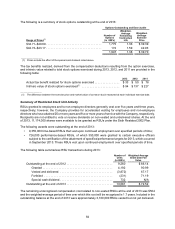
Interest income and other, net includes:
2013 2012 2011
Interest income . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 44 $ 49 $ 41
Foreign-currency transactions gains, net . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 40 9
Other, net . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 14 10
Interest income and other, net . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 97 $103 $ 60