Qantas 2010 Annual Report Download - page 98
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 98 of the 2010 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
THE QANTAS GROUP 96
for the year ended 30 June 2010
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
A nancial instrument is any contract that gives rise to both a nancial asset of one entity and a nancial liability or equity instrument of another
entity. The Qantas Group is subject to liquidity, interest rate, foreign exchange, fuel price and credit risks. These risks are an inherent part of the
operations of an international airline. The Qantas Group manages these risk exposures using various nancial instruments, using a set of policies
approved by the Board. Qantas Group policy is not to enter, issue or hold derivative nancial instruments for speculative trading purposes.
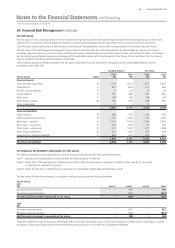
The Qantas Group uses different methods to assess and manage different types of risk to which it is exposed. These methods include correlations
between risk types, sensitivity analysis in the case of interest rate, foreign exchange and other price risks, and ageing analysis and sensitivity analysis
for liquidity risk and credit risk.
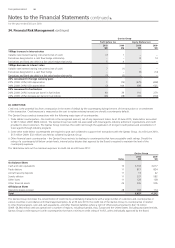
(A) LIQUIDITY RISK
Liquidity risk is the risk that an entity will encounter dif culty in meeting obligations associated with nancial liabilities. The Qantas Group manages
liquidity risk by targeting a minimum liquidity level, ensuring long-term commitments are managed with respect to forecast available cash in ow,
maintaining access to a variety of additional funding sources including commercial paper and standby facilities and managing maturity pro les.
The following tables summarise the contractual timing of cash ows, including estimated interest payments, of nancial liabilities and derivative
instruments. Contractual amount assumes current interest rates and foreign exchange rates.
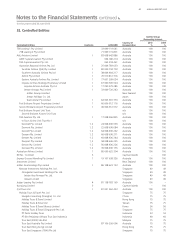
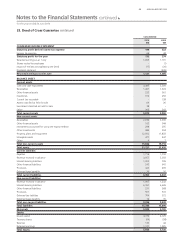
Qantas Group
2010
$M
Less than
1 Year
1 to 5
Years
More than
5 Years Total
FINANCIAL LIABILITIES
Trade creditors 600––600
Bank loans – secured1520 1,991 1,323 3,834
Bank loans – unsecured145 805 – 850
Other loans – unsecured183 752 589 1,424
Lease and hire purchase liabilities141 471 – 512
Derivatives – in ows (240) (1,467) (610) (2,317)
Derivatives – out ows 264 1,748 748 2,760
Net other nancial assets/liabilities – in ows (30) (38) – (68)
Total nancial liabilities 1,283 4,262 2,050 7,595
1. Recognised nancial liability carrying values are shown pre-hedging.
2009
$M
FINANCIAL LIABILITIES
Trade creditors 597 – – 597
Bank loans – secured1424 1,769 1,115 3,308
Bank loans – unsecured123 641 – 664
Other loans – unsecured178 818 685 1,581
Lease and hire purchase liabilities1164 344 175 683
Derivatives – in ows (270) (1,782) (815) (2,867)
Derivatives – out ows 290 1,973 886 3,149
Net other nancial assets/liabilities – (in ows)/out ows 100 (174) – (74)
Total nancial liabilities 1,406 3,589 2,046 7,041
1. Recognised nancial liability carrying values are shown pre-hedging.
34. Financial Risk Management