CVS 2011 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2011 CVS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
CVS CAREMARK 66 2011 ANNUAL REPORT
employers, and (iii) if the Company chooses to stop par-
ticipating in some of its multiemployer plans, the Company
may be required to pay those plans an amount based on
the underfunded status of the plan, referred to as a with-
drawal liability.
None of the multiemployer pension plans the Company par-
ticipates in are individually significant to the Company. Total
Company contributions to multiemployer pension plans were
$11 million, $12 million and $10 million in 2011, 2010 and
2009, respectively.
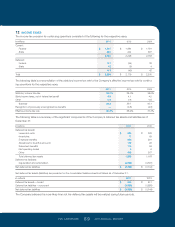
11 STOCK INCENTIVE PLANS
Stock-based compensation expense is measured at the
grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recog-
nized as expense over the applicable requisite service period
of the stock award (generally three to five years) using the
straight-line method. Stock-based compensation costs are
included in selling, general and administrative expenses.
Compensation expense related to stock options, which
includes the 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2007
ESPP”) totaled $112 million, $127 million and $136 million
for 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The recognized tax
benefit was $38 million, $42 million and $45 million for 2011,
2010 and 2009, respectively. Compensation expense related
to restricted stock awards totaled $21 million, $23 million
and $29 million for 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
The 2007 ESPP provides for the purchase of up to 15 mil-
lion shares of common stock. Under the 2007 ESPP, eligible
employees may purchase common stock at the end of each
six month offering period at a purchase price equal to 85% of
the lower of the fair market value on the first day or the last
day of the offering period. During 2011, approximately
3 million shares of common stock were purchased under the
provisions of the 2007 ESPP at an average price of $26.90
per share. As of December 31, 2011, approximately 5 million
shares of common stock were available for issuance under
the 2007 ESPP.
The fair value of stock-based compensation associated with
the 2007 ESPP is estimated on the date of grant (i.e., the
beginning of the offering period) using the Black-Scholes
Option Pricing Model.
The discount rate is determined by examining the current
yields observed on the measurement date of fixed-interest,
high quality investments expected to be available during the
period to maturity of the related benefits on a plan by plan
basis. The discount rate for the plans was 4.75% in 2011
and 5.5% in 2010. The expected long-term rate of return on
plan assets is determined by using the plan’s target allocation
and historical returns for each asset class on a plan by plan
basis. The expected long-term rate of return for all plans was
7.25% in 2011 and 2010 and 8.5% in 2009.
Historically, the Company used an investment strategy, which
emphasized equities in order to produce higher expected
returns, and in the long run, lower expected expense and
cash contribution requirements. The qualified pension plan
asset allocation targets were 60% equity and 40% fixed
income. As the result of a detailed asset liability study per-
formed during 2009, the Company revised the pension plan
target asset allocation to 50% equity and 50% fixed income
with the transition to the new targets beginning in 2010.
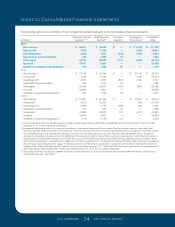
As of December 31, 2011, the Company’s qualified defined
benefit pension plan assets consisted of 47% equity, 51%
fixed income, and 2% money market securities of which
82% were classified as Level 1 and 18% as Level 2 in the fair
value hierarchy. The Company’s qualified defined benefit pen-
sion plan assets as of December 31, 2010 consisted of 57%
equity, 42% fixed income, and 1% money market securities
of which 71% were classified as Level 1 and 29% as Level 2
in the fair value hierarchy.
The Company contributed $92 million, $65 million and
$50 million to the pension plans during 2011, 2010 and
2009, respectively. The Company plans to make approxi-
mately $34 million in contributions to the pension plans
during 2012.
The Company also contributes to a number of multiem-
ployer pension plans under the terms of collective-bargain-
ing agreements that cover its union-represented employees.
The risks of participating in these multiemployer plans are
different from single-employer pension plans in the following
aspects: (i) assets contributed to the multiemployer plan by
one employer may be used to provide benefits to employ-
ees of other participating employers, (ii) if a participating
employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obliga-
tions of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating
127087_Financial.indd 66 3/9/12 9:42 PM