HSBC 2007 Annual Report Download - page 195
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 195 of the 2007 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
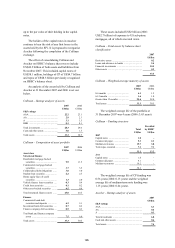 187
187 -
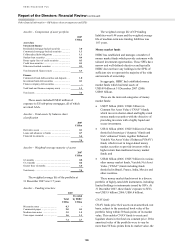 188
188 -
 189
189 -
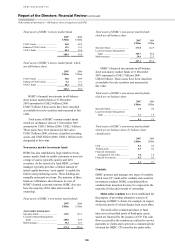 190
190 -
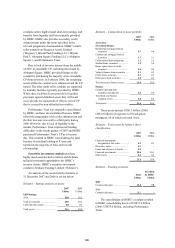 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390 -
 391
391 -
 392
392 -
 393
393 -
 394
394 -
 395
395 -
 396
396 -
 397
397 -
 398
398 -
 399
399 -
 400
400 -
 401
401 -
 402
402 -
 403
403 -
 404
404 -
 405
405 -
 406
406 -
 407
407 -
 408
408 -
 409
409 -
 410
410 -
 411
411 -
 412
412 -
 413
413 -
 414
414 -
 415
415 -
 416
416 -
 417
417 -
 418
418 -
 419
419 -
 420
420 -
 421
421 -
 422
422 -
 423
423 -
 424
424 -
 425
425 -
 426
426 -
 427
427 -
 428
428 -
 429
429 -
 430
430 -
 431
431 -
 432
432 -
 433
433 -
 434
434 -
 435
435 -
 436
436 -
 437
437 -
 438
438 -
 439
439 -
 440
440 -
 441
441 -
 442
442 -
 443
443 -
 444
444 -
 445
445 -
 446
446 -
 447
447 -
 448
448 -
 449
449 -
 450
450 -
 451
451 -
 452
452 -
 453
453 -
 454
454 -
 455
455 -
 456
456 -
 457
457 -
 458
458 -
 459
459 -
 460
460 -
 461
461 -
 462
462 -
 463
463 -
 464
464 -
 465
465 -
 466
466 -
 467
467 -
 468
468 -
 469
469 -
 470
470 -
 471
471 -
 472
472 -
 473
473 -
 474
474 -
 475
475 -
 476
476
 |
 |
193
restrictions on the acquisition of local banks or
regulations requiring a specified percentage of local
ownership; and restrictions on investment and other
financial flows entering or leaving the country. The
supervisory and regulatory regimes of the countries
where HSBC operates will determine to some degree
HSBC’s ability to expand into new markets, the
services and products that HSBC will be able to
offer in those markets and how HSBC structures
specific operations.
The FSA supervises HSBC on a consolidated
basis. In addition, each operating bank, finance
company or insurance operation within HSBC is
regulated by local supervisors. The primary
regulatory authorities are those in the UK, Hong
Kong and the US, the Group’s principal areas of
operation.
In June 2004, the Basel Committee on Banking
Supervision introduced a new capital adequacy
framework to replace the 1988 Basel Capital Accord
in the form of a final Accord (commonly known as
‘Basel II’). Details of the EU’s implementation of
Basel II and how this will affect HSBC are set out
on page 284.
UK regulation and supervision
UK banking and financial services institutions are
subject to multiple regulations. The primary UK
statute is the Financial Services and Markets Act
2000 (‘FSMA’). Additionally, data privacy is
regulated by the Data Protection Act 1998. Other
UK financial services legislation is derived from EU
directives relating to banking, securities, insurance,
investment and sales of personal financial services.
The FSA is responsible for authorising and
supervising UK financial services institutions and
regulates all HSBC’s businesses in the UK which
require authorisation under the FSMA. These
include deposit taking, retail banking, life and
general insurance, pensions, investments, mortgages,
custody and branch share-dealing businesses, and
treasury and capital markets activity. HSBC Bank is
HSBC’s principal authorised institution in the UK.
FSA rules establish the minimum criteria for
authorisation for banks and financial services
businesses in the UK. They also set out reporting
(and, as applicable, consent) requirements with
regard to large individual exposures and large
exposures to related borrowers. In its capacity as
supervisor of HSBC on a consolidated basis, the
FSA receives information on the capital adequacy of,
and sets requirements for, HSBC as a whole. Further
details on capital measurement are included in
‘Capital management and allocation’ on pages 282 to
284. The FSA’s approach to capital requirements for
UK insurers is to require minimum capital to be
calculated on two bases. First, firms must calculate
their liabilities on a prudent basis and add a statutory
solvency margin (Pillar 1). Secondly, firms must
calculate their liabilities on a realistic basis then add
to this their own calculation of risk-based capital.
The sum of realistic reserves and risk-based capital
(Pillar 2) is agreed with the FSA. Insurers are
required to maintain capital equal to the higher of
Pillars 1 and 2. The FSA has the right to object, on
prudential grounds, to persons who hold, or intend to
hold, 10 per cent or more of the voting power of a
financial institution.
The regulatory framework of the UK financial
services system has traditionally been based on
co-operation between the FSA and authorised
institutions. The FSA monitors authorised
institutions through ongoing supervision and the
review of routine and ad hoc reports relating to
financial and prudential matters. The FSA may
periodically obtain independent reports, usually from
the auditors of the authorised institution, as to the
adequacy of internal control procedures and systems
as well as procedures and systems governing records
and accounting. The FSA meets regularly with
HSBC’s senior executives to discuss HSBC’s
adherence to the FSA’s prudential guidelines. They
also regularly discuss fundamental matters relating
to HSBC’s business in the UK and internationally,
including areas such as strategic and operating plans,
risk control, loan portfolio composition and
organisational changes, including succession
planning.
Consumers of UK financial services institutions
are covered by the Financial Services Compensation
Scheme (‘FSCS’), which is the UK’s statutory fund
of last resort. It deals with claims against authorised
institutions that are unable, or likely to be unable, to
pay claims against them, for example if an institution
has stopped trading or is in insolvency. FSCS
protects deposits, investments, insurance and
mortgage advice and arranging, and is funded by
levies on institutions authorised by the FSA. The
maximum levels of compensation are available on
www.fscs.org.uk/consumer.
Hong Kong regulation and supervision
Banking in Hong Kong is subject to the provisions
of the Banking Ordinance, and to the powers,
functions and duties ascribed by the Banking
Ordinance to the Hong Kong Monetary Authority
(the ‘HKMA’). The principal function of the HKMA
is to promote the general stability and effective
working of the banking system in Hong Kong. The
