Toyota 2011 Annual Report Download - page 86
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 86 of the 2011 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
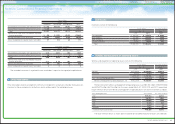
Short-term borrowings and long-term debt:
13
Product warranties and recalls and other safety measures:
14
0822
Financial Section and
Investor Information
Business and
Performance Review
Special FeatureMessage/Vision
Management and
Corporate Information
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Short-term borrowings at March 31, 2010 and 2011 consist of the following:
Long-term debt at March 31, 2010 and 2011 comprises the following:
The aggregate amounts of annual maturities of long-term debt during the next five years are as follows:
Yen in millions
U.S. dollars in millions
March 31, March 31,
2010 2011 2011
Loans, principally from banks, with a weighted-average interest at
March 31, 2010 and March 31, 2011 of 1.55% and of 1.57% per
annum, respectively ¥ 804,066 ¥1,140,066 $13,711
Commercial paper with a weighted-average interest at March 31, 2010
and March 31, 2011 of 0.44% and of 0.67% per annum, respectively 2,475,607 2,038,943 24,521
¥3,279,673 ¥3,179,009 $38,232
As of March 31, 2011, “Loans, principally from
banks” amount includes secured loans by finance
receivables securitization of ¥335,539 million
($4,035 million).
As of March 31, 2011, Toyota has unused
short-term lines of credit amounting to ¥1,954,330
As of March 31, 2011, approximately 31%,
24%, 12% and 33% of long-term debt are denomi-
nated in Japanese yen, U.S. dollars, euros, and
other currencies, respectively.
As of March 31, 2011, property, plant and
equipment with a book value of ¥57,237 million
Standard agreements with certain banks in
Japan include provisions that collateral (including
sums on deposit with such banks) or guarantees
will be furnished upon the banks’ request and that
any collateral furnished, pursuant to such
agreements or otherwise, will be applicable to all
present or future indebtedness to such banks.
million ($23,504 million) of which ¥464,564 million
($5,587 million) related to commercial paper
programs. Under these programs, Toyota is
authorized to obtain short-term financing at
prevailing interest rates for periods not in excess
of 360 days.
($688 million) and in addition, other assets
aggregating ¥1,128,957 million ($13,577 million)
were pledged as collateral mainly for certain debt
obligations of subsidiaries. These other assets
principally consist of securitized finance
receivables.
During the year ended March 31, 2011, Toyota
has not received any significant such requests
from these banks.
As of March 31, 2011, Toyota has unused
long-term lines of credit amounting to ¥8,073,898
million ($97,100 million).
Yen in millions
U.S. dollars in millions
March 31, March 31,
2010 2011 2011
Unsecured loans, representing obligations principally to banks, due 2010 to
2029 in 2010 and due 2011 to 2029 in 2011 with interest ranging from 0.00%
to 29.25% per annum in 2010 and from 0.00% to 29.00% per annum in 2011
¥ 2,942,012 ¥ 3,386,854 $ 40,732
Secured loans, representing obligations principally to finance receivables securitization
due 2010 to 2019 in 2010 and due 2011 to 2050 in 2011 with interest ranging from
0.49% to 6.65% per annum in 2010 and from 0.37% to 5.35% per annum in 2011
381,307 619,380 7,449
Medium-term notes of consolidated subsidiaries, due 2010 to 2047 in 2010 and
due 2011 to 2047 in 2011 with interest ranging from 0.04% to 15.25% per
annum in 2010 and from 0.01% to 15.25% per annum in 2011
3,814,439 3,314,589 39,863
Unsecured notes of parent company, due 2010 to 2019 in 2010 and due 2012
to 2019 in 2011 with interest ranging from 1.07% to 3.00% per annum in 2010
and from 1.07% to 3.00% per annum in 2011
580,000 530,000 6,374
Unsecured notes of consolidated subsidiaries, due 2010 to 2031 in 2010 and
due 2011 to 2031 in 2011 with interest ranging from 0.25% to 17.03% per
annum in 2010 and from 0.27% to 15.48% per annum in 2011
1,473,732 1,349,307 16,227
Long-term capital lease obligations, due 2010 to 2028 in 2010 and due 2011 to
2028 in 2011 with interest ranging from 0.43% to 14.40% per annum in 2010
and from 0.38% to 14.40% per annum in 2011
42,243 21,917 263
9,233,733 9,222,047 110,908
Less - Current portion due within one year (2,218,324) (2,772,827) (33,347)
¥ 7,015,409 ¥ 6,449,220 $ 77,561
Years ending March 31, Yen in millions
U.S. dollars in millions
2012 ¥2,772,827 $33,347
2013 1,834,556 22,063
2014 1,522,659 18,312
2015 900,120 10,825
2016 1,106,492 13,307
Toyota provides product warranties for certain
defects mainly resulting from manufacturing
based on warranty contracts with its customers at
the time of sale of products. Toyota accrues
estimated warranty costs to be incurred in the
future in accordance with the warranty contracts.
In addition to product warranties, Toyota initiates
recalls and other safety measures to repair or to
replace parts which might be expected to fail
from products safety perspectives or customer
satisfaction standpoints. Toyota accrues for costs
of recalls and other safety measures at the time of
vehicle sale based on the amount estimated from
historical experience.
Liabilities for product warranties and liabilities
for recalls and other safety measures have been
combined into a single table showing an
aggregate liability for quality assurances due to
the fact that both are liabilities for costs to repair
or replace defects of vehicles and the amounts
incurred to repair or replace defects of vehicles
may affect the amounts incurred for product
warranties and vice versa.
86
TOYOTA ANNUAL REPORT 2011