Columbia Sportswear 2014 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 55 of the 2014 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
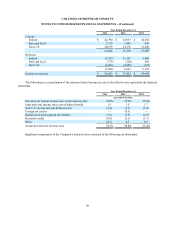
COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
51
investments are classified as trading securities and are recorded at fair value with unrealized gains and losses reported as a
component of operating income.
Accounts receivable:
Accounts receivable have been reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts. The Company makes ongoing estimates
of the collectability of accounts receivable and maintains an allowance for estimated losses resulting from the inability of
the Company’s customers to make required payments.
Inventories:
Inventories consist primarily of finished goods and are carried at the lower of cost or market. Cost is determined using
the first-in, first-out method. The Company periodically reviews its inventories for excess, close-out or slow moving items
and makes provisions as necessary to properly reflect inventory value.
Property, plant, and equipment:
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided using the
straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. The principal estimated useful lives are: land improvements,
15 years; buildings and building improvements, 15-30 years; furniture and fixtures, 3-10 years; and machinery, software
and equipment, 3-10 years. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the lesser of the estimated useful life of the
improvement, which is most commonly 7 years, or the remaining term of the underlying lease.
Improvements to property, plant and equipment that substantially extend the useful life of the asset are capitalized.
Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. Internal and external costs directly related to the development of
internal-use software during the application development stage, including costs incurred for third party contractors and
employee compensation, are capitalized and depreciated over a 3-10 year estimated useful life.
Impairment of long-lived assets:
Long-lived assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives and are measured for impairment only when events
or circumstances indicate the carrying value may be impaired. In these cases, the Company estimates the future undiscounted
cash flows to be derived from the asset or asset group to determine whether a potential impairment exists. If the sum of
the estimated undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying value of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment
loss, measured as the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset. Impairment charges
for long-lived assets are included in SG&A expense and were $73,000, $8,995,000 and $1,653,000 for the years ended
December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Charges during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2012 were
recorded in the United States and EMEA regions for retail stores. The charge during the year ended December 31, 2013
was recorded in the EMEA region for its European distribution center.
Intangible assets and goodwill:
Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives and goodwill are not amortized but are periodically evaluated for
impairment. Intangible assets that are determined to have finite lives are amortized using the straight-line method over their
estimated useful lives and are measured for impairment only when events or circumstances indicate the carrying value may
be impaired.
Impairment of intangible assets and goodwill:
The Company reviews and tests its intangible assets with indefinite useful lives and goodwill for impairment in the
fourth quarter of each year and when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets
may be impaired. The Company’s intangible assets with indefinite lives consist of trademarks and trade names. Substantially
all of the Company’s goodwill is recorded in the United States segment and impairment testing for goodwill is performed