Rite Aid 2014 Annual Report Download - page 34
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 34 of the 2014 Rite Aid annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
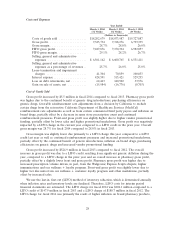
Income Taxes
Income tax expense of $0.8 million, income tax benefit of $110.6 million and income tax benefit of
$23.7 million, has been recorded for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Net income for fiscal 2014
included income tax expense of $0.8 million primarily attributable to an increase in the deferred tax
valuation allowance to offset the windfall tax benefits recorded in APIC pursuant to the tax law
ordering approach offset by adjustments to unrecognized tax benefits due to the lapse of statute of
limitations.
ASC 740, ‘‘Income Taxes’’ requires a company to evaluate its deferred tax assets on a regular basis
to determine if a valuation allowance against the net deferred tax assets is required. We take into
account all available positive and negative evidence with regard to the recognition of a deferred tax
asset including our past earnings history, expected future earnings, the character and jurisdiction of
such earnings, unsettled circumstances that, if unfavorably resolved, would adversely affect recognition
of a deferred tax asset, carryback and carryforward periods and tax planning strategies that could
potentially enhance the likelihood of realization of a deferred tax asset. A cumulative loss in recent
years is significant negative evidence in considering whether deferred tax assets are realizable. Based on
the negative evidence, ASC 740 precludes relying on projections of future taxable income to support
the recognition of deferred tax assets. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon
the existence of sufficient taxable income generated in the carryforward periods.
Net Income for fiscal 2013 included income tax benefit of $110.6 million primarily comprised of
adjustments to unrecognized tax benefits for the appellate settlements of the Brooks Eckerd IRS Audit
for the fiscal years 2004 - 2007 and the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Audit for fiscal years
2005 - 2007 as well as for the lapse of statute of limitations. The appellate settlements as well as the
majority of the lapse of statute of limitations is offset by a reversal of the related tax indemnification
asset which was recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses as these audits were related to
pre-acquisition periods. The fiscal 2012 income tax benefit of $23.7 million was primarily comprised of
adjustments to unrecognized tax benefits due to the lapse of statute of limitations. Additionally, the
income tax expense for 2014 and benefit for 2013 and 2012 was recorded net of adjustments to
maintain a full valuation allowance against our net deferred tax assets. We monitor all available
evidence related to our ability to utilize our remaining net deferred tax asset. We maintained a full
valuation allowance of $2,060.8 million and $2,224.0 million against remaining net deferred tax assets as
a result of a cumulative loss at fiscal year end 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Dilutive Equity Issuances
On March 1, 2014, 971.3 million shares of common stock, which includes unvested restricted
shares, were outstanding and an additional 80.8 million shares of common stock were issuable related
to outstanding stock options and convertible notes.
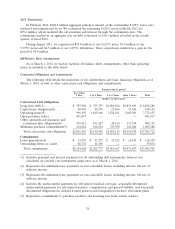
On March 1, 2014, our 80.8 million shares of potentially issuable common stock consisted of the
following (shares in thousands):
Outstanding
Stock Convertible
Strike price Options(a) Notes Total
$0.99 and under ............................ 3,419 — 3,419
$1.00 to $1.99 .............................. 43,373 — 43,373
$2.00 to $2.99 .............................. 4,768 24,800 29,568
$3.00 to $3.99 .............................. 383 — 383
$4.00 to $4.99 .............................. 1,549 — 1,549
$5.00 to $5.99 .............................. 663 — 663
$6.00 and over ............................. 1,811 — 1,811
Total issuable shares ......................... 55,966 24,800 80,766
(a) The exercise of these options would provide cash of $92.5 million.
33