Mazda 2010 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 2010 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
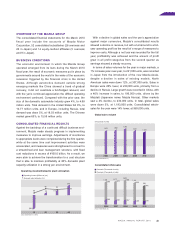
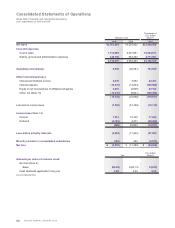
Dividend
Mazda’s policy is to set a dividend that reflects each year’s
earnings and operating environment, and to pay a stable
dividend while striving to increase the amount. For the
March 2010 fiscal year, a year-end dividend of ¥3.0 per
share was paid with no interim dividend. As a result, the
full-year dividend was ¥3.0 per share.
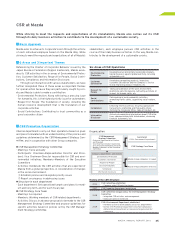
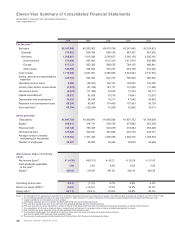
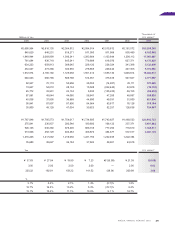
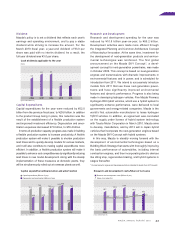
Capital Expenditures
Capital expenditures for the year were reduced by ¥52.0
billion from the previous fiscal year, to ¥29.8 billion. In addition
to the product lineup being in place, this reduction was the
result of the establishment of a flexible production system
and improved investment efficiency. Depreciation and amor-
tization expenses decreased ¥7.6 billion, to ¥76.4 billion.
In terms of production capacity, progress was made in building
a flexible production system to increase productivity. A flexible
production system will make it possible to shorten production
lead times and to quickly develop models for various markets,
and it will also contribute to making capital expenditures more
efficient. In addition, a flexible production system will make it
possible to enhance cost competitiveness by significantly reducing
lead times in new model development. Along with the steady
implementation of these measures at domestic plants, they
will be simultaneously rolled out at overseas plants as well.
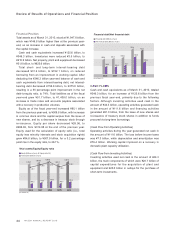
Research and Development
Research and development spending for the year was
reduced by ¥10.8 billion year-on-year, to ¥85.2 billion.
Development activities were made more efficient through
the Integrated Planning and Common Architecture Concept
of Monotsukuri Innovation. At the same time, investment for
the development of next-generation products and environ-
mental technologies was reinforced. The first global
announcement on the Mazda SKY Concept*, a devel-
opment concept for next-generation powertrains, was made
in October 2009. This concept is based on next-generation
engines and transmissions with dramatic improvements in
environmental features and in power, and is scheduled for
introduction from 2011. We intend to successively introduce
models from 2011 that use these next-generation power-
trains and have significantly improved environmental
features and dynamic performance. Progress is also being
made in developing hydrogen vehicles. Five Mazda Premacy
Hydrogen RE Hybrid vehicles, which use a hybrid system to
significantly enhance performance, were delivered to local
governments and energy-related companies. Mazda is the
world’s first automobile manufacturer to lease hydrogen
hybrid vehicles. In addition, an agreement was concluded
on the supply under license of hybrid system technology
with Toyota Motor Corporation in March 2010. Mazda aims
to develop, manufacture, and by 2013 sell in Japan hybrid
vehicles that incorporate the next-generation engines based
on the Mazda SKY Concept with hybrid systems.
In this way, Mazda is steadily moving forward with the
development of environmental technologies based on a
Building Block Strategy that starts with thoroughly improving
the basic performance of automobiles, including internal
combustion engines, and then incorporating electric devices
like idling stop, regenerative braking, and hybrid systems in
stages thereafter.
* Concept name for engines and transmissions that are intended for launch from 2011 onward.
5.0
6.0
3.0 3.0
6.0
(Yen)
)''- )''. )''/ )''0 )'('
(Years ended March 31)
:Xj_[`m`[\e[jXggc`ZXYc\kfk_\p\Xi
45.8 47.0
74.2
72.1
79.6 75.5
84.0
81.8
29.8
76.4
Capital expenditures (Billions of yen)
Depreciation and amortization (Billions of yen)
)''- )''. )''/ )''0 )'('
(Years ended March 31)
:Xg`kXc\og\e[`kli\j&;\gi\Z`Xk`feXe[Xdfik`qXk`fe
95.7
3.3 3.3 3.3 3.8 3.9
114.4
96.0
85.2
107.6
Research and development costs (Billions of yen)
Share of net sales (%)
)''- )''. )''/ )''0 )'('
(Years ended March 31)
I\j\XiZ_Xe[[\m\cfgd\ekZfjkj&J_Xi\f]e\kjXc\j
43