Konica Minolta 2009 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2009 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
35
(n) Practical Solution on Unification of Accounting Policies
Applied to Foreign Subsidiaries for Consolidated Financial
Statements
Changes in Accounting Standards
Effective from the year ended March 31, 2009, the Company applied
the “Practical Solution on Unification of Accounting Policies Applied
to Foreign Subsidiaries for Consolidated Financial Statements”
(ASBJ Practical Issues Task Force (PITF) No. 18, issued by the
ASBJ on May 17, 2006). Accordingly, the Company uses financial
statements of the foreign subsidiaries prepared in accordance with
International Financial Reporting Standards or accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States for preparation of the con-
solidated financial statements, except for certain adjustments
required to be made in consolidation to comply with accounting
principles generally accepted in Japan and amended the consoli-
dated financial statements as required.
As a result, the effect of this change was not material to the con-
solidated statement of income. For the year ended March 31, 2009,
lease receivables and investment assets increased ¥13,598 million
($138,430 thousand) in consolidated balance sheet.
(o) Service Expenses from SG&A Expenses to Cost of Sales
Changes in Accounting Policy
Previously, some consolidated subsidiaries recognized service
expenses (related to digital multifunction devices and other products)
as SG&A expense. Effective from the year ended March 31, 2009,
the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries recognize service
expense as cost of sales, following a change in accounting policy.
As a result of this change, gross profit decreased ¥28,126 million
($286,328 thousand) when compared to the previous method.
(p) Loss on Disposal of Inventories
Changes in Accounting Policy
Previously, some consolidated subsidiaries recognized loss on
disposal of inventories as non-operating expenses.
Effective from the year ended March 31, 2009, the Company and
its consolidated subsidiaries recognize the loss on disposal of
inventories as cost of sales, following the accounting policy review
caused by the introduction of adoption of ASBJ Statement No. 9,
“Accounting Standards for Measurement of Inventories”, issued by
the ASBJ on July 5, 2006.
As a result of this change, gross profit and operating income
decreased ¥2,606 million ($26,530 thousand) when compared to the
previous method.
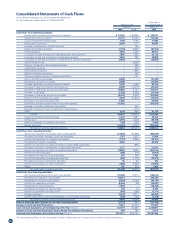
(q) Cash Flows from Operating Activities
“Decrease in provision for bonuses”, “Decrease in accounts receiv-
able-other” and “Decrease in accounts payable-other and accrued
expenses”, which were included within “Other” in the “Cash flows
from operating activities” section of the consolidated statements of
cash flows in the previous fiscal year, are now segmentalized in each
account from the year ended March 31, 2009.
“Increase in allowance for doubtful accounts”, “Increase in
accrued consumption tax payable” and “Reversal of reserve for loss
on impairment of lease assets”, which were segmentalized in the
“Cash flows from operating activities” section of the consolidated
statements of cash flows in the previous fiscal year, are now
included within “Other” from the year ended March 31, 2009.
3. U.S. Dollar Amounts
The translation of Japanese yen amounts into U.S. dollars is
included solely for the convenience of the reader, using the pre-
vailing exchange rate at March 31, 2009, which was ¥98.23 to
U.S.$1.00. The translations should not be construed as representa-
tions that the Japanese yen amounts have been, could have been,
or could in the future be, converted into U.S. dollars at this or any
other exchange rate.
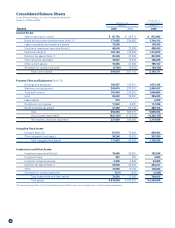
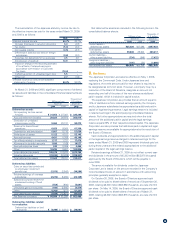
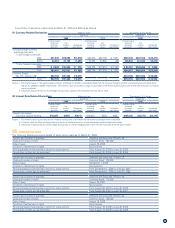
4. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of March 31, 2009 and 2008, consist of:
Millions of yen
Thousands of
U.S. dollars
March 31 March 31
2009 2008 2009
Cash on hand and in banks ¥ 85,753 ¥ 89,218 $ 872,982
Time deposits (over 3 months) (26) (31) (265)
Short-term investments 48,000 33,000 488,649
Cash and cash equivalents ¥133,727 ¥122,187 $1,361,366
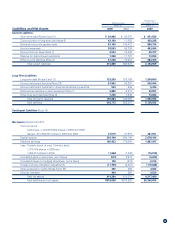
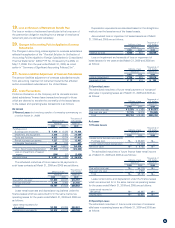
5. Investment Securities
As of March 31, 2009
(1) Other Securities with Quoted Market Values
Millions of yen
Original purchase
value
Market value at the
consolidated
balance sheet date
Unrealized gains
(losses)
Securities for which the amounts in the consolidated balance sheet
exceed the original purchase value
(1) Shares ¥ 7,287 ¥ 8,823 ¥ 1,536
(2) Bonds – – –
(3) Other 8 8 0
Subtotal ¥ 7,295 ¥ 8,832 ¥ 1,536
Securities for which the amounts in the consolidated balance sheet
do not exceed the original purchase value
(1) Shares ¥ 8,426 ¥ 6,031 ¥(2,395)
(2) Bonds – – –
(3) Other 8 6 (1)
Subtotal ¥ 8,435 ¥ 6,037 ¥(2,397)
Total ¥15,730 ¥14,869 ¥ (861)
Thousands of U.S. dollars
Total $160,134 $151,369 $(8,765)
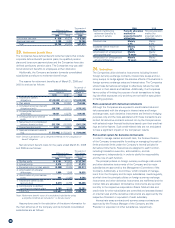
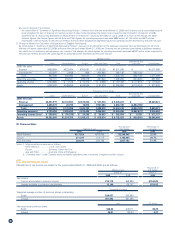
(2) Other Securities Sold during the Year Ended March 31, 2009
Millions of yen
Sale value Total profit Total loss
Other securities ¥15 ¥6 ¥0
Thousands of U.S. dollars
Other securities $153 $61 $0
(3) Composition and Amounts on the Consolidated Balance Sheet
of Other Securities without Market Values
Millions of yen Thousands of U.S. dollars
Negotiable deposits ¥48,000 $488,649
Unlisted stocks 648 6,597