EasyJet 2008 Annual Report Download - page 16
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 16 of the 2008 EasyJet annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
easyJet plc
Annual report and accounts 2008
Financial review
continued
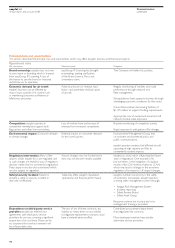
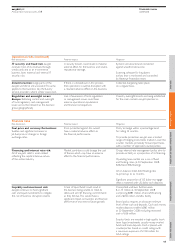
Principal risks and uncertainties
This section describes the principal risks and uncertainties which may affect easyJet’s business and financial prospects.
Operational risks
Risk description Potential impact Mitigation
Brand ownership: easyJet does not own easyGroup IP Licensing has brought The Company will defend its position.
its own name or branding which is licensed proceedings seeking clarification
from easyGroup IP Licensing. A loss of of the Brand Licence. This is not
the licence to use the brand or imposed a monetary claim.
restrictions on its operation.
Economic demand for air travel: Adverse pressure on revenue, load Regular monitoring of markets and route
easyJet’s business can be affected by factors and potentially residual values performance through network and
macro issues outside of its control such of aircraft. fleet management.
as weakening consumer confidence or
inflationary pressures. Strong balance sheet supports business through
challenging economic conditions for the sector.
Committed undrawn borrowing facilities of
$1,135 million to support funding requirements.
Appropriate mix of owned and leased aircraft
reduces residual value exposure.
Competition: easyJet operates in Loss of market share and erosion of Routine monitoring of competitor activity.
competitive marketplaces against both revenue from increased competition.
flag carriers and other low-cost airlines. Rapid response in anticipation of/to changes.
Environmental impact: Consumer attitude Potential impact on consumer demand Environmental Management Group that
to climate change. for the core business. co-ordinates environmental policy and
public communications.
easyJet operates modern, fuel-efficient aircraft
operating at high capacity and flies to
conveniently located airports.
Regulatory intervention: Many of the Airport charges may rise. Furthermore, easyJet has a key role in influencing the future
airports which easyJet fly to are regulated, and slots may not become readily available. state of regulations. One example of its
as such charges are levied by way of regulatory pro-activeness is the instigation of a judicial
decision rather than by commercial negotiation. review of the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA)
Many airports are also slot constrained which which may lead to changes in the economic
are also subject to regulation. regulation of increases to UK airport charges.
Safety/security incident: Failure to Adversely affect easyJet’s reputation, easyJet’s number one priority is the safety
prevent a safety or security incident or operational and financial performance. of customers and people. easyJet operates
deal with it effectively. a strong safety management system through:
• Fatigue Risk Management System
• Incident reporting
• Safety Review Board
• Safety Audit Group
Response systems are in place and crisis
management training is provided.
Dependence on third-party service The loss of any of these contracts, any Centralised procurement department
providers: easyJet has entered into inability to renew them or any inability that negotiates key contracts.
agreements with third-party service to negotiate replacement contracts could
providers for services covering a significant have a material adverse effect. Most developed markets have suitable
proportion of its cost base. There can be alternative service providers.
no assurance that contract renewals will
be at favourable rates.
14