Honda 2013 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2013 Honda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
than 5-speed automatic transmissions of the same class. In
addition, development of a new catalytic converter cut the
volume of rhodium by 50% and total precious metals by
22%, reducing the cost of catalytic converters by 37%.
Honda also developed new technology for welding steel and
aluminum for reducing structural weight by 25% and improv-
ing fuel economy, and applied it for the first time in the world
to the front subframe of a mass-production vehicle. Separately,
Honda developed a new technology joining steel and alumi-
num for reducing structural weight 17%, and in another
world first applied it to the outer door panel of a mass-
production vehicle.
R&D expenses in this segment in fiscal 2013 amounted to
¥464.0 billion.
Power Product and Other Businesses
The Power Products business policy is to proactively propose
new and useful ideas that will bring joy to customers worldwide.
Core R&D programs focus on (1) creating new technology for
developed countries to take account of socioeconomic, life-
style and energy use changes, (2) developing strategic prod-
ucts for emerging markets, (3) building a platform to expand
overseas production, and (4) building and testing eco-friendly
and self-contained household systems for generating and
consuming energy.
Among key R&D developments, Honda has created an
industry-first low-pressure liquefied propane gas (LPG) gen-
erator capable of operating reliably for long periods during a
disaster or emergency. Demand for emergency power genera-
tors has risen in Japan since the power outages caused by
the Great East Japan Earthquake. The product operates on
LPG, a long-storage fuel already used with other household
equipment. These units are being furnished to LPG equipment
suppliers. Honda has also developed a gas engine
cogeneration unit for households designed for autonomous
operation in power outages, provided that the supply of gas
remains intact. Sales have begun in Japan via gas utilities.
Elsewhere, Honda launched the Salad CG FFV300 gas-
powered tiller, which runs on widely used household gas can-
isters. Honda also put the Miimo robotic lawn mower on sale
in Europe as part of developing this new market. The product
boasts low noise and automatic recharging capabilities.
In other R&D developments, a special test house in
Saitama City was built with the Honda Smart Home System,
a residential energy management system that integrates
household gas and solar power with electromotive mobility.
System testing is underway.
R&D expenses in this segment in fiscal 2013 amounted to
¥29.7 billion.
Fundamental Research
During fiscal 2013, Honda continued its fundamental research
activities to develop technologies in a diverse range of fields
that will support the products of the future.
Please note that expenses incurred in fundamental
research are allocated among each business segment.
Patents and Licenses
At March 31, 2013, Honda owned more than 19,400 patents
in Japan and more than 25,200 patents abroad. Honda also
had applications pending for more than 10,800 patents in
Japan and for more than 15,800 patents abroad. While
Honda considers that, in the aggregate, Honda’s patents are
important, it does not consider any one of such patents, or
any related group of them, to be of such importance that the
expiration or termination thereof would materially affect
Honda’s business.
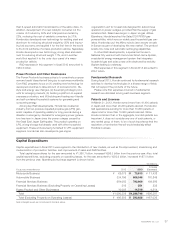
Capital Expenditures
Capital expenditures in fiscal 2013 were applied to the introduction of new models, as well as the improvement, streamlining and
modernization of production facilities, and improvement of sales and R&D facilities.
Total capital expenditures for the year amounted to ¥1,386.7 billion, increased ¥296.3 billion from the previous year. Also, total
capital expenditures, excluding property on operating leases, for the year amounted to ¥593.6 billion, increased ¥187.0 billion
from the previous year. Spending by business segment is shown below.
Yen (millions)
Fiscal years ended March 31 2012 2013
Increase
(Decrease)
Motorcycle Business ¥ 62,075 ¥ 73,513 ¥ 11,438
Automobile Business 334,196 505,045 170,849
Financial Services Business 684,083 793,669 109,586
Financial Services Business (Excluding Property on Operating Leases) 316 551 235
Power Product and Other Businesses 10,005 14,519 4,514
Total ¥1,090,359 ¥1,386,746 ¥296,387
Total (Excluding Property on Operating Leases) ¥ 406,592 ¥ 593,628 ¥187,036
Note: Intangible assets are not included in the table above.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. 37