Mazda 2015 Annual Report Download - page 24
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 24 of the 2015 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.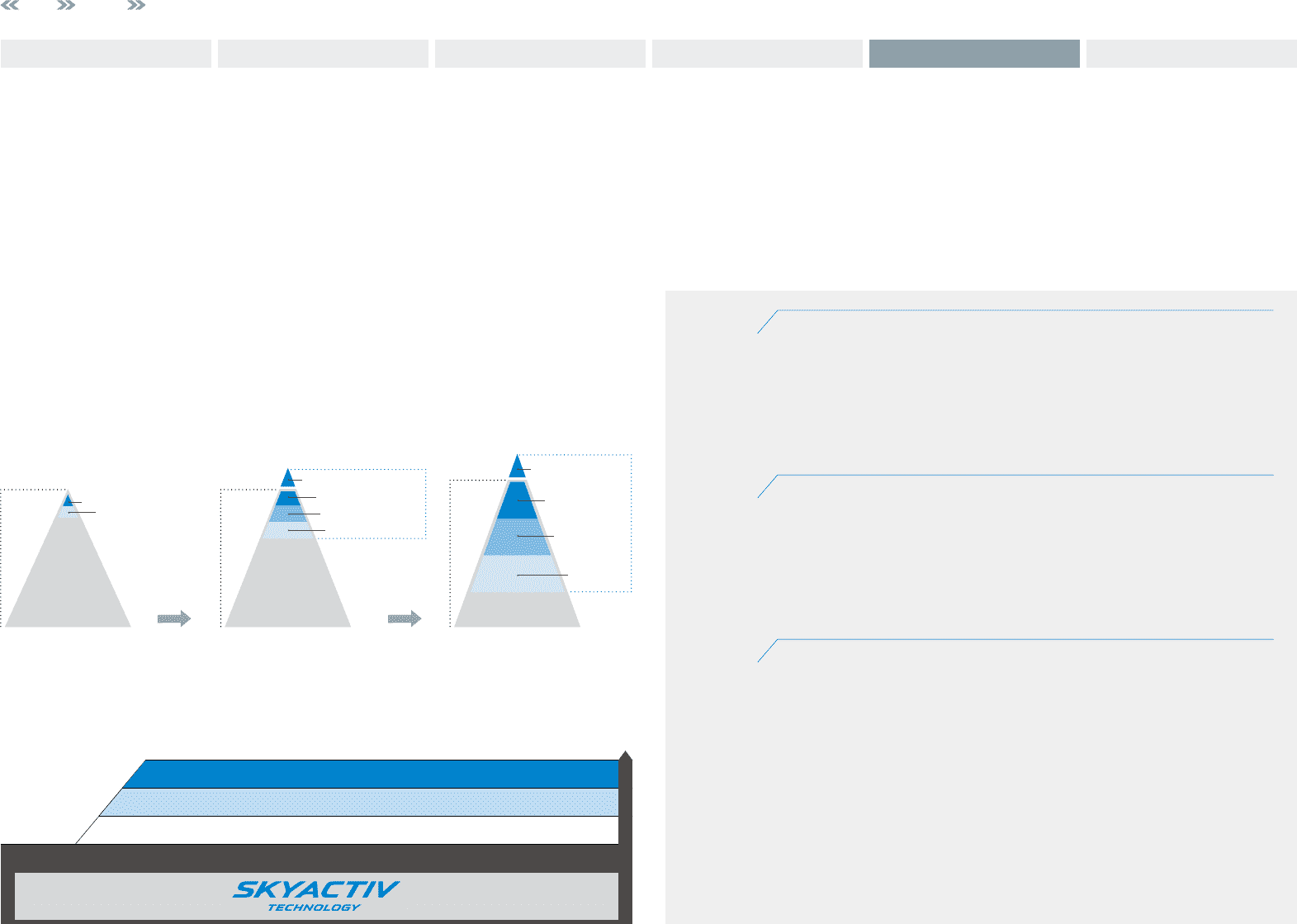
We anticipate that petroleum resources will still be the main energy and internal combustion
engines the main drive technology in the global automobile market in 2020. As a result of having
made dramatic improvements to the base technologies for a car’s basic performance—including
to the engine, transmission, body, and chassis—we are pursuing a Building-Block Strategy of
gradually adding electric devices, such as regenerative braking and hybrid systems. Our
approach is to effectively reduce CO2 emissions by providing all customers with driving pleasure
and outstand ing environmental and safety performance, rather than to rely heavily on a subset
of environmentally friendly vehicles.
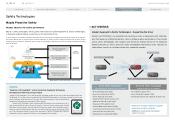
Building-Block Strategy
Step 1 Battery Management Technology (Idling Stop System “i-stop”)
This system saves fuel by automatically shutting off the engine when the driver brings the car to a standstill and
restarting the engine when the vehicle returns to motion. Mazda’s i-stop is an idling stop system that significantly
improves fuel efficiency while maintaining a natural driving feel. In addition to realizing a quick engine restart
through the latest control technologies and a natural, comfortable feel, the i-stop system improves fuel efficiency
by approximately 8% (JC08 mode) compared with conventional idling stop systems.
Installed in the Mazda3 in 2009, the i-stop system has been expanded to other models. In February 2012, i-stop
was installed in the CX-5 equipped with the SKYACTIV-D 2.2 clean diesel engine, marking the first use of an idling
stop system in a diesel engine passenger car in Japan.
Step 2 Regenerative Braking Technology
(Regenerative Braking System “i-ELOOP”)
Mazda has developed i-ELOOP, the world’s first passenger vehicle regenerative braking system that uses a capaci-
tor. A regenerative braking system recaptures (generates) as electricity part of the kinetic energy lost as a vehicle
decelerates, energy that previously went to waste. The system stores the electricity so that it can be reused. The
electrical power stored by energy regeneration is used to power a variety of electrical components, such as the air
conditioner, headlamps, and audio equipment, thereby enabling the saving of fuel that was previously used to
generate electricity.
The models equipped with i-ELOOP have been expanded since November 2012 when the system was fitted on
the Mazda6.
Step 3 Electric Motor Drive Technology
(Hybrid System “SKYACTIV-HYBRID”)
This type of system improves overall energy efficiency using an electric motor to assist gasoline engines at times when
energy efficiency is low, such as when a vehicle is running at low engine speeds or during low-load operation. The
combination of this hybrid system with the systems mentioned in steps 1 and 2 above can produce a substantial boost
in overall efficiency (fuel efficiency).
In November 2013, Mazda launched the new Axela Hybrid onto the Japanese market. Developed under the concept
of “the hybrid with Mazda DNA,” the Axela realizes a unique
driving pleasure
sensation and, as it stands, a low fuel
consumption in JC08 mode of 30.8km/L*.
* The rate of fuel consumption (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport review value) was the value achieved under
stipulated test conditions. The rate of fuel consumption will differ depending on, for example, the environment in which customers
use the car (climate, traffic conditions, etc.) and how the car is driven (sudden accelerations, air conditioner usage, etc.).
Mazda’s revolutionary base technology, SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY, is improving the car’s
powertrain efficiency, such as the basic performance of the engine and transmission, and bringing
about profound improvements in such areas as vehicle weight reduction and aerodynamics. Based
on a Building-Block Strategy, base technologies and electric device technologies are combined in
the following three steps.
Mazda developed the Demio EV that combines to an advanced level the sporty driving people expect from Mazda
with the remarkable driving range for an EV of 200km (Mazda-measured value in JC08 mode). Mazda began leas-
ing the Demio EV to local government bodies and corporate customers in Japan in 2012. Mazda is also in
the process of developing a range extender that charges the batteries of EVs by a rotary engine to increase their
driving range.
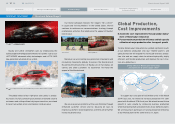
Anticipated Expansion in Adoption of Environmental Technologies (Through 2020)
Graphic representation of global market share of powertrain technologies
Building-Block Strategy
Long-Term Vision for Technology Development
Internal
combustion
engines
Internal
combustion
engines
Internal
combustion
engines
Base engines
(internal
combustion engines)
Base engines
(internal
combustion engines)
Base engines
(internal
combustion engines)
Electric devices
Electric devices
Hybrids
Idling stop systems
Hybrids / Plug-in hybrids
Regenerative braking
Hybrids /
Plug-in hybrids
Regenerative
braking
Idling stop
systems
Idling stop systems
2009 20202015
EVs
EVs
• Introduction of hybrid technology
and idling stop technology
• Expanded use of electric device
technologies and increased
introduction of electric vehicles (EVs)
• Stricter fuel economy standards globally
• Need for big boost in energy efficiency
• Expanded adoption of electric device
technologies
Base Technologies Powertrains, Reduced Body Weight, etc.
Battery Management Technology Idling Stop System “i-stop”
step 1
Regenerative Braking Regenerative Braking System “i-ELOOP”
step 2
Electric Drive Technology Hybrid System “SKYACTIV-HYBRID”
step 3
Mazda Annual Report 2015
22
Foundations Underpinning
Sustainable Growth
CONTENTS
Growth Strategy
Message from Management
Corporate Data
Introduction
Review of Operations