Harley Davidson 2015 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2015 Harley Davidson annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.37
Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company’s financial statements are based on the selection and application of significant accounting policies, which
require management to make significant estimates and assumptions. Management believes that the following are some of the
more critical judgment areas in the application of accounting policies that currently affect the Company’s financial condition
and results of operations. Management has discussed the development and selection of these critical accounting estimates with
the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
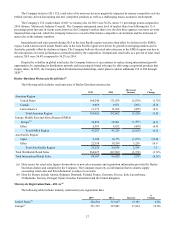
Allowance for Credit Losses on Finance Receivables – The allowance for uncollectible accounts is maintained at a level
management believes is adequate to cover the losses of principal in the existing finance receivables portfolio.
The retail portfolio consists of a large number of small balance, homogeneous finance receivables. The Company
performs a periodic and systematic collective evaluation of the adequacy of the retail allowance. The Company utilizes loss
forecast models which consider a variety of factors including, but not limited to, historical loss trends, origination or vintage
analysis, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, the value of the underlying collateral, recovery rates and current economic
conditions including items such as unemployment rates.
The wholesale portfolio is primarily composed of large balance, non-homogeneous finance receivables. The Company's
wholesale allowance evaluation is first based on a loan-by-loan review. A specific allowance is established for wholesale
finance receivables determined to be individually impaired when management concludes that the borrower will not be able to
make full payment of contractual amounts due based on the original terms of the loan agreement. The impairment is determined
based on the cash that the Company expects to receive discounted at the loan’s original interest rate or the fair value of the
collateral, if the loan is collateral-dependent. In establishing the allowance, management considers a number of factors
including the specific borrower’s financial performance as well as ability to repay. Finance receivables in the wholesale
portfolio that are not individually evaluated for impairment are segregated, based on similar risk characteristics, according to
the Company’s internal risk rating system and collectively evaluated for impairment. The related allowance is based on factors
such as the Company’s past loan loss experience, current economic conditions as well as the value of the underlying collateral.
Product Warranty – Estimated warranty costs are reserved for motorcycles, motorcycle parts and motorcycle accessories
at the time of sale. The warranty reserve is based upon historical Company claim data used in combination with other known
factors that may affect future warranty claims. The Company updates its warranty estimates quarterly to ensure that the
warranty reserves are based on the most current information available.
The Company believes that past claim experience is indicative of future claims; however, the factors affecting actual
claims can be volatile. As a result, actual claims experience may differ from estimated which could lead to material changes in
the Company’s warranty provision and related reserves. The Company’s warranty liability is discussed further in Note 1 of
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Pensions and Other Postretirement Healthcare Benefits – The Company has a defined benefit pension plan and several
postretirement healthcare benefit plans, which cover employees of the Motorcycles segment. The Company also has unfunded
supplemental employee retirement plan agreements (SERPA) with certain employees which were instituted to replace benefits
lost under the Tax Revenue Reconciliation Act of 1993.
U.S. GAAP requires that companies recognize in their statement of financial position a liability for defined benefit
pension and postretirement plans that are underfunded or an asset for defined benefit pension and postretirement benefit plans
that are overfunded.
Pension, SERPA and postretirement healthcare obligations and costs are calculated through actuarial valuations. The
valuation of benefit obligations and net periodic benefit costs relies on key assumptions including discount rates, mortality,
long-term expected return on plan assets, future compensation and healthcare cost trend rates.
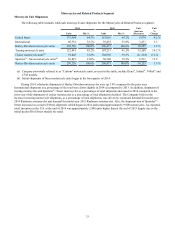
The Company determines its discount rate assumptions by referencing high-quality long-term bond rates that are matched to
the duration of its own benefit obligations. Based on this analysis, the Company increased the weighted-average discount rate
for pension and SERPA obligations from 4.21% as of December 31, 2014 to 4.53% as of December 31, 2015. The Company
increased the weighted-average discount rate for postretirement healthcare obligations from 3.99% to 4.29%. The Company
determines its healthcare trend assumption for the postretirement healthcare obligation by considering factors such as estimated
healthcare inflation, the utilization of healthcare benefits and changes in the health of plan participants. Based on the
Company’s assessment of this data as of December 31, 2015, the Company set its healthcare cost trend rate at 7.5% as of
December 31, 2015. The Company expects the healthcare cost trend rate to reach its ultimate rate of 5.0% by 2021.(1) These
assumption changes were reflected immediately in the benefit obligation and will be amortized into net periodic benefit costs
over future periods.