Kia 2013 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2013 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment within the
next fiscal year are included in the following notes:
· Note 16 : Employee Benefits
· Note 17 : Provisions
· Note 18 : Commitments and Contingencies
· Note 26 : Income Tax Expense
(e) Fair value measurement
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-
financial assets and liabilities.
The Company has an established control framework with respect to the measurement of fair values. This includes a valuation team that
has overall responsibility for overseeing all significant fair value measurements, including Level 3 fair values, and reports directly to the CFO.
The valuation team regularly reviews significant unobservable inputs and valuation adjustments. If third party information, such as
broker quotes or pricing services, is used to measure fair values, then the valuation team assesses the evidence obtained from
the third parties to support the conclusion that such valuations meet the requirements of K-IFRS, including the level in the fair value
hierarchy in which such valuations should be classified.
(f) Changes in accounting policies
(i) Amendments to K-IFRS No. 1001, ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’
The Company has retrospectively applied the amendments to K-IFRS No. 1001, ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ since January
1, 2013. The amendments require presenting in other comprehensive income on the basis of whether they are potentially reclassifiable
to profit or loss subsequently (reclassification adjustments). The consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the year ended
December 31, 2012 is restated.
(ii) Amendments to K-IFRS No. 1019, ‘Employee Benefits’
The Company has applied the amendments to K-IFRS No. 1019, ‘Employee Benefits’ since January 1, 2013. The standard requires
recognition of actuarial gains and losses immediately in other comprehensive income and to calculate expected return on plan assets
based on the rate used to discount the defined benefit obligation. The amendments to K-IFRS No. 1019 are not applied retrospectively,
as the Company believes that the impact on prior period financial statements is immaterial.
(iii) Amendments to K-IFRS No. 1107, ‘Disclosures-Offsetting Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities’
As a result of the amendments to K-IFRS No. 1107, the Company has expanded its disclosures about the offsetting of financial assets
and financial liabilities (see Note 30(g)).
(iv) K-IFRS No. 1110, ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’
The Company adopted K-IFRS No. 1110, ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’ since January 1, 2013. As a result, the Company has
changed its accounting policy with respect to determining whether it has control over and consequently whether it consolidates its
investees. K-IFRS No. 1110 introduces a new control model that is applicable to all investees; among other things, it requires the
consolidation of an investee if the Company controls the investee on the basis of de facto circumstances. The adoption of K-IFRS
No.1110 does not result in any change to the Company’s consolidation scope.
(v) K-IFRS No. 1111, ‘Joint Arrangements’
The Company adopted K-IFRS No. 1111, ‘Joint Arrangements’ since January 1, 2013. The standard classifies joint arrangements into
two types - joint operations and joint ventures. A joint operation is a joint arrangement whereby the parties that have joint control of the
arrangement (i.e. joint operators) have rights to the assets, and obligations for the liabilities, relating to the arrangement. A joint venture
is a joint arrangement whereby the parties that have joint control of the arrangement (i.e. joint ventures) have rights to the net assets of
the arrangement. The standard requires a joint operator to recognize and measure the assets and liabilities (and recognize the related
revenues and expenses) in relation to its interest in the arrangement in accordance with relevant K-IFRSs applicable to the particular
assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. The standard requires a joint venture to recognize an investment and to account for that
investment using the equity method. In Accordance with K-IFRS No. 1111, The Company has re-evaluated its involvement in its only
joint arrangement and has reclassified the investment from jointly controlled entity to joint venture. Notwithstanding the reclassification,
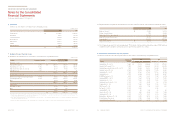
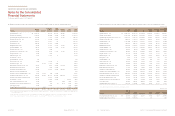
(c) Financial information of subsidiaries
Financial information of significant subsidiaries (before eliminating intra-group transaction) as of and for the years ended December 31,
2013 and 2012 are summarized as follows:
(i) Financial information as of and for the year ended December 31, 2013
KMA ₩3,275,282 2,474,823 12,869,946 532,610
KMMG 1,984,718 1,256,690 8,073,095 207,923
KMS 2,767,738 1,572,813 6,464,346 335,564
KMR 772,588 414,746 4,187,462 170,430
(In millions of won)
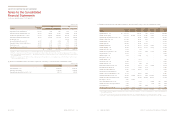
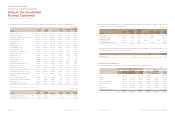
KMA ₩2,847,423 2,275,194 12,699,059 386,712
KMMG 2,077,148 1,345,709 7,771,212 206,090
KMS 2,636,049 1,591,732 5,675,685 225,141
KMR 815,037 310,153 4,268,189 295,920
(In millions of won)
(ii) Financial information as of and for the year ended December 31, 2012
For the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
2. Basis of Preparation
(a) Statement of compliance
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards (“K-IFRS”)
as prescribed in
the Act on External Audit of Corporations in the Republic of Korea.
(b) Basis of measurement
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis, except for the following material items in the
consolidated statements of financial position:
· Available-for-sale financial assets are measured at fair value
· Liabilities for defined benefit plans are recognized at the net of total present value of defined benefit obligations less the fair value of
plan assets
(c) Functional and presentation currency
The consolidated financial statements are presented in Korean won, which is the Parent Company’s functional currency and the
currency of the primary economic environment in which the Company operates.
(d) Use of estimates and judgments
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with K-IFRS requires management to make judgments,
estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income
and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the
period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.