Square Enix 2012 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2012 Square Enix annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
44
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (JPNGAAP)
4) Method of calculation for depreciation:
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method over a useful life with no residual value.
(Impairment loss)
No impairment loss was recognized on leased assets.
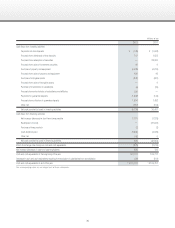
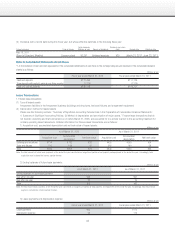
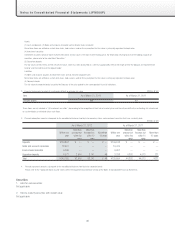
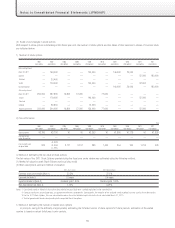
2. Operating lease transactions
Future lease payments on noncancellable leases:
Millions of yen
As of March 31, 2012 As of March 31, 2011
Due within one year ¥251 ¥655
Due after one year 46 124
Total ¥298 ¥779
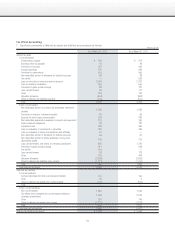
Notes Regarding Financial Instruments
1. Matters concerning financial instruments
(1) Policies regarding financial instruments
With regard to the management of funds, the Group only utilizes
financial instruments with low market risk, such as deposits. With
regard to fund procurement, the Group utilizes the issuance of
corporate bonds and borrowings from financial institutions.
Forward-exchange transactions are carried out within the
amount of foreign currency-denominated transactions conducted
by the Group. It is the Group’s policy not to engage in derivative
transactions for speculative purposes.
(2) Types of financial instruments held, risks associated with these
financial instruments and the risk management system
The Group is exposed to customer credit risk through notes
and accounts receivable, which are trade receivables. The Group
endeavors to reduce this risk by managing the outstanding balance
and due date for each transaction in accordance with internal
rules at each Group company for sales management. Owing to
the Group’s global business operations, a portion of its notes
and accounts receivable are denominated in foreign currencies,
which are exposed to exchange rate fluctuation risk. Although the
Group, in principle, does not engage in derivative transactions,
for the purpose of hedging against the risk of future fluctuations
in foreign-exchange rates, it enters into forward foreign exchange
contracts from time to time. Although forward foreign exchange
contracts involve exposure to exchange rate fluctuation risk, each
counterparty to these transactions is, without exception, a highly
creditworthy bank. Hence, the Group judges that credit risk through
counterparty breach of contract (counterparty risk) is negligible.
With regard to forward foreign exchange transactions, all risk is
centrally managed by the accounting division under the approval
of a representative director and the director assigned to oversee
accounting and finance matters.
Corporate taxes receivable is a refund of corporate taxes that is
recouped in a short period of time.
Investment securities mainly comprise stock market listed
shares, and, hence, exposed to market price fluctuation risk.
However, fair values are monitored and regularly reported to the
Board of Directors.
Guarantee deposits consist of deposits required to be furnished
by the Group when it enters into real estate leases relating to
the Group’s headquarters, other offices and amusement arcade
facilities. Although these deposits involve exposure to counterparty
credit risk, for the headquarters and other offices, and for amusement
arcades, the general affairs division and the sales division,
respectively, confirm the creditworthiness of the lessors through
regular contact. In addition, the accounting division checks with
each of these divisions on the situation at the end of each fiscal
year.
Notes and accounts payable are defined as those trade payables
due within one year. Short-term loans are used to meet short-term
working capital requirements. The Group avoids the settlement
liquidity risk associated with short-term payables, including notes
and accounts payable, accrued corporate taxes and short-term
loans, through the monthly review of its funding plan and other
methods. Although foreign currency-denominated trade payables
involve exposure to exchange rate fluctuations, the Group reduces
this risk through similar methods to those used to manage the risk
associated with foreign currency-denominated trade receivables.
The Group is exposed to interest rate risk through short-term loans.
The Group, however, is able to respond flexibly to interest rate
fluctuations since the borrowing periods are short.
Corporate bonds comprise euro yen zero-coupon convertible
bonds due 2015. As zero-coupon bonds, they are not exposed to
the risk of interest rate fluctuations.