Audi 2007 Annual Report Download - page 191
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 191 of the 2007 Audi annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
188
At each balance sheet date an assessment is made as to whether there is any objective
basis for impairment of a financial asset or group of financial assets.
Originated financial instruments
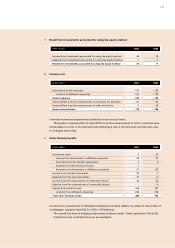
Investments in subsidiaries excluded from consolidation and in participating interests are
generally shown at their respective cost of purchase, because no active market exists for
these companies and no fair value can reliably be determined with a justifiable amount of
effort. Where there is evidence that the fair value is lower, this fair value is reported.
Loans and receivables originated by the enterprise, as well as liabilities, are measured at
amortized cost. These include, in particular
– loans advanced,
– trade receivables and payables,
– other current assets and liabilities,
– financial liabilities.
In the case of current items, the fair values to be additionally indicated in the Notes cor-
respond to the amortized cost. For non-current assets and liabilities with more than one
year to maturity, fair values are determined by discounting future cash flows at market
rates.
Liabilities from financial lease agreements are carried at the present value of the leasing
installments.
Available-for-sale financial assets include, in particular, cash pool deposits at affiliated
companies and securities. These are fundamentally measured at the fair value that corre-
sponds to the market value on the balance sheet date in the case of listed financial instru-
ments. The fluctuations in value of available-for-sale securities are accounted for within a
separate equity reserve with no effect on income, after taking into account deferred tax.
Unless there is evidence of lasting impairment, the financial result includes only capital
gains or losses. If there is evidence of a lasting decline in value, the cumulative loss is re-
corded in the equity reserve and recognized in the Income Statement. Once impairment
losses have been included in the Income Statement they are, however, no longer reversed
by recognition in the Income Statement. In the 2007 fiscal year – as in previous years – there
was no evidence of lasting impairment of the securities portfolio.
Derivative financial instruments and hedge accounting
Derivative financial instruments are used as a hedge against foreign exchange and raw ma-
terials price risks for items on the Balance Sheet and for future cash flows. Futures, as well
as options in the case of foreign exchange risks, are used for this purpose. A requirement of
hedge accounting is that a clear hedging relationship between the underlying transaction
and the hedge must be documented and its effectiveness must be demonstrated. How the
fair value changes in hedges are accounted depends on the nature of the hedging relation-
ship.
In the case of hedges against the risk of changes in value of balance sheet items (fair
value hedges), both the hedging transaction and the hedged risk portion of the underlying
transaction are recognized at fair value. Changes in the value of hedging and underlying
transactions are included in the financial result.
When hedging future cash flows, the fluctuations in the market value of the effective por-
tion of a derivative financial instrument are initially reported in a special reserve within eq-
uity, with no effect on income, and are only recognized as income or expense once the
hedged item is due. The ineffective portion of a hedge is recognized immediately in income.