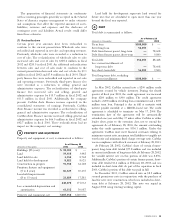
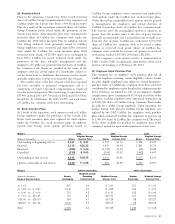
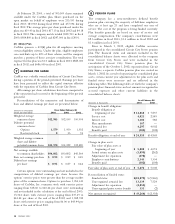
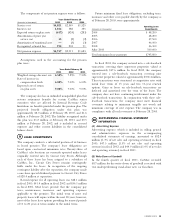
CarMax 2003 Annual Report Download - page 35
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 35 of the 2003 CarMax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
CARMAX 2003 33
undivided ownership interest in the receivables securitized
through the warehouse facility. Retained interests are
carried at fair value and changes in fair value are included
in earnings. See Notes 11 and 12 for additional discussion
on securitizations.
(D) Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying value of the company’s cash and cash
equivalents, receivables including automobile loan
receivables, accounts payable, short-term borrowings and
long-term debt approximates fair value. The company’s
retained interests in securitized receivables and derivative
financial instruments are recorded on the consolidated
balance sheets at fair value.
(E) Trade Accounts Receivable
Trade accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful
accounts, include certain amounts due from finance
companies and customers, as well as from manufacturers for
incentives and warranty reimbursements, and for other
miscellaneous receivables. The estimate for doubtful
accounts is based on historical experience and trends.
(F) Inventory
Inventory is comprised primarily of vehicles held for sale
or for reconditioning and is stated at the lower of cost or
market. Vehicle inventory cost is determined by specific
identification. Parts and labor used to recondition vehicles,
as well as transportation and other incremental expenses
associated with acquiring and reconditioning vehicles, are
included in inventory. Certain manufacturer incentives and
rebates for new car inventory, including holdbacks, are
recognized as a reduction to new car inventory when
CarMax purchases the vehicles. Volume-based incentives
are recognized as a reduction to new car inventory cost
when achievement of volume thresholds are determined
to be probable.
(G) Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated
depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and
amortization are calculated using the straight-line method
over the assets’ estimated useful lives.
(H) Computer Software Costs
External direct costs of materials and services used in the
development of internal-use software and payroll and payroll-
related costs for employees directly involved in the
development of internal-use software are capitalized.
Amounts capitalized are amortized on a straight-line basis
over a period of five years.
(I) Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Effective March 1, 2002, the company adopted SFAS No.
142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets,” which
establishes accounting and reporting standards for
intangible assets and goodwill. SFAS No. 142 requires that
goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite useful lives
no longer be amortized, but rather tested for impairment at
least annually. The company performed the required
transition impairment tests of goodwill and other
intangible assets as of March 1, 2002, and determined that
no impairment existed. Additionally, as of February 28,
2003, no impairment of goodwill or intangible assets
resulted from the annual impairment test. Prior to March 1,
2002, goodwill was amortized on a straight-line basis over
15 years. The carrying amount of goodwill was $19.7
million as of February 28, 2003, and $20.1 million as of
February 28, 2002.
(J) Defined Benefit Plan and Insurance Liabilities
Defined benefit retirement plan obligations and insurance
liabilities are included in accrued expenses and other
current liabilities on the company's consolidated balance
sheets. The defined benefit retirement plan obligations are
determined by independent actuaries using a number of
assumptions provided by the company. Key assumptions in
measuring the plan obligations include the discount rate,
the rate of salary increases and the estimated future return
on plan assets. Insurance liability estimates for workers'
compensation, general liability and employee-related
health care benefits are determined by considering
historical claims experience, demographic factors and other
actuarial assumptions.
(K) Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets
The company reviews long-lived assets for impairment when
circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an asset may
not be recoverable. Impairment is recognized when the sum
of undiscounted estimated future cash flows expected to
result from the use of the asset is less than the carrying value.
(L) Store Opening Expenses
Costs relating to store openings, including preopening costs,
are expensed as incurred.
(M) Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes reflect the impact of temporary
differences between the amounts of assets and liabilities
recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amounts
recognized for income tax purposes, measured by applying
currently enacted tax laws. A deferred tax asset is recognized
if it is more likely than not that a benefit will be realized.