Toyota 2010 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2010 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
TOYOTA ANNUAL REPORT 2010 81
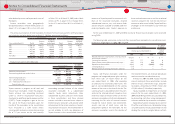
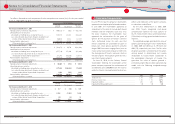
The following table summarizes Toyotas stock option activity:
Yen Yen in
millions
Number of
shares
Weighted-
average
exercise
price
Weighted-
average
remaining
contractual
life in years
Aggregate
intrinsic
value
Options outstanding at March 31, 2007 ····················· 6,292,700 ¥ 5,175 5.53 ¥ 14,947
Granted ······················································································· 3,264,000 7,278
Exercised ···················································································· (792,100) 4,208
Canceled ···················································································· (423,000) 6,196
Options outstanding at March 31, 2008 ····················· 8,341,600 6,038 5.71 1,753
Granted ······················································································· 3,494,000 4,726
Exercised ···················································································· (119,900) 3,626
Canceled ···················································································· (375,000) 6,889
Options outstanding at March 31, 2009 ····················· 11,340,700 5,631 5.51 1
Granted ······················································································· 3,492,000 4,193
Exercised ···················································································· (157,800) 3,116
Canceled ···················································································· (958,200) 4,646
Options outstanding at March 31, 2010 ····················· 13,716,700 ¥ 5,363 5.23 ¥ ̶
Options exercisable at March 31, 2008 ························· 2,354,600 ¥ 4,225 2.76 ¥ 1,753
Options exercisable at March 31, 2009 ························· 4,971,700 ¥ 5,302 3.76 ¥ 1
Options exercisable at March 31, 2010 ························· 7,515,700 ¥ 6,132 3.86 ¥ ̶
The total intrinsic value of options exercised for
the years ended March 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010
was ¥1,651 million, ¥97 million and ¥113 million
($1 million), respectively.
As of March 31, 2010, there were unrecognized
compensation expenses of ¥1,822 million
($20 million) for stock options granted. Those
expenses are expected to be recognized over a
weighted-average period of 1.1 years.
Cash received from the exercise of stock
options for the years ended March 31, 2008, 2009
and 2010 was ¥3,333 million, ¥435 million and
¥492 million ($5 million), respectively.
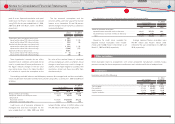
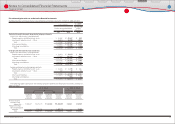
The following table summarizes information for options outstanding and options exercisable at March
31, 2010:
Outstanding Exercisable
Exercise price
range
Weighted-
average
exercise
price
Weighted-
average
exercise
price
Weighted-
average
remaining
life
Weighted-
average
exercise
price
Weighted-
average
exercise
price
Yen
Number of
shares Yen Dollars Years
Number of
shares Yen Dollars
¥4,193 − 6,000 8,133,700 ¥4,429 $48 5.50 1,932,700 ¥4,427 $48
6,001 − 7,278 5,583,000 6,723 72 4.85 5,583,000 6,723 72
4,193 − 7,278 13,716,700 5,363 58 5.23 7,515,700 6,132 66
Pension and severance plans
Upon terminations of employment, employees
of the parent company and subsidiaries in Japan
are entitled, under the retirement plans of each
company, to lump-sum indemnities or pension
payments, based on current rates of pay and
lengths of service or the number of points
mainly determined by those. Under normal
circumstances, the minimum payment prior to
retirement age is an amount based on voluntary
retirement. Employees receive additional
benefi ts on involuntary retirement, including
retirement at the age limit.
Eff ective October 1, 2004, the parent company
amended its retirement plan to introduce a
point based retirement benefi t plan. Under
the new plan, employees are entitled to lump-
sum or pension payments determined based
on accumulated points vested in each year of
service.
There are three types of points that vest
in each year of service consisting of service
period points which are attributed to the
length of service, job title points which are
attributed to the job title of each employee,
and performance points which are attributed
to the annual performance evaluation of each
employee. Under normal circumstances, the
minimum payment prior to retirement age is an
amount refl ecting an adjustment rate applied
to represent voluntary retirement. Employees
receive additional benefi ts upon involuntary
retirement, including retirement at the age limit.
Eff ective October 1, 2005, the parent company
partly amended its retirement plan and
introduced the quasi cash-balance plan under
which benefi ts are determined based on the
variable-interest crediting rate rather than the
fi xed-interest crediting rate as was in the pre-
amended plan.
The parent company and most subsidiaries
in Japan have contributory funded defi ned
benefi t pension plans, which are pursuant to
the Corporate Defi ned Benefi t Pension Plan
Law (CDBPPL). The contributions to the plans
are funded with several fi nancial institutions
in accordance with the applicable laws and
regulations. These pension plan assets consist
principally of common stocks, government
bonds and insurance contracts.
Most foreign subsidiaries have pension plans or
severance indemnity plans covering substantially
all of their employees under which the cost of
benefi ts are currently invested or accrued. The
benefi ts for these plans are based primarily on
lengths of service and current rates of pay.
Toyota uses a March 31 measurement date for
its benefi t plans.
Financial Section
Financial Section
Investor Information
Corporate Information
Special Feature
Consolidated
Performance Highlights
Business Overview
Top Messages
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Employee benefi t plans:
19