Logitech 2007 Annual Report Download - page 127
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 127 of the 2007 Logitech annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
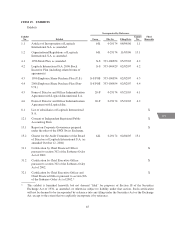
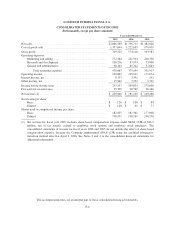
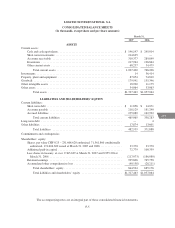
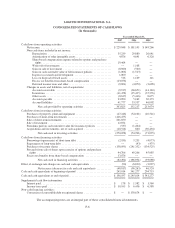
LOGITECH INTERNATIONAL S.A.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Foreign Currencies
The functional currency of the Company’s operations is primarily the U.S. dollar. To a lesser extent, certain
operations use the Euro, Swiss franc and Japanese yen as their functional currencies. The financial statements of
the Company’s subsidiaries whose functional currency is other than the U.S. dollar are translated to U.S. dollars
using period-end rates of exchange for assets and liabilities and monthly average rates for revenues and expenses.
Cumulative translation gains and losses are included as a component of shareholders’ equity in accumulated
other comprehensive loss. Gains and losses arising from transactions denominated in currencies other than a
subsidiary’s functional currency are reported in other income, net in the statement of income.
Revenue Recognition
Revenues are recognized when all of the following criteria are met:
• evidence of an arrangement exists between the Company and the customer;
• delivery has occurred and title and risk of loss transfer to the customer;
• the price of the product is fixed or determinable; and
• collectibility of the receivable is reasonably assured.
Revenues from sales to distributors and authorized resellers are recognized net of estimated product returns
and expected payments for cooperative marketing arrangements, customer incentive programs and price
protection. Significant management judgments and estimates must be used to determine the cost of these
programs in any accounting period.
The Company grants limited rights to return product, and return rights vary by customer. Estimates of
expected future product returns are recognized as a reduction of revenue at the time of sale, based on analyses of
historical trends by customer and by product, distributor and retailer inventory levels, and other factors.
Cooperative marketing arrangements include contractual customer marketing and sales incentive programs.
Under the customer marketing programs, the Company generally offers customers an allowance for marketing
activities equal to a negotiated percentage of sales. Other sales incentive programs include various fixed discount
and rebate programs. The costs of cooperative marketing arrangements are recognized as a reduction of the sale
price at the time of sale and are estimated based on the negotiated fixed percentage of the customer’s purchases
in the period the Company recognizes revenue. Accruals for sales incentive programs are recorded at the time of
sale based on negotiated terms, historical experience and inventory levels in the channel.
Customer incentive programs include volume and consumer rebates. Volume rebates are related to purchase
volumes or sales of specific products by distributors to specified retailers. Consumer rebates are offered from
time to time at the Company’s discretion directly to end-users. Contractual volume rebates to distribution or
retail customers are recognized as a reduction of the sale price at the time of shipment, and are estimated based
on the negotiated terms and the Company’s historical experience. The costs of consumer rebates are recorded at
the time the incentive is offered and are estimated based on historical experience and the specific terms and
conditions of the incentive.
The Company has contractual agreements with certain of its customers that contain terms allowing price
protection credits to be issued for customers’ on-hand or in transit new inventory if the Company, in its sole
discretion, lowers the price of the product. The estimated costs of price protection programs are recorded as a
reduction of revenue at the time of sale based on planned price reductions, units held by qualifying customers
and historical trends by customer and by product.
F-9
CG