Columbia Sportswear 2014 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2014 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
53
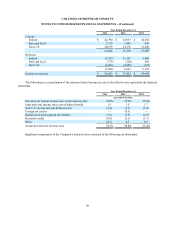
The effective portion of changes in fair values of outstanding cash flow hedges is recorded in other comprehensive
income until earnings are affected by the hedged transaction, and any ineffective portion is included in current income. In
most cases amounts recorded in other comprehensive income will be released to earnings some time after maturity of the
related derivative. The Consolidated Statements of Operations classification of effective hedge results is the same as that
of the underlying exposure. Results of hedges of product costs are recorded in cost of sales when the underlying hedged
transaction affect earnings. Results of hedges of revenue are recorded in net sales when the underlying hedged transactions
affects earnings. Unrealized derivative gains and losses, which are recorded in assets and liabilities, respectively, are non-
cash items and therefore are taken into account in the preparation of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows based on
their respective balance sheet classifications. See Note 20 for more information on derivatives and risk management.
Foreign currency translation:
The assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries have been translated into U.S. dollars using the exchange
rates in effect at period end, and the net sales and expenses have been translated into U.S. dollars using average exchange
rates in effect during the period. The foreign currency translation adjustments are included as a separate component of
accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders’ equity and are not currently adjusted for income taxes when
they relate to indefinite net investments in non-U.S. operations.
Revenue recognition:
The Company records wholesale, distributor, e-commerce and licensed product revenues when title passes and the
risks and rewards of ownership have passed to the customer. Title generally passes upon shipment to, or upon receipt by,
the customer depending on the terms of sale with the customer. Retail store revenues are recorded at the time of sale.
Revenue is recorded net of sales taxes, value added taxes or similar taxes, which are collected on behalf of local taxing
authorities.
Where title passes upon receipt by the customer, predominantly in the Company’s European wholesale business,
precise information regarding the date of receipt by the customer is not readily available. In these cases, the Company
estimates the date of receipt by the customer based on historical and expected delivery times by geographic location. The
Company periodically tests the accuracy of these estimates based on actual transactions. Delivery times vary by geographic
location, generally from one to five days. To date, the Company has found these estimates to be materially accurate.
At the time of revenue recognition, the Company also provides for estimated sales returns and miscellaneous claims
from customers as reductions to revenues. The estimates are based on historical rates of product returns and claims as well
as events and circumstances that indicate changes to historical rates of returns and claims. However, actual returns and
claims in any future period are inherently uncertain and thus may differ from the estimates. If actual or expected future
returns and claims are significantly greater or lower than the reserves that have been established, the Company would record
a reduction or increase to net revenues in the period in which it made such determination.
Cost of sales:
The expenses that are included in cost of sales include all direct product and conversion-related costs, and costs related
to shipping, duties and importation. Specific provisions for excess, close-out or slow moving inventory are also included
in cost of sales. In addition, some of the Company’s products carry limited warranty provisions for defects in quality and
workmanship. A warranty reserve is established at the time of sale to cover estimated costs based on the Company’s history
of warranty repairs and replacements and is recorded in cost of sales.
Selling, general and administrative expense:
SG&A expense consists of personnel-related costs, advertising, depreciation and other selling and general operating
expenses related to the Company’s business functions, including planning, receiving finished goods, warehousing,
distribution, retail operations and information technology.