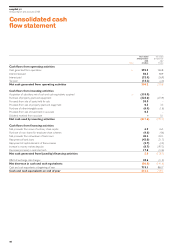
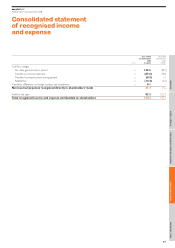
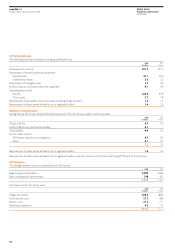
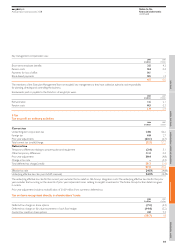
EasyJet 2008 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2008 EasyJet annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
easyJet plc
Annual report and accounts 2008
Notes to the
financial statements
continued
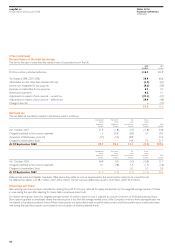
Basis of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements incorporate those of easyJet plc
and its subsidiaries for the years ended 30 September 2007 and 2008,
together with the attributable share of results and reserves of associated
undertakings, adjusted where appropriate to conform with easyJet’s
accounting policies.
A subsidiary is an entity controlled by easyJet. Control exists when easyJet
has the power, directly or indirectly, to govern the financial and operating
policies of an entity so as to benefit from its activities. A minority interest is
the portion of the profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable
to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through
subsidiaries, by easyJet.
Associates are those entities in which easyJet has significant influence, but
not control over the financial and operating policies. They are accounted
for using the equity method.
Intragroup balances, transactions and any unrealised gains and losses arising
from intragroup transactions are eliminated in preparing the consolidated
financial statements.
Foreign currencies
The primary economic environment in which a subsidiary operates
determines its functional currency. The functional currency of easyJet plc
is sterling. Certain subsidiaries have operations that are primarily
influenced by a currency other than sterling. Exchange differences arising
on the translation of these foreign operations are taken to reserves until
all or part of the interest is sold, when the relevant portion of the exchange
is recognised in income. Profits and losses of foreign operations are
translated into sterling at average rates of exchange during the year.
Transactions arising in foreign currencies are recorded using the rate
of exchange ruling at the date of the transaction. Monetary assets and
liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into sterling
using the rate of exchange ruling at the balance sheet date and (except
where the asset or liability is designated as a cash flow hedge) the gains
or losses on translation are included in the consolidated income statement.
Non monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are
translated into sterling at foreign exchange rates ruling at the dates the
transactions were effected.
Revenue recognition
Revenues comprise the invoiced value of airline services, net
of air passenger duty, VAT and discounts, plus ancillary revenue.
Passenger revenue arises from the sale of flight seats and is recognised
when the service is provided. Unearned revenue represents flight seats
sold but not yet flown and is included in trade and other payables until
it is released to the income statement when the service is provided.
Ancillary revenue is generally recognised when the flight to which it relates
departs. Certain types of ancillary revenue are recognised at the time the
benefit of the service provided passes to the customer. Ancillary revenue
in the form of fixed annual fees is recognised evenly throughout the year.
Amounts paid by “no-show” customers are recognised as revenue when
the booked service is provided as such customers are not generally
entitled to change flights or seek refunds once a flight has departed.
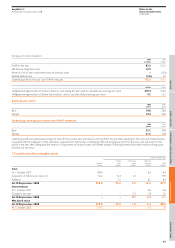
Business combinations
Business combinations are accounted for by applying the purchase method.
The cost of the acquisition is measured at the aggregate of the fair values,
at the date of exchange, of assets given and liabilities incurred or assumed
plus any costs directly attributable to the business combination. The acquiree’s
identifiable assets and liabilities are recognised at their fair values at the
acquisition date. Goodwill arising on acquisition is recognised as an asset
and initially measured at cost, being the excess of the cost of the business
combination over the Group’s interest in the net fair value of the
identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities recognised.
Goodwill and other intangible assets
Goodwill and landing rights at Gatwick have indefinite expected useful
lives and are tested for impairment annually or where there is any
indication of impairment. They are stated at cost less any accumulated
impairment losses.
Landing rights at Gatwick are considered to have an indefinite useful life
as they will remain available for use for the foreseeable future provided
minimum utilisation requirements are observed.
Other intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated amortisation,
which is calculated to write off their cost, less estimated residual value, on
a straight-line basis over their expected useful lives. Expected useful lives
are reviewed annually.
Expected useful life
Computer software 3 years
Contractual rights Over the length of the
related contracts
49
OverviewDirectors’ reportReport on Directors’ remunerationFinancial informationOther information