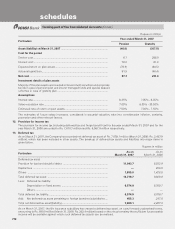
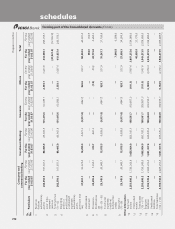
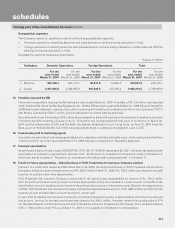
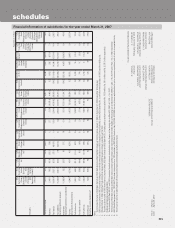
ICICI Bank 2007 Annual Report Download - page 150
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 150 of the 2007 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F80
amalgamation, although ICICI Bank was the legal acquirer. On the acquisition date, ICICI held a 46% ownership
interest in ICICI Bank. Accordingly, the acquisition of the balance 54% ownership interest has been accounted for as
a step-acquisition. Under Indian GAAP, ICICI Bank Limited was recognised as the legal and the accounting acquirer
and the assets and liabilities of ICICI Limited were incorporated in the books of ICICI Bank Limited in accordance
with the purchase method of accounting. Further, under US GAAP, the amalgamation resulted in goodwill and
intangible assets while the amalgamation under Indian GAAP resulted in a capital reserve (negative goodwill),
which was accounted for as Revenue and Other Reserves according to the scheme of amalgamation.
Further, for certain acquisitions made by the Company, no goodwill has been accounted for under Indian GAAP
primarily due to accounting for the amalgamation by the pooling of interests method. However, under US GAAP,
goodwill has been accounted for in accordance with Statement No. 141 on “Business Combinations” and Statement
No. 142 on “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets”.
Under US GAAP subsequent to the adoption of Statement No. 142, the Company does not amortise goodwill and
intangibles with infinite life but instead tests the same for impairment at least annually. The annual impairment
test under Statement No. 142 does not indicate an impairment loss for fiscal 2005, fiscal 2006 and fiscal 2007.
Under US GAAP intangible assets are amortised over their estimated useful lives in proportion to the economic
benefits consumed in each period.
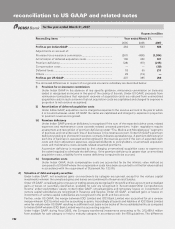
The estimated useful life of intangible assets is as follows.
No. of years
Customer-related intangibles .............................................................................. 10
Other intangibles ................................................................................................. 5
In fiscal 2006, the Company recorded goodwill under US GAAP of Rs. 1,196.8 million in relation to the acquisitions
of software, business process outsourcing and asset management companies in India and the United States for
an aggregate cash consideration of Rs 1,480.1 million. The revenue and total assets of the acquired companies
are immaterial to the consolidated results of operations and financial position of the Company. The Company has
also entered into a contract with some of the companies acquired, to pay additional amounts if certain criteria
are met.
c) Consolidation
The differences on account of consolidation are primarily on account of:
i) Consolidation of insurance subsidiaries.
ii) Equity affiliates and majority owned subsidiaries.
iii) Variable interest entities.
Under Indian GAAP, the Company has not consolidated certain entities in which control is intended to be
temporary. However under US GAAP, these entities have been consolidated in accordance with Statement No.
94 on “Consolidation of majority owned subsidiaries” which requires consolidation of such entities.
Under Indian GAAP, consolidation is required only if there is ownership of more than one-half of the voting
power of an enterprise or control of the composition of the board of directors in the case of a company or of the
composition of the governing body in case of any other enterprise.
However, under US GAAP, the Company is required to consolidate entities deemed to be Variable Interest Entities
(VIEs) where the Company is determined to be the primary beneficiary under FIN 46.
The Company’s venture capital subsidiary is involved with entities that may be deemed VIEs. The FASB permitted
non-registered investment companies to defer consolidation of VIEs with which they are involved until the
proposed Statement of Position on the clarification of the scope of the Investment Company Audit Guide is
finalised. Following issuance of the Statement of Position, the FASB will consider further modification to FIN
46R to provide an exception for companies that qualify to apply the revised Audit Guide. Following issuance of
the revised Audit Guide and further modification, if any, to FIN 46R, the Company will assess the effect of such
guidance on its venture capital business.
Under Indian GAAP, the insurance subsidiaries (ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Company Limited and ICICI Lombard
General Insurance Company Limited) are fully consolidated whereas under US GAAP, these subsidiaries are
accounted for by the equity method of accounting as the minority shareholders have substantive participating
rights as defined in Issue No. 96-16 issued by the Emerging Issues Task Force.
The significant differences between Indian GAAP and US GAAP in case of our life insurance subsidiary are given
below.
reconciliation to US GAAP and related notes
for the year ended March 31, 2007