Kia 2013 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2013 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
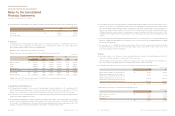
For the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
29.
Finance Risk Management
The Company’s activities are exposed to a variety of financial risks: credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk (comprised of foreign
exchange risk and interest rate risk). The treasury department monitors and manages the financial risk arising from the Company’s
underlying operations in accordance with the risk management policies and procedures authorized by the board of directors.
(a) Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a customer or counterparty to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual
obligations. The Company has transacted with customers before evaluating on their credit rating and have their collaterals to control
customers on default.
(b) Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will encounter difficulty in meeting the obligations associated with its financial liabilities that
are settled by delivering cash or another financial asset. Management believes the Company maintains adequate sources of liquidity
to settle short-term financial liabilities. In addition, based on periodic analysis of expected cash outflows, the Company also considers
other alternatives, including seeking additional external financing or disposition of financial instruments for investment purpose, to
mitigate liquidity risk.
(c) Market risk
Market risk is the risk of fluctuations in fair value of financial instrument and future cash flow by changes of market price. The purpose
for managing market price is to optimize profits, while manage and control on exposure to market risk within acceptable limits.
(i) Foreign exchange risk
The Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from high proportion of export in sales amount, which is denominated in
foreign currencies. The Company’s primary exposure is to the US dollar and Euro and the Company manages to minimize financial
risk on fluctuations in foreign exchange in order to stabilize operating activities. The Company consistently evaluates on various foreign
exchange risk according to the Company’s own guideline for foreign exchange and transaction policy. If necessarily, the Company may
enter into foreign currency forwards contracts to hedge its foreign currency risk and strictly limit on speculative transaction.
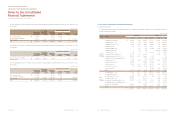
(ii) Interest rate risk
The Company’s asset and liability is exposed to interest rate risk on deposits and loans. In order to minimize actual Interest cost, the
Company continuously monitors current status of market interest rate, make a prediction on market data and reviews on method for
borrowing and joining financial instruments on deposit. Also, the Company’s management monitors the level of interest rates and
maintains the balance of borrowings at variable rates and fixed rates.
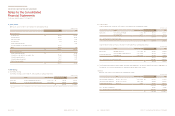
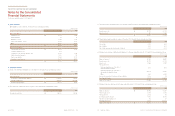
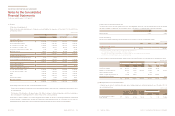
(d) Management of capital risk
The fundamental goal of capital management is to maintain on financial structure. As for this to be maintained, the Company use debt
ratio as indicator of capital management. The debt ratio is calculated as total liability divided by total equity.
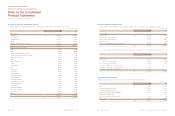
30.
Risk Management of Financial Instruments
(a) Credit and counterparty risk
(i) Exposure to credit and counterparty risk
The carrying amount of financial assets means maximum exposure in respect of credit and counterparty risk. The maximum exposure
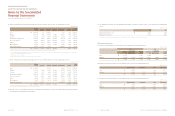
as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 are as follows:
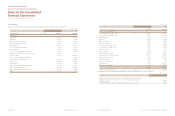
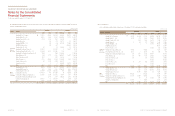
(In millions of won)
Cash and cash equivalents (*) ₩2,310,787 1,902,988
Short-term financial instruments 4,035,379 2,367,230
Accounts and notes receivable - trade 2,072,818 1,801,731
Accounts and notes receivable - other 468,210 485,696
Other current assets 98,796 152,090
Long-term financial instruments 294,377 58,990
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets 1,237,107 1,606,358
Long-term accounts and notes receivable - trade 1,662 2,675
Guarantee deposits 162,190 166,463
Other non-current assets 93,154 122,936
₩10,774,480 8,667,157
(*) Cash on hand is excluded.
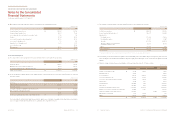
(ii) Loss on impairment
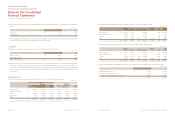
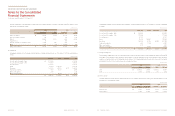
The carrying amount of trade account and notes receivable and other receivable based on by maturity as of December 31, 2013 and
2012 are as follows:
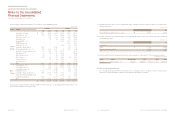
Not overdue ₩1,958,343 691,216 1,500,279 806,588
Past due less than 3 month 84,981 39,860 260,421 80,463
Past due 4~ 6 month 3,962 21,973 19,123 6,471
Past due 7~12 month 23,296 1,220 43,142 17,481
Past due over 12 month 104,931 47,043 100,836 21,868
₩2,175,513 801,312 1,923,801 932,871
(In millions of won)
(*) Other receivables are comprised of other accounts and notes receivables, long-term other accounts and notes receivables, accrued income, short-term loans and guarantee deposits.