Cigna 2012 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2012 Cigna annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PART II
ITEM 7 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
the line of credit agreement, the Company has an additional life and health insurance companies. The RBC rules recommend a
$5.3 billion of borrowing capacity in addition to the $5.2 billion of minimum level of capital depending on the types and quality of
debt outstanding. investments held, the types of business written and the types of
liabilities incurred. If the ratio of the insurer’s adjusted surplus to its
The Company maintains a capital management strategy to risk-based capital falls below statutory required minimums, the
permanently invest the earnings for certain of its foreign operations insurer could be subject to regulatory actions ranging from increased
overseas. During the first quarter of 2012 the Company expanded this scrutiny to conservatorship.
strategy to its China and Indonesia operations. As of December 31,
2012 the Company’s cash and cash equivalents in its foreign In addition, various non-U.S. jurisdictions prescribe minimum
operations were $768 million, and permanently reinvested earnings surplus requirements that are based upon solvency, liquidity and
were approximately $628 million. Repatriation of foreign cash via a reserve coverage measures. During 2012, the Company’s HMOs and
dividend of these permanently reinvested earnings would result in a life and health insurance subsidiaries, as well as non-U.S. insurance
charge for the incremental U.S. taxes due on the repatriation. Because subsidiaries, were compliant with applicable RBC and non-U.S.
of the size, strength and diversity of earnings from domestic sources, surplus rules.
management does not believe this global capital management strategy Solvency II. Cigna’s businesses in the European Union will be subject
materially limits the Company’s ability to meet its liquidity and to the directive on insurance regulation and solvency requirements
capital needs in the United States. known as Solvency II. This directive will impose economic risk-based
Though the Company believes it has adequate sources of liquidity, solvency requirements and supervisory rules and is expected to
continued significant disruption or volatility in the capital and credit become effective in January 2014, although certain regulators are
markets could affect the Company’s ability to access those markets for requiring companies to demonstrate technical capability and comply
additional borrowings or increase costs associated with borrowing with increased capital levels in advance of the effective date. Cigna’s
funds. European insurance companies are capitalized at levels consistent with
projected Solvency II requirements and in compliance with
Solvency regulation. Many states have adopted some form of the anticipated technical capability requirements.
National Association of Insurance Commissioners (‘‘NAIC’’) model
solvency-related laws and risk-based capital rules (‘‘RBC rules’’) for
Guarantees and Contractual Obligations
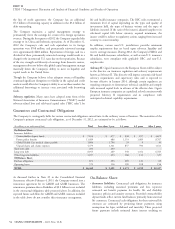
The Company is contingently liable for various contractual obligations entered into in the ordinary course of business. The maturities of the
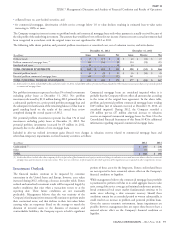
Company’s primary contractual cash obligations, as of December 31, 2012, are estimated to be as follows:
(In millions, on an undiscounted basis)
Total Less than 1 year 1-3 years 4-5 years After 5 years
On-Balance Sheet:
Insurance liabilities:
Contractholder deposit funds $ 7,104 $ 677 $ 938 $ 817 $ 4,672
Future policy benefits 11,489 486 1,153 1,083 8,767
Global Health Care medical claims payable 1,864 1,796 29 9 30
Unpaid claims and claims expenses 4,379 1,321 857 590 1,611
Short-term debt 200 200 - - -
Long-term debt 8,955 269 549 1,352 6,785
Other long-term liabilities 1,037 433 166 111 327
Off-Balance Sheet:
Purchase obligations 871 393 289 120 69
Operating leases 570 116 190 108 156
TOTAL $ 36,469 $ 5,691 $ 4,171 $ 4,190 $ 22,417
As discussed further in Note 25 to the Consolidated Financial
On-Balance Sheet:
Statements, effective February 4, 2013, the Company entered into a
Insurance liabilities. Contractual cash obligations for insurance
reinsurance agreement for its GMDB and GMIB businesses. The
liabilities, excluding unearned premiums and fees, represent
reinsurance premium due to Berkshire of $2.2 billion is not included
estimated net benefit payments for health, life and disability
in the contractual obligations table presented above. In addition, the
insurance policies and annuity contracts. Recorded contractholder
expected future cash flows for GMDB and GMIB contracts included
deposit funds reflect current fund balances primarily from universal
in the table above do not consider this reinsurance arrangement.
life customers. Contractual cash obligations for these universal life
contracts are estimated by projecting future payments using
assumptions for lapse, withdrawal and mortality. These projected
future payments include estimated future interest crediting on
54 CIGNA CORPORATION - 2012 Form 10-K
•