Mazda 2010 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2010 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
66
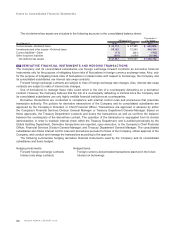
The net deferred tax assets are included in the following accounts in the consolidated balance sheet:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
As of March 31 2010 2009 2010
Current assets—Deferred taxes ¥ 60,311 ¥ 67,985 $ 648,505
Investments and other assets—Deferred taxes 88,182 72,940 948,194
Current liabilities—Other (71) (261) (763)
Other long-term liabilities (855) (1,099) (9,194)
Net deferred tax assets ¥147,567 ¥139,565 $1,586,742
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries use foreign exchange forward contracts as derivative financial
instruments only for the purpose of mitigating future risks of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Also, only
for the purpose of mitigating future risks of fluctuations in interest rates with respect to borrowings, the Company and
its consolidated subsidiaries use interest rate swap contracts.
Forward foreign exchange contracts are subject to risks of foreign exchange rate changes. Also, interest rate swap
contracts are subject to risks of interest rate changes.
Use of derivatives to manage these risks could result in the risk of a counterparty defaulting on a derivative
contract. However, the Company believes that the risk of a counterparty defaulting is minimal since the Company and
its consolidated subsidiaries use only highly credible financial institutions as counterparties.
Derivative transactions are conducted in compliance with internal control rules and procedures that prescribe
transaction authority. The policies for derivative transactions of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries are
approved by the Company’s President or Chief Financial Officer. Transactions are approved in advance by either
the Company’s Financial Services Division General Manager or Treasury Department General Manager. Based on
these approvals, the Treasury Department conducts and books the transactions as well as confirms the balance
between the counterparty of the derivatives contract. The operation of the transaction is segregated from its clerical
administration, in order to maintain internal check within the Treasury Department, and is audited periodically by the
Global Auditing Department. Derivative transactions are reported, upon execution, to the Company’s Chief Financial
Officer, Financial Services Division General Manager, and Treasury Department General Manager. The consolidated
subsidiaries also follow internal control rules and procedures pursuant to those of the Company, obtain approval of the
Company, and conduct and manage the transactions according to the approval.
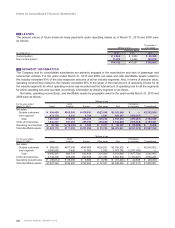
The following summarizes hedging derivative financial instruments used by the Company and its consolidated
subsidiaries and items hedged:
Hedging instruments: Hedged items:
Forward foreign exchange contracts Foreign currency-denominated transactions planned in the future
Interest rate swap contracts Interest on borrowings