Mazda 2010 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2010 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
64
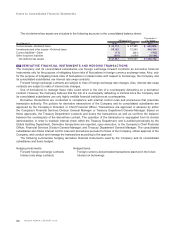
The liabilities for severance and retirement benefits as of March 31, 2010 and 2009 consisted of the following:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
As of March 31 2010 2009 2010
Projected benefit obligation ¥ 289,069 ¥ 302,253 $ 3,108,269
Unrecognized prior service costs 17,152 19,428 184,430
Unrecognized actuarial differences (53,833) (95,144) (578,849)
Less fair value of pension assets (172,610) (143,292) (1,856,022)
Prepaid pension cost 4,775 7,676 51,344
Liability for severance and retirement benefits ¥ 84,553 ¥ 90,921 $ 909,172
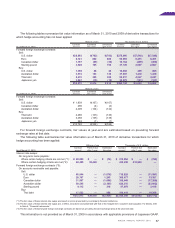
Severance and retirement benefit expenses for the years ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 consisted of the
following:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
For the years ended March 31 2010 2009 2010
Service costs—benefits earned during the year ¥11,344 ¥12,195 $121,979
Interest cost on projected benefit obligation 6,518 6,486 70,086
Expected return on plan assets (2,962) (5,589) (31,849)
Amortization of prior service costs (2,423) (2,232) (26,054)
Amortization of actuarial differences 10,156 8,030 109,204
Severance and retirement benefit expenses ¥22,633 ¥18,890 $243,366
The discount rates and the rates of expected return on plan assets were primarily 2.1% and 1.5%, respectively, for
the year ended March 31, 2010. The respective rates were primarily 2.0% and 3.0% for the year ended March 31, 2009.
For both the years ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, the estimated amount of all retirement benefits to be paid at
the future retirement dates is allocated equally to each service year using the estimated number of total service years.
For the years ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, accrued pension costs related to defined contribution plans
amounted to ¥1,940 million ($20,860 thousand) and ¥2,079 million, respectively.
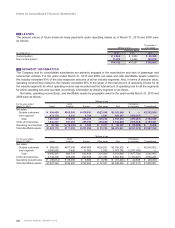
Contingent liabilities as of March 31, 2010 were as follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
Factoring of receivables with recourse ¥ 340 $ 3,656
Guarantees of loans and similar agreements 11,854 127,462
Under Japanese laws and regulations, the entire amount paid for new shares is required to be designated as common
stock. However, a company may, by a resolution of the Board of Directors, designate an amount not exceeding one
half of the price of the new shares as additional paid-in capital, which is included in capital surplus.
Under the Corporate Law (“the Law”), in cases where dividend distribution of surplus is made, the smaller of an
amount equal to 10% of the dividend or the excess, if any, of 25% of common stock over the total of additional paid-in
capital and legal earnings reserve, must be set aside as additional paid-in capital or legal earnings reserve. Legal
earnings reserve is included in retained earnings in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Legal earnings
reserve and additional paid-in capital could be used to eliminate or reduce a deficit or could be capitalized by a
resolution of the shareholder’s meeting. Additional paid-in capital and legal earnings reserve may not be distributed as
dividends. Under the Law, all additional paid-in capital and legal earnings reserve may be transferred to other capital
surplus and retained earnings, respectively, which are potentially available for dividends. The maximum amount
that the Company can distribute as dividends is calculated based on the non-consolidated financial statements of
the Company in accordance with the Law. Cash dividends charged to retained earnings during the fiscal year were
year-end cash dividends for the preceding fiscal year and interim cash dividends for the current fiscal year.