3M 2009 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2009 3M annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report. 96
NOTE 13. Fair Value Measurements
As discussed in Note 1, 3M adopted the new fair value measurements standard, codified in ASC 820, prospectively
effective January 1, 2008, with respect to fair value measurements of (a) nonfinancial assets and liabilities that are
recognized or disclosed at fair value in the Company’s financial statements on a recurring basis (at least annually)
and (b) all financial assets and liabilities. 3M adopted the remaining aspects of the fair value measurement standard
relative to nonfinancial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value, but are recognized and disclosed at fair
value on a nonrecurring basis, prospectively effective January 1, 2009.
Under the new standard, fair value is defined as the exit price, or the amount that would be received to sell an asset
or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants as of the measurement date. The
standard also establishes a hierarchy for inputs used in measuring fair value that maximizes the use of observable
inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs by requiring that the most observable inputs be used when
available. Observable inputs are inputs market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability developed
based on market data obtained from sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that
reflect the Company’s assumptions about the factors market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability
developed based upon the best information available in the circumstances. The hierarchy is broken down into three
levels. Level 1 inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 2 inputs
include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or
liabilities in markets that are not active, and inputs (other than quoted prices) that are observable for the asset or
liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. Categorization
within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
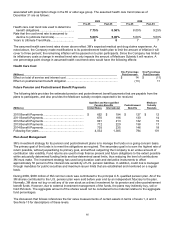
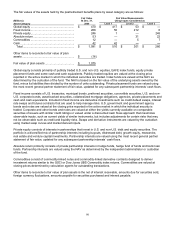
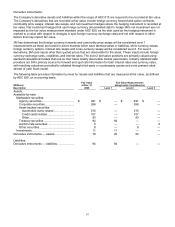
Assets and Liabilities that are Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis:
As described in Note 1, at 3M, effective January 1, 2008, fair value measurement under ASC 820 principally applied
to financial asset and liabilities such as available-for-sale marketable securities, available-for-sale investments
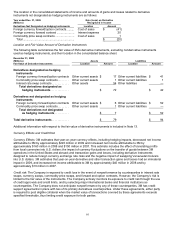
(included as part of investments in the Consolidated Balance Sheet) and certain derivative instruments. Derivatives
include cash flow hedges, interest rate swaps and most net investment hedges. These items were previously and will
continue to be marked-to-market at each reporting period; however, the definition of fair value used for these mark-
to-markets is now applied using ASC 820. The information in the following paragraphs and tables primarily
addresses matters relative to these financial assets and liabilities. The information incorporates guidance relating to
determining the fair value of a financial asset when the market for that asset is not active, which was effective for 3M
beginning with the quarter ended September 30, 2008. The information also incorporates the new guidance
described in Note 1 related to determining fair values when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability
have significantly decreased and identifying transactions that are not orderly, which was effective for 3M beginning
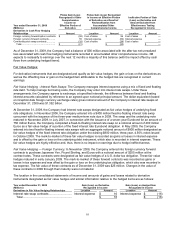
April 1, 2009. Separately, there were no material fair value measurements with respect to nonfinancial assets or
liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the Company’s financial statements on a recurring basis
subsequent to the effective date of the new standard (as impacted by associated updates codified in ASC 820).
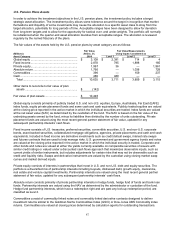
3M uses various valuation techniques, which are primarily based upon the market and income approaches, with
respect to financial assets and liabilities. Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for the
respective financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value.
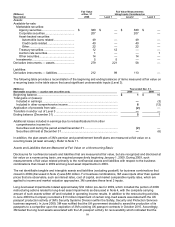
Available-for-sale marketable securities — except auction rate securities:
Marketable securities, except auction rate securities, are valued utilizing multiple sources. A weighted average price
is used for these securities. Market prices are obtained for these securities from a variety of industry standard data
providers, security master files from large financial institutions, and other third-party sources. These multiple prices
are used as inputs into a distribution-curve-based algorithm to determine the daily fair value to be used. 3M classifies
treasury securities as level 1, while all other marketable securities (excluding auction rate securities) are classified as
level 2. Marketable securities are discussed further in Note 9.
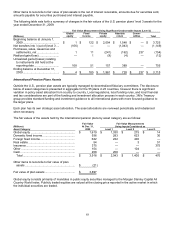
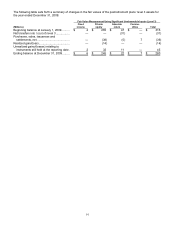
Available-for-sale marketable securities — auction rate securities only:
As discussed in Note 9, auction rate securities held by 3M failed to auction since the second half of 2007. As a result,
investments in auction rate securities are valued utilizing broker-dealer valuation models and third-party indicative bid
levels in markets that are not active. 3M classifies these securities as level 3.
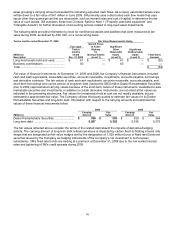
Available-for-sale investments:
Investments include equity securities that are traded in an active market. Closing stock prices are readily available
from active markets and are used as being representative of fair value. 3M classifies these securities as level 1.