Mazda 2015 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 2015 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Basis of measuring fair value of financial instruments
The fair values of some financial instruments are based on market prices. When market
prices are unavailable, the fair values are based on reasonably estimated values. The esti-
mated values may vary depending on the assumptions and variables used in the estimation.
Assets
1) Trade notes and accounts receivable
Trade notes and accounts receivable with short maturities are stated at carrying value as it
approximates fair value. The fair values of other receivables are calculated by grouping the
receivables according to their time to maturity, and then by discounting the amount of those
receivables by group to present values. The discount rates used in computing the present
values reflect the time to maturity as well as credit risk.
2) Investment securities
As for listed stocks included in investment securities, their quoted prices on the stock
exchange are used as their fair values.
For notes on securities by classification, refer to “Securities” under Note 2, “Significant
Accounting Policies”, and Note 5, “Securities”.
3) Long-term loans receivable
Long-term loans receivable consist of variable interest loans. As such, the interest rates on
these loans reflect the market rates of interest within short periods of time. Also, the credit
standings of borrowers of these loans have not changed significantly since the execution of
these loans. Accordingly, the carrying values are used as the fair values of these loans
receivable.
For loans receivable at a high risk, the fair value is calculated mainly based on amounts
estimated to be collectible through collateral and guarantees.
Liabilities
1) Trade notes and accounts payable, 2) Other accounts payable, and 3) Short-term debt
These payables are settled within short periods of time. Hence, their carrying values
approximate their fair values. Accordingly, carrying values are used as the fair values of
these payables.
4) Long-term debt
a) Bonds payable
The fair value of bonds issued by the Group is based on the market price where such a
price is available. Otherwise, the sum of the present value of principal and interest pay-
ments is used as the fair value of bonds payable. The discount rates used in computing
the present value reflect the time to maturity of the bonds as well as credit risk.
b) Long-term loans payable and c) Finance lease obligations
The fair value of these liabilities is calculated by the sum of the principal and interest
payments discounted to present value, using the imputed interest rate that would be
required to newly execute a similar borrowing or lease transaction.
For some long-term loans payable with variable interest rates, interest rate swaps are
used as a hedge against interest rate fluctuations. When such interest rate swaps meet
certain hedging criteria, the net amount to be paid or received under the interest rate
swap contract is added to or deducted from the interest on the long-term loans payable.
In such cases, the resulting net interest on the long-term loans payable is used in cal-
culating the present value.
Derivative instruments
Refer to Note 15, “Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Transactions”.
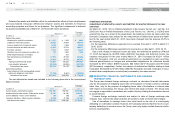
Scheduled amounts of receivables were as follows:
Millions of yen Thousands of U.S. dollars
As of March 31, 2015 Within 1 year
Over 1 year,
within 5
years
Over 5 years,
within 10
years
Over 10
years Within 1 year
Over 1 year,
within 5
years
Over 5 years,
within 10
years
Over 10
years
T rade notes and
accounts receivable ¥215,161 ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — $1,793,008 $ — $ — $ —
L ong-term loans
receivable 354 5,365 366 305 2,950 44,708 3,050 2,542
Total ¥215,515 ¥5,365 ¥366 ¥305 $1,795,958 $44,708 $3,050 $2,542
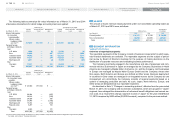
Millions of yen
As of March 31, 2014 Within 1 year
Over 1 year,
within 5
years
Over 5 years,
within 10
years
Over 10
years
T rade notes and
accounts receivable
¥180,544 ¥ — ¥ — ¥ —
L ong-term loans
receivable
278 5,632 582 337
Total
¥180,822 ¥5,632 ¥582 ¥337
For the schedule of repayment of long-term debt after the consolidated balance sheet
date, refer to Note 9, “Short-Term Debt and Long-Term Debt”.
Mazda Annual Report 2015
51
C
CONTENTS
Growth Strategy
Message from Management
Introduction
Review of Operations
Foundations Underpinning
Sustainable Growth